 W
WThe Akaiwa Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Hauterivian-Barremian) geologic formation in central Honshu, Japan. Indeterminate ornithischian fossils are known from the formation. Fossil ornithopod tracks have been reported from the formation. As well as the turtle Kappachelys
 W
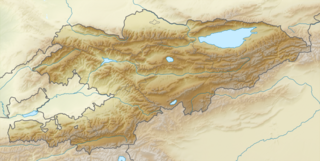
WThe Alamyshik Formation is a geological formation in Kyrgyzstan whose strata date back to the Albian stage of the Early Cretaceous. Pterosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Amagodani Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Japan. An indeterminate iguanodontian tooth has been recovered from the formation. as well as indeterminate pterosaur remains. Dinosaur footprints are also known from the formation.
 W
WThe Andaikhudag Formation, in older literature referred to as Unduruh Formation or Ondorukhaa Formation, is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Mongolia. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Baiying Bologai Formation, in other literature named Bayan Bologai Formation, is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in the Ömnögovi Province of Mongolia. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.
 W
WThe Batylykh Formation is a geological formation in Yakutia, Russia. It is of an uncertain Early Cretaceous age, probably dating between the Berriasian and the Barremian. It is the oldest unit of the 1,500 metres (4,900 ft) thick Sangar Series within the Vilyuy syneclise. The mudstones, sandstones and shales of the formation were deposited in a fluvial to lacustrine environment.
 W
WThe Bazhenov Formation or Bazhenov Shale is a geological stratum in the West Siberian basin. It was formed from sediment deposited in a deep-water sea in Tithonian–early Berriasian time. The sea covered more than one million square kilometers in the central basin area. Highly organic-rich siliceous shales were deposited during this time in anoxic conditions on the sea bottom. The sea was connected to the world's oceans and contains trace minerals derived from dissolved minerals and organic materials similar to sapropel sediments in the Black Sea.
 W
WThe Bukachacha Formation is a geological formation in Zabaykalsky Krai, Russia dating to the Early Cretaceous (Barremian). The tuffaceous mudstones of the formation were deposited in a lacustrine environment.
 W
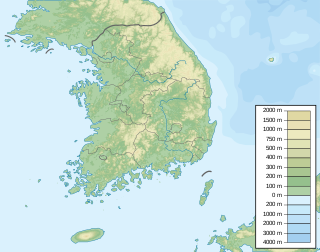
WThe Chilgog Formation, also known as the Chilgok Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in South Korea. Formerly dated to the Berriasian to Hauterivian, later dating has established an Albian age. Dinosaur remains, possibly of sauropods, are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus.
 W
WThe Dushihin Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Aptian) geologic formation in the Övörkhangai Province of Mongolia. The formation preserves fossils of Psittacosaurus mongoliensis and fossil eggs described as Trachoolithus faticanus.
 W
WThe Ejinhoro Formation is a geological formation in Inner Mongolia, north China, whose strata date back to the Early Cretaceous period (Aptian/Albian age.
 W
WThe Feitianshan Formation is a geological formation in China. It dates back to the Early Cretaceous. Among the known ichnofossils are footprints of dinosaurs.
 W
WThe Geoncheonri Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Albian) geologic formation of the Hayang Group in the Gyeongsang Basin of southeast South Korea. Fossil ornithopod tracks, as well as fossils of Kirgizemys have been reported from the lacustrine siltstones and mudstones of the formation.
 W
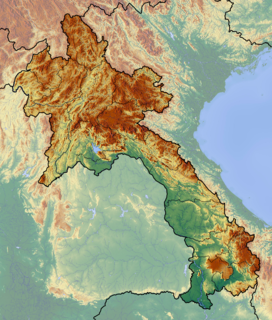
WThe Grès supérieurs Formation is a geological formation in Laos whose strata date back to the Aptian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. It is equivalent to the Khok Kruat Formation of Thailand.
 W
WThe Gugyedong Formation, also known as the Guyedong Beds, is an Aptian to Albian geologic formation in South Korea. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Haman Formation is an Early Cretaceous geological formation in South Korea. It has been dated to the Albian, with an estimated maximum depositional age of 105.4 ± 0.4 Ma. The deposit is known for its tracks, including those of dinosaurs, pterosaurs and birds. It overlies the Silla Congomerate which overlies the Chilgok Formation. It is laterally equivalent to the Sagog Formation.
 W
WThe Hasandong Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in South Korea. It has been dated to the late Aptian and earliest Albian, between 118.0 ± 2.6 Ma and 112.4 ± 1.3 Ma. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Tracks of the pterosaur ichnogenus Pteraichnus have also been recovered from the unit.
 W
WThe Hekou Group is a geological group in Gansu Province, China. It is Early Cretaceous in age. Dinosaur body fossils have also been recovered from the Hekou Group, including the iguanodont Lanzhousaurus and the titanosaurs Daxiatitan, Huanghetitan and Yongjinglong, and the nodosaur Taohelong. Fossil eggs are rare, but one oogenus, Polyclonoolithus, was discovered in the Hekou Group. The group spans the Valanginian to Albian and can be subdivided into four formations. Fossil pterosaur tracks have been recovered.
 W
WHigh pressure terranes along the ~1200 km long east-west trending Bangong-Nujiang suture zone (BNS) on the Tibetan Plateau have been extensively mapped and studied. Understanding the geodynamic processes in which these terranes are created is key to understanding the development and subsequent deformation of the BNS and Eurasian deformation as a whole.
 W
WThe Khuren Dukh Formation, also known as the Hühteeg Svita, is a geological formation in Mongolia whose strata date back to the middle to late Albian. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Öösh Formation, also known as the Tevsh Formation or Hühteeg Svita, is a geological formation of Lower Cretaceous strata in Mongolia. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. It overlies folded and metamorphosed basement strata of the Gobi region, and is capped by basalt. The succession is around 600 metres thick and consists of red claystones and sandstones, along with black thinly laminated shales. The claystones and sandstones were deposited as part of an alluvial fan system, while the shales were deposited in lakes present in the foot of the fan. Many of the fossils come from the "Cannonball beds", which comprise the lowest 60 metres of the unit and consist of green siltstone.
 W
WThe Ilek Formation is a Lower Cretaceous geologic formation in Western Siberia. Many different fossils have been recovered from the formation. It overlies the Late Jurassic Tyazhin Formation and underlies the Albian Kiya Formation.
 W
WThe Jehol Biota includes all the living organisms – the ecosystem – of northeastern China between 133 and 120 million years ago. This is the Lower Cretaceous ecosystem which left fossils in the Yixian Formation and Jiufotang Formation. These deposits are composed of layers of tephra and sediment. It is also believed to have left fossils in the Sinuiju series of North Korea. The ecosystem in the Lower Cretaceous was dominated by wetlands and numerous lakes. Rainfall was seasonal, alternating between semiarid and mesic conditions. The climate was temperate. The Jehol ecosystem was interrupted periodically by ash eruptions from volcanoes to the west. The word "Jehol" is a historical transcription of the former Rehe Province.
 W
WThe Jeomgog Formation is an Early Cretaceous (Albian) geologic formation of the Hayang Group in the Gyeongsang Basin of South Korea.
 W
WThe Jingchuan Formation is a Barremian geologic formation in China. Various dinosaur fossils and tracks have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Jinju Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in South Korea. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although none have yet been referred to a specific genus. It has been dated to the Albian stage. It predominantly consists of black shale, interbedded with sandstone packets, deposited in a fluvial-lacustrine setting.
 W
WThe Jiufotang Formation is an Early Cretaceous geological formation in Chaoyang, Liaoning which has yielded fossils of feathered dinosaurs, primitive birds, pterosaurs, and other organisms. It is a member of the Jehol group. The exact age of the Jiufotang has been debated for years, with estimates ranging from the Late Jurassic to the Early Cretaceous. He et al. (2004) used argon - isotope radiometry to confirm biostratigraphic age estimates. They confirmed an Early Cretaceous, Aptian age for the Jiufotang Formation, 120.3 +/-0.7 million years ago. Fossils of Microraptor and Jeholornis are from the Jiufotang.
 W
WThe Khilok Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Buryatia, Russia. While the lower portion of the formation consists of sandstones and conglomerates, the upper portion of the formation largely consists of trachybasalt, these deposits have been dated to the Aptian. A thin 20 cm bed is known from the formation containing the remains of numerous indetermiate vertebrates, including dinosaur and pterosaurs and an indeterminate species of Kirgizemys.
 W
WThe Khodzhaosmansk or Khodzhaosman Formation is an Aptian to Albian geologic formation in Kyrgyzstan. Dinosaur remains and fossil dinosaur eggs have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Khok Kruat Formation is a rock formation found in northeastern Thailand. It is the uppermost formation of the Khorat Group. It is dated to the Aptian stage of the Early Cretaceous period, and is notable for its fossils of dinosaurs. It is equivalent to the Gres superieurs Formation of Laos. The group is a fluvial formation consisting primarily of red siltstones and sandstones.
 W
WThe Khorat Group is a stratigraphic group located within the Khorat Plateau in the Isan region of Thailand. It was first defined as the Khorat Series by Brown et al in 1953 and was redefined as the Khorat Group by Ward and Bunnag in 1964, which gave it its current constituent formations as well as including the Nam Phong Formation, which is now excluded from the group. Subsequently the sequence underwent several different stratigraphic proposals with several alternative divisions, but the formations proposed in Ward and Bunnag are the most widely used. Initially thought to be Triassic, the sequence has been show to be of Early Cretaceous in age, Dating from the Berriasian to Aptian. It overlies the Nam Phong Formation and is overlain by the evaporitic deposits of the Maha Sarakham Formation. It consists of continental freshwater deposits largely of alternating sandstones and mudstones. The Group is notable for its fossil content, including those of dinosaurs.
 W
WThe Kitadani Formation is a unit of Lower Cretaceous sedimentary rock which crops out near the city of Katsuyama in the Fukui Prefecture of Japan, and it is the primary source of Cretaceous-aged non-marine vertebrate fossils in Japan. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, but it also preserves a diverse assemblage of plants, invertebrates, and other vertebrates. Most, if not all, of the fossil specimens collected from the Kitadani Formation are reposited at the Fukui Prefectural Dinosaur Museum.
 W
WThe Kiyosu-e Formation is a Middle Jurassic (Callovian) to Early Cretaceous (Berriasian) geologic formation of the Toyonishi Group in Yamaguchi Prefecture, Japan. Fossil ornithopod tracks have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Liangtoutang Formation, also referred to as the Laijia Formation is a geological formation located in Zhejiang, China. Its strata date back to the Albian to Cenomanian stages of the Cretaceous period. The lithology primarily consists of red sandstone.
 W
WThe Lianmuqin Formation, also transcribed as Lianmugin Formation, is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation composed of "interbedded red green and yellow variegated mudstones and siltstones". Dinosaur remains have been recovered from it.
 W
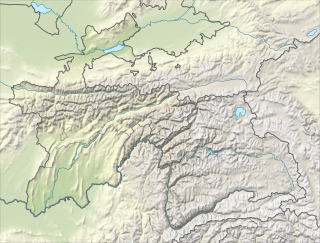
WThe Luchak Formation is an Albian geologic formation in Tajikistan.
 W
WThe Luohandong Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation of the Ordos Basin in Inner Mongolia, China. The formation was initially dated to the earliest Cretaceous; Valanginian to Barremian, but later dating established an Aptian to Albian age. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Pterosaur fossils have also been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Murtoi Formation is a geologic formation in vicinity of Lake Gusinoye in Russia. It was deposited in the late Barremian to the mid Aptian of the Early Cretaceous.
 W
WThe Neocomian Sands is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Atyrau, Kazakhstan. Dinosaur remains have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Early Cretaceous Phra Wihan Formation is the second lowest member of the Mesozoic Khorat Group which outcrops in Northeast Thailand.
 W
WThe Early Cretaceous Phu Kradung Formation is the lowest member of the Mesozoic Khorat Group which outcrops on the Khorat Plateau in Isan, Thailand. This geological formation consists of micaceous, brown to reddish-brown siltstone beds with minor brown and grey shale and sandstone beds. Occasional lime-noduled conglomerate occurs.
 W
WThe Phu Phan Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Thailand. Fossil theropod tracks have been reported from the formation.
 W
WThe Qingshan Group is a geological group in Shandong, China, whose strata date back to the Barremian to Albian stages of the Early Cretaceous. The group contains the Doushan Formation. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Sagog Formation is an Albian geologic formation in South Korea.
 W
WThe Sao Khua Formation is a middle member of the Khorat Group. It consists of an alteration of pale red to yellowish-gray, fine to medium-grained sandstone and grayish-reddish brown siltstone and clay. Rare pale red to light gray conglomerates, containing carbonate pebbles, are also characteristic of this formation. This geological formation in Thailand, dates to the Early Cretaceous age.
 W
WThe Sebayashi Formation is a Barremian to Albian geologic formation in Japan. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation, although only one species, Siamosaurus, has been referred to a specific genus.
 W
WThe Shirabad Formation is a late Albian geologic formation in Tajikistan.
 W
WThe Sinuiju Formation is a geologic formation in North Korea. Formerly of uncertain age, it is now thought to be Early Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains diagnostic to the genus level are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. Compression fossils of insects are also known from the formation.
 W
WThe Tsagaantsav Formation, Tsagantsab Formation or Tsagan-Tsab Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Mongolia. Indeterminate sauropod and psittacosaurid remains have been recovered from the formation. Remains of the pterosaur Noripterus, which were originally given their own genus, "Phobetor" have also been recovered from the formation.
 W
WThe Tuchengzi Formation is a geological formation in China whose strata span the Tithonian to Berriasian ages. Dinosaur fossils, particularly footprints, have been found from the formation.
 W
WThe Xiagou Formation is the middle strata of the Xinminbao Group. It is named for its type site in Xiagou, in the Changma Basin of Gansu Province, northwestern China and is considered Early Cretaceous in age. It is known outside the specialized world of Chinese geology as the site of a Lagerstätte in which the fossils were preserved of Gansus yumenensis, the earliest true modern bird.
 W
WThe Xinlong Formation is an Early Cretaceous geologic formation in Guangxi, southern China.
 W
WThe Yixian Formation is a geological formation in Jinzhou, Liaoning, People's Republic of China, that spans 11 million years during the early Cretaceous period. It is known for its exquisitely preserved fossils, and is mainly composed of basalts interspersed with siliciclastic sediments.