 W
WSatellite geodesy is geodesy by means of artificial satellites — the measurement of the form and dimensions of Earth, the location of objects on its surface and the figure of the Earth's gravity field by means of artificial satellite techniques. It belongs to the broader field of space geodesy. Traditional astronomical geodesy is not commonly considered a part of satellite geodesy, although there is considerable overlap between the techniques.
 W
WANNA 1B was a United States satellite launched on October 31, 1962 from Cape Canaveral, on a Thor rocket.
 W
WChallenging Minisatellite Payload (CHAMP) was a German satellite launched July 15, 2000 from Plesetsk, Russia and was used for atmospheric and ionospheric research, as well as other geoscientific applications, such as GPS radio occultation.
 W
WGEOS-3, or Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite 3, or GEOS-C, was the third and final satellite as part of NASA's Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite/Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite program (NGSP) to better understand and test satellite tracking systems. For GEOS missions 1 and 2, GEOS stands for Geodetic Earth Orbiting Satellite; this was changed to Geodynamics Experimental Ocean Satellite for GEOS-3.
 W
WThe GEOSAT was a U.S. Navy Earth observation satellite, launched on March 12, 1985 into an 800 km, 108° inclination orbit, with a nodal period of about 6040 seconds. The satellite carried a radar altimeter capable of measuring the distance from the satellite to sea surface with a relative precision of about 5 cm. The initial phase was an 18-month classified Geodetic Mission (GM) have a ground-track with a near-23-day repeat with closure to within 50 kilometers. The effect of atmospheric drag was such that by fall 1986 GEOSAT was in an almost exact 23-day repeat orbit.
 W
WThe Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE) was a joint mission of NASA and the German Aerospace Center (DLR). Twin satellites took detailed measurements of Earth's gravity field anomalies from its launch in March 2002 to the end of its science mission in October 2017. The Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment Follow-On (GRACE-FO) is a continuation of the mission on near-identical hardware, launched in May 2018.
 W
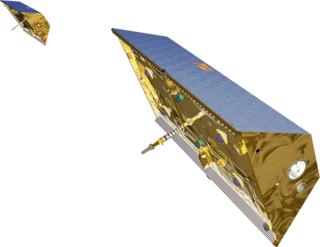
WThe Gravity Field and Steady-State Ocean Circulation Explorer (GOCE) was the first of ESA's Living Planet Programme satellites intended to map in unprecedented detail the Earth's gravity field. The spacecraft's primary instrumentation was a highly sensitive gravity gradiometer consisting of three pairs of accelerometers which measured gravitational gradients along three orthogonal axes.