 W
WA stream is a body of water with surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface water, subsurface water and groundwater. The surface and subsurface water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of precipitation. The stream encompasses surface, subsurface and groundwater fluxes that respond to geological, geomorphological, hydrological and biotic controls.
 W
WAn anabranch is a section of a river or stream that diverts from the main channel or stem of the watercourse and rejoins the main stem downstream. Local anabranches can be the result of small islands in the watercourse. In larger anabranches, the flow can diverge for a distance of several kilometers before rejoining the main channel.
 W
WIn sedimentary geology and fluvial geomorphology, avulsion is the rapid abandonment of a river channel and the formation of a new river channel. Avulsions occur as a result of channel slopes that are much less steep than the slope that the river could travel if it took a new course.
 W
WIn geography, a bank is the land alongside a body of water. Different structures are referred to as banks in different fields of geography, as follows.
 W
WA bar in a river is an elevated region of sediment that has been deposited by the flow. Types of bars include mid-channel bars, point bars, and mouth bars. The locations of bars are determined by the geometry of the river and the flow through it. Bars reflect sediment supply conditions, and can show where sediment supply rate is greater than the transport capacity.
 W
WBraid bars, or mid-channel bars, are river landforms typically present in braided river channels. These formations have many names, including medial, longitudinal, crescentic, and transverse bars, as well as the more colloquial sandflat. Braid bars are distinguished from point bars due to their presence in the middle of a flow channel, rather than along a bank of the river channel.
 W
WA braided river, or braided channel, consists of a network of river channels separated by small, often temporary, islands called braid bars or, in English usage, aits or eyots. Braided streams tend to occur in rivers with high sediment loads and/or coarse grain sizes, and in rivers with steeper slopes than typical rivers with straight or meandering channel patterns. They are also associated with rivers with rapid and frequent variation in the amount of water they carry, i.e., with "flashy" rivers, and with rivers with weak banks. Braided channels are found in a variety of environments all over the world, including gravelly mountain streams, sand bed rivers, on alluvial fans, on river deltas, and across depositional plains.
 W
WIn local usage, a burn is a kind of watercourse. The term applies to a large stream or a small river. The word is used in Scotland and England and in parts of Ulster, Australia and New Zealand.
 W
WChalk streams are rivers that rise from springs in landscapes with chalk bedrock. Since chalk is permeable, water percolates easily through the ground to the water table and chalk streams therefore receive little surface runoff. As a result, the water in the streams contains little organic matter and sediment and is generally very clear. The beds of the rivers are generally composed of clean, compacted gravel and flints, which are good spawning areas for Salmonidae fish species.
 W
WIn physical geography, a channel is a type of landform consisting of the outline of a path of relatively shallow and narrow body of fluid, most commonly the confine of a river, river delta or strait. The word is cognate to canal, and sometimes takes this form, e.g. the Hood Canal.
 W
WA stream is a body of water with surface water flowing within the bed and banks of a channel. The flow of a stream is controlled by three inputs – surface water, subsurface water and groundwater. The surface and subsurface water are highly variable between periods of rainfall. Groundwater, on the other hand, has a relatively constant input and is controlled more by long-term patterns of precipitation. The stream encompasses surface, subsurface and groundwater fluxes that respond to geological, geomorphological, hydrological and biotic controls.
 W
WA current, in a river or stream, is the flow of water influenced by gravity as the water moves downhill to reduce its potential energy. The current varies spatially as well as temporally within the stream, dependent upon the flow volume of water, stream gradient, and channel geometry. In tidal zones, the current in rivers and streams may reverse on the flood tide before resuming on the ebb tide.
 W
WDaylighting can be defined as "“opening up buried watercourses and restoring them to more natural conditions". An alternative definition refers to "“the practice of removing streams from buried conditions and exposing them to the Earth's surface in order to directly or indirectly enhance the ecological, economic and/or socio-cultural well-being of a region and its inhabitants”. The term is used to refer to the restoration of an originally open-air watercourse, which had at some point been diverted below ground, back into an above-ground channel. Typically, the rationale behind returning the riparian environment of a stream, wash, or river to a more natural state is to reduce runoff, create habitat for species in need of it, or improve an area's aesthetics. In the UK, the practice is also known as deculverting.
 W
WIn the geography of rivers, streams, and glaciers, a debouch, or debouche, is a place where runoff from a small, confined space emerges into a larger, broader space. The term is of French origin and means to cause to emerge. The term also has a military usage.
 W
WIn topography, a drainage divide, water divide, divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be harder to discern.
 W
WA drainage basin is any area of land where precipitation collects and drains off into a common outlet, such as into a river, bay, or other body of water. The drainage basin includes all the surface water from rain runoff, snowmelt, hail, sleet and nearby streams that run downslope towards the shared outlet, as well as the groundwater underneath the earth's surface. Drainage basins connect into other drainage basins at lower elevations in a hierarchical pattern, with smaller sub-drainage basins, which in turn drain into another common outlet.
 W
WIn topography, a drainage divide, water divide, divide, ridgeline, watershed, water parting or height of land is elevated terrain that separates neighboring drainage basins. On rugged land, the divide lies along topographical ridges, and may be in the form of a single range of hills or mountains, known as a dividing range. On flat terrain, especially where the ground is marshy, the divide may be harder to discern.
 W
WIn geomorphology, drainage systems, also known as river systems, are the patterns formed by the streams, rivers, and lakes in a particular drainage basin. They are governed by the topography of the land, whether a particular region is dominated by hard or soft rocks, and the gradient of the land. Geomorphologists and hydrologists often view streams as part of drainage basins. This is the topographic region from which a stream receives runoff, throughflow, and its saturated equivalent, groundwater flow. The number, size, and shape of the drainage basins varies and the larger and more detailed the topographic map, the more information is available.
 W
WA ford is a shallow place with good footing where a river or stream may be crossed by wading, or inside a vehicle getting its wheels wet. A ford may occur naturally or be constructed. Fords may be impassable during high water. A low water crossing is a low bridge that allows crossing over a river or stream when water is low but may be covered by deep water when the river is high.
 W
WA French drain or weeping tile is a trench filled with gravel or rock or containing a perforated pipe that redirects surface water and groundwater away from an area.
 W
WIn hydrology, a mainstem is "the primary downstream segment of a river, as contrasted to its tributaries". Water enters the mainstem from the river's drainage basin, the land area through which the mainstem and its tributaries flow. A drainage basin may also be referred to as a watershed or catchment.
 W
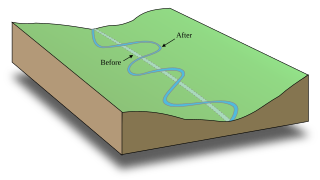
WA meander is one of a series of regular sinuous curves, bends, loops, turns, or windings in the channel of a river, stream, or other watercourse. It is produced by a stream or river swinging from side to side as it flows across its floodplain or shifts its channel within a valley. A meander is produced by a stream or river as it erodes the sediments comprising an outer, concave bank and deposits this and other sediment downstream on an inner, convex bank which is typically a point bar. The result of sediments being eroded from the outside concave bank and their deposition on an inside convex bank is the formation of a sinuous course as a channel migrates back and forth across the down-valley axis of a floodplain. The zone within which a meandering stream shifts its channel across either its floodplain or valley floor from time to time is known as a meander belt. It typically ranges from 15 to 18 times the width of the channel. Over time, meanders migrate downstream, sometimes in such a short time as to create civil engineering problems for local municipalities attempting to maintain stable roads and bridges.
 W
WA misfit stream is a river that is either too large or too small to have eroded the valley or cave passage in which it flows. This term is also used for a stream or river with meanders that obviously are not proportional in size to the meanders of the valley or meander scars cut into its valley walls. If the misfit stream is too large for either its valley or meanders, it is known as an overfit stream. If the misfit stream is too small for either its valley or meanders, it is known as an underfit stream.
 W
WA mountain stream is a brook or stream, usually with a steep gradient, flowing down a mountainside. Its swift flow rate often transports large quantities of rock, gravel, soil, wood or even entire logs with the stream. The main characteristic of mountain streams in the Alpine region is their steep gradient and sharply varying rates of flow within a short period of time, as a result of snowmelt and sudden storms. Streams of such nature are rarer in gently rolling countryside, although they may occur on scarp slopes where, although the height difference is not so great, they tend to have a larger catchment area than mountain streams.
 W
WIn estimating erosion, Playfair's law is an empirical relationship that relates the size of a stream to the valley it runs through. It is better defined as a theory rather than law.
 W
WA plunge pool is a deep depression in a stream bed at the base of a waterfall or shut-in. It is created by the erosional forces of cascading water on the rocks at formation's base where the water impacts. The term may refer to the water occupying the depression, or the depression itself.
 W
WA point bar is a depositional feature made of alluvium that accumulates on the inside bend of streams and rivers below the slip-off slope. Point bars are found in abundance in mature or meandering streams. They are crescent-shaped and located on the inside of a stream bend, being very similar to, though often smaller than, towheads, or river islands.
 W
WA precipitationshed is the upwind ocean and land surface that contributes evaporation to a given, downwind location's precipitation. The concept has been described as an "atmospheric watershed". The concept itself rests on a broad foundation of scholarly work examining the evaporative sources of rainfall. Since its formal definition, the precipitationshed has become an element in water security studies, examinations of sustainability, and mentioned as a potentially useful tool for examining vulnerability of rainfall dependent ecosystems.
 W
WRapids are sections of a river where the river bed has a relatively steep gradient, causing an increase in water velocity and turbulence.
 W
WA riffle is a shallow landform in a flowing channel, and it has specific topographic, sedimentary, and hydraulic indicators. These are almost always assessed at a very low discharge compared to the flow that fills the channel, and as a result the water moving over a riffle appears shallow and fast, with a wavy, disturbed water surface. The water's surface over a riffle at low flow also has a much steeper slope than that over other in-channel landforms. Channel sections with a mean water surface slope of roughly 0.1 to 0.5% exhibit riffles, though they can occur in steeper or gentler sloping channels with coarser or finer bed materials, respectively. Except in the period after a flood, the sediment on the riverbed in a riffle is usually much coarser than on that in any other in-channel landform.
 W
WIn a flowing stream, a riffle-pool sequence develops as a stream's hydrological flow structure alternates from areas of relatively shallow to deeper water. This sequence is present only in streams carrying gravel or coarser sediments. Riffles are formed in shallow areas by coarser materials, such as gravel deposits, over which water flows. Pools are deeper, calmer areas whose bed load is made up of finer material such as silt. Streams with only sand or silt laden beds do not develop the feature. The sequence within a stream bed commonly occurs at intervals of from 5 to 7 stream widths. Meandering streams with relatively coarse bed load tend to develop a riffle-pool sequence with pools in the outsides of the bends and riffles in the crossovers between one meander to the next on the opposite margin of the stream. The pools are areas of active erosion and the material eroded tends to be deposited in the riffle areas between them.
 W
WA riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the terrestrial biomes of the Earth. Plant habitats and communities along the river margins and banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by hydrophilic plants. Riparian zones are important in ecology, environmental resource management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grasslands, woodlands, wetlands, or even non-vegetative areas. In some regions, the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, riparian corridor, and riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone. The word riparian is derived from Latin ripa, meaning "river bank".
 W
WRiparian-zone restoration is the ecological restoration of riparian-zone habitats of streams, rivers, springs, lakes, floodplains, and other hydrologic ecologies. A riparian zone or riparian area is the interface between land and a river or stream. Riparian is also the proper nomenclature for one of the fifteen terrestrial biomes of the earth; the habitats of plant and animal communities along the margins and river banks are called riparian vegetation, characterized by Aquatic plants and animals that favor them. Riparian zones are significant in ecology, environmental management, and civil engineering because of their role in soil conservation, their habitat biodiversity, and the influence they have on fauna and aquatic ecosystems, including grassland, woodland, wetland or sub-surface features such as water tables. In some regions the terms riparian woodland, riparian forest, riparian buffer zone, or riparian strip are used to characterize a riparian zone.
 W
WA river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of water. Small rivers can be referred to using names such as stream, creek, brook, rivulet, and rill. There are no official definitions for the generic term river as applied to geographic features, although in some countries or communities a stream is defined by its size. Many names for small rivers are specific to geographic location; examples are "run" in some parts of the United States, "burn" in Scotland and northeast England, and "beck" in northern England. Sometimes a river is defined as being larger than a creek, but not always: the language is vague.
 W
WRiver bifurcation occurs when a river flowing in a single stream separates into two or more separate streams which continue downstream. Some rivers form complex networks of distributaries, especially in their deltas. If the streams eventually merge again or empty into the same body of water, then the bifurcation forms a river island.
 W
WA river delta is a landform created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river as the flow leaves its mouth and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or another river that cannot carry away the supplied sediment. The size and shape of a delta is controlled by the balance between watershed processes that supply sediment, and receiving basin processes that redistribute, sequester, and export that sediment. The size, geometry, and location of the receiving basin also plays an important role in delta evolution. River deltas are important in human civilization, as they are major agricultural production centers and population centers. They can provide coastline defense and can impact drinking water supply. They are also ecologically important, with different species' assemblages depending on their landscape position.
 W
WRiver ecosystems are flowing waters that drain the landscape, and include the biotic (living) interactions amongst plants, animals and micro-organisms, as well as abiotic (nonliving) physical and chemical interactions of its many parts. River ecosystems are part of larger watershed networks or catchments, where smaller headwater streams drain into mid-size streams, which progressively drain into larger river networks.
 W
WThe headwaters of a river or stream is the farthest place in that river or stream from its estuary or downstream confluence with another river, as measured along the course of the river. It is also known as a river's source.
 W
WA stream bed or streambed is the channel bottom of a stream or river, the physical confine of the normal water flow. The lateral confines or channel margins are known as the stream banks or river banks, during all but flood stage. Under certain conditions a river can branch from one stream bed to multiple stream beds. A flood occurs when a stream overflows its banks and flows onto its flood plain. As a general rule, the bed is the part of the channel up to the normal water line, and the banks are that part above the normal water line. However, because water flow varies, this differentiation is subject to local interpretation. Usually, the bed is kept clear of terrestrial vegetation, whereas the banks are subjected to water flow only during unusual or perhaps infrequent high water stages and therefore might support vegetation some or much of the time.
 W
WA stream pool, in hydrology, is a stretch of a river or stream in which the water depth is above average and the water velocity is below average.
 W
WStream restoration or river restoration, also sometimes referred to as river reclamation, is work conducted to improve the environmental health of a river or stream, in support of biodiversity, recreation, flood management and/or landscape development. Stream restoration approaches can be divided into two broad categories: form-based restoration, which relies on physical interventions in a stream to improve its conditions; and process-based restoration, which advocates the restoration of hydrological and geomorphological processes to ensure a stream's resilience and ecological health. Form-based restoration techniques include deflectors; cross-vanes; weirs, step-pools and other grade-control structures; engineered log jams; bank stabilization methods and other channel-reconfiguration efforts. These induce immediate change in a stream, but sometimes fail to achieve the desired effects if degradation originates at a wider scale. Process-based restoration includes restoring lateral or longitudinal connectivity of water and sediment fluxes and limiting interventions within a corridor defined based on the stream's hydrology and geomorphology. The beneficial effects of process-based restoration projects may sometimes take time to be felt since changes in the stream will occur at a pace that depends on the stream dynamics.
 W
WA subterranean river is a river that runs wholly or partly beneath the ground surface – one where the riverbed does not represent the surface of the Earth. It is distinct from an aquifer, which may flow like a river but is contained within a permeable layer of rock or other unconsolidated materials. A river flowing below ground level in an open gorge is not classed as subterranean.
 W
WIn geography and fluvial geomorphology, a thalweg or talweg is the line of lowest elevation within a valley or watercourse.
 W
WA tidal creek, tidal channel, or estuary is the portion of a stream that is affected by ebb and flow of ocean tides, in the case that the subject stream discharges to an ocean, sea or strait. Thus this portion of the stream has variable salinity and electrical conductivity over the tidal cycle, and flushes salts from inland soils. Tidal creeks are characterized by slow water velocity resulting in buildup of fine, organic sediment in wetlands. Creeks may often be a dry to muddy channel with little or no flow at low tide, but with significant depth of water at high tide. Due to the temporal variability of water quality parameters within the tidally influenced zone, there are unique biota associated with tidal creeks which are often specialised to such zones. Nutrients and organic matter are delivered downstream to habitats normally lacking these, while the creeks also provide access to inland habitat for salt-water organisms.
 W
WA tributary or affluent is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage basin of its surface water and groundwater, leading the water out into an ocean.
 W
WAn urban stream is a formerly natural waterway that flows through a heavily populated area. Urban streams are often polluted by urban runoff and combined sewer outflows. Water scarcity makes flow management in the rehabilitation of urban streams problematic.
 W
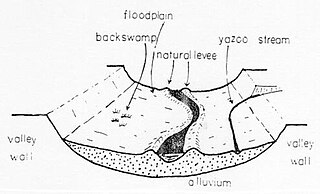
WA Yazoo stream is a geologic and hydrologic term for any tributary stream that runs parallel to, and within the floodplain of a larger river for considerable distance, before eventually joining it. This is especially the characteristic when such a stream is forced to flow along the base of the main river's natural levee. Where the two meet is known as a "belated confluence" or a "deferred junction". The name is derived from an exterminated Native American tribe, the Yazoo Indians. The Choctaw word is translated to "River of Death" because of the strong flows under its bank full stage.