 W
WAlgoasaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaur from the Berriasian-early Valanginian-age Early Cretaceous Upper Kirkwood Formation of Cape Province, South Africa. It was a neosauropod; although it has often been assigned to the Titanosauridae, there is no evidence for this, and recent reviews have considered it to be an indeterminate sauropod.
 W
WAlopecognathus is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids from the Late Permian of South Africa.
 W
WAloposaurus is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids from the Late Permian of South Africa. It was first named by Robert Broom in 1910, and contains the type species A. gracilis, and possibly a second species A. tenuis. This small gorgonopsid had a slender narrow skull only 12 centimetres (4.7 in) long, with a total body length of 60–70 cm (2.0–2.3 ft). Aloposaurus is known from a single weathered skull from a probable immature individual.
 W
WArctognathus is an extinct genus of gorgonopsids that throve during the Late Permian in the Karoo basin of what is now South Africa.
 W
WBauria is an extinct genus of the suborder Therocephalia that existed during the Early Triassic period, around 246-251 million years ago. It belonged to the family Bauriidae. Bauria was probably a carnivore or insectivore. It lived in South Africa, specifically in the Burgersdorp Formation in South Africa.
 W
WRobert Broom FRS FRSE was a Scottish South African doctor and palaeontologist. He qualified as a medical practitioner in 1895 and received his DSc in 1905 from the University of Glasgow.
 W
WBurnetia is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids in the family Burnetiidae, from the Late Permian of South Africa. Burnetia is known so far from a single holotype skull lacking the lower jaws described by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1923. Due to erosion and dorsoventral crushing, features of the skull are hard to interpret. Stutural lines are further distorted by the unusual shape of the skull roof, including many bosses and protuberances.
 W
WThe mountain pygmy possum is a small, mouse-sized nocturnal marsupial of Australia found in dense alpine rock screes and boulder fields, mainly southern Victoria and around Mount Kosciuszko in Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales at elevations from 1,300 to 2,230 metres. At almost 14 cm (5.5 in), its prehensile tail is longer than its 11 cm (4.3 in) combined head and body length. Its diet consists of insects, fleshy fruits, nuts, nectar and seeds. Its body is covered in a thick coat of fine grey fur except for its stomach, which is cream coloured; its tail is hairless. On the underside of the female's body is a pouch containing four teats. This possum is the only extant species in the genus Burramys. It is also the only Australian mammal restricted to alpine habitat.
 W
WGolden moles are small insectivorous burrowing mammals endemic to Southern Africa. They comprise the family Chrysochloridae and as such they are taxonomically distinct from the true moles, family Talpidae, and other mole-like families, all of which, to various degrees, they resemble as a result of evolutionary convergence.
 W
WClelandina is an extinct genus of rubidgeine gorgonopsian from the Late Permian of Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone of South Africa. It was first named by Broom in 1948. The type and only species is C. rubidgei. It is relatively rare, with only four known specimens.
 W
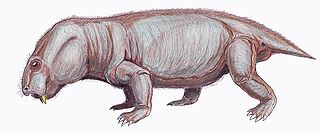
WDicynodontoides is a genus of small to medium-bodied, herbivorous, emydopoid dicynodonts from the Late Permian. The name Dicynodontoides references its “dicynodont-like” appearance due to the caniniform tusks featured by most members of this infraorder. Kingoria, a junior synonym, has been used more widely in the literature than the more obscure Dicynodontoides, which is similar-sounding to another distantly related genus of dicynodont, Dicynodon. Two species are recognized: D. recurvidens from South Africa, and D. nowacki from Tanzania.
 W
WDinanomodon is a genus of dicynodont from Late Permian (Changhsingian) of the Lystrosaurus Assemblage Zone, Katberg Formation, and Cistecephalus Assemblage Zone, Balfour Formation Beaufort Group, Karoo Basin of South Africa.
 W
WDinogorgon is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name Dinogorgon is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name rubidgei is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is D. rubidgei.
 W
WDuthie's golden mole is a species of mammal in the family Chrysochloridae. It is endemic to South Africa. Its natural habitats are subtropical or tropical moist lowland forests, moist savanna, temperate grassland, arable land, pastureland, plantations, rural gardens, urban areas, and introduced vegetation. It is threatened by habitat destruction. The specific name duthieae was given in honour of Dr. Augusta Vera Duthie, a South African botanist.
 W
WEmydops is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsid from the Permian of South Africa. Emydops was first named by South African paleontologist Robert Broom in 1912 when he described Emydops minor. In the following years, the genus grew to include thirteen species. Many of these species were erected on the basis of differences in the teeth and the positioning of the frontal and parietal bones. A 2008 study narrowed Emydops down to two species, E. arctatus and the newly described E. oweni.
 W
WEriphostoma is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian therapsids known from the Middle Permian of Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone, South Africa. It has one known species, Eriphostoma microdon, and was first named by Robert Broom in 1911. It is the oldest known gorgonopsian and among the smallest and most basal members of the clade.
 W
WErythrosuchus is an extinct genus of archosauriform reptile from the Triassic of South Africa. Remains have been found from the Cynognathus Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo of South Africa.
 W
WEuchambersia is a genus of therocephalian therapsid that lived during the Late Permian, approximately 255 million years ago, in what is now South Africa. The genus contains a single species, Euchambersia mirabilis, named by paleontologist Robert Broom in 1931 from a skull missing the lower jaws; a second skull, belonging to an immature individual, was later described. It is a member of the family Akidnognathidae, which historically has also been referred by as the synonymous Euchambersiidae.
 W
WEuparkeria is an extinct genus of archosauriform from the Middle Triassic of South Africa. It was a small reptile that lived between 245-230 million years ago, and was close to the ancestry of Archosauria, the group that includes dinosaurs, pterosaurs, and modern birds and crocodilians.
 W
WGalechirus is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids. It was about 30 cm (1 ft) long.
 W
WGaleops is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids.
 W
WGalepus is an extinct genus of anomodont therapsids.
 W
WGeranosaurus is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur from the Early Jurassic. It is known only from crushed fragments of the skull, a single jaw bone with nine tooth stubs and limb elements discovered in the Clarens Formation, South Africa in 1871. Because of the limited remains, it is considered a nomen dubium. It is classified as an ornithischian based on the jaw, probably a heterodontosaurid. It was around 0.6 metres (2.0 ft) tall and around 1.2 metres (3.9 ft) long when fully grown.
 W
WGlanosuchus is a genus of scylacosaurid therocephalian from the Late Permian of South Africa. The type species G. macrops was named by Robert Broom in 1904. Glanosuchus had a middle ear structure that was intermediate between that of early therapsids and mammals. Ridges in the nasal cavity of Glanosuchus suggest it had an at least partially endothermic metabolism similar to modern mammals.
 W
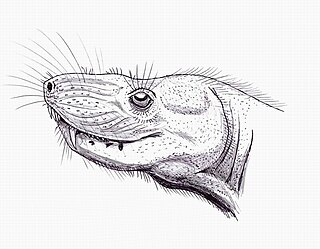
WHeleosarus scholtzi is an extinct species of basal synapsids, known as pelycosaurs, in the family of Varanopidae during the middle Permian. At first H. scholtzi was mistakenly classified as a diapsid. Members of this family were carnivorous and had dermal armor, and somewhat resembled monitor lizards. This family was the most geologically long lived, widespread, and diverse group of early amniotes. To date only two fossils have been found in the rocks of South Africa. One of these fossils is an aggregation of five individuals.
 W
WHofmeyria is an extinct genus of therocephalians.
 W
WIctidorhinus is an extinct genus of biarmosuchian therapsids. Fossils have been found from the Dicynodon Assemblage Zone of the Beaufort Group in the Karoo Basin, South Africa and are of Late Permian age. It had a short snout and proportionally large orbits. These characteristics may be representative of a juvenile animal, possibly of Lycaenodon. However, these two genera are not known to have existed at the same time, making it unlikely for Ictidorhinus material to be from a juvenile form of Lycaenodon.
 W
WIctidosuchoides is an extinct genus of ictidosuchid therocephalians. Fossils have been found from the Karoo Basin in South Africa. The genus is known to have been one of the few therocephalians to have survived the Permian-Triassic extinction event in this area, although its numbers were quite low after the extinction.
 W
WLemurosaurus is a genus of extinct biarmosuchian therapsids from the Late Permian of South Africa. The generic epithet Lemursaurus is a mix of Latin, lemures “Ghosts, sprits”, and Greek, sauros, “lizard”. Lemurosaurus is easily identifiable by its prominent eye crests, and large eyes. The name Lemurosaurus pricei was coined by paleontologist Robert Broom in 1949, based on a single small crushed skull, measured at approximately 86 millimeters in length, found on the Dorsfontein farm in Graff-Reinet. To date, only two skulls of the Lemurosaurus have been discovered, so body size is unknown. The second larger, more intact, skull was found in 1974 by a team from the National Museum in Bloemfontein.
 W
WLycaenops ("wolf-face") is a genus of carnivorous therapsids. It lived during the late mid-Permian to the early Late Permian, about 270.6-251 mya, in what is now South Africa.
 W
WLycosuchus is an extinct genus of carnivorous therocephalians which lived in the Middle Permian 265—260 Ma existing for approximately 5 million years . It was a medium-sized predator, reaching 1.2 m (3.8 ft) in length with a skull 23 cm long.
 W
WLydekkerina is an extinct genus of stereospondyl temnospondyl. It is the type genus of the family Lydekkerinidae. Fossils have been collected from Early Triassic deposits in South Africa and Australia. The type species is L. huxleyi, first described in 1889. While most other stereospondyls were semiaquatic, Lydekkerina was exclusively terrestrial.
 W
WMilleretta is an extinct genus of millerettid parareptile from the Late Permian of South Africa. Fossils have been found in the Balfour Formation. Milleretta was a moderately sized, lizard-like animal, about 60 centimetres (24 in) in length. It was probably insectivorous. Its only known species is Milleretta rubidgei, making Milleretta a monospecific genus.
 W
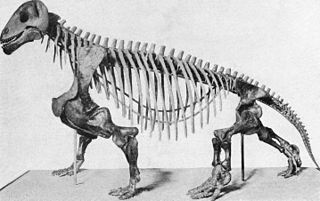
WMoschops is an extinct genus of therapsids that lived in the Guadalupian epoch, around 265–260 million years ago. They were heavily built plant eaters, and they may have lived partly in water, as hippopotamuses do. They had short, thick heads and might have competed by head-butting each other. Their elbow joints allowed them to walk with a more mammal-like gait rather than crawling. Their remains were found in the Karoo region of South Africa, belonging to the Tapinocephalus Assemblage Zone. Therapsids, such as Moschops, are synapsids, the dominant land animals in the Permian period, which ended 252 million years ago.
 W
WMoschorhinus is an extinct genus of therocephalian in the family Akidnognathidae, with only one species: M. kitchingi. It was a carnivorous, lion-sized synapsid which has been found in the Late Permian to Early Triassic of the South African Karoo Supergroup. It had a broad, blunt snout which bore long, straight canines. It appears to have replaced the gorgonopsids ecologically, and hunted much like a big cat. While most abundant in the Late Permian, it survived a little after the Permian Extinction, though these Triassic individuals had stunted growth.
 W
WThe mountain pygmy possum is a small, mouse-sized nocturnal marsupial of Australia found in dense alpine rock screes and boulder fields, mainly southern Victoria and around Mount Kosciuszko in Kosciuszko National Park in New South Wales at elevations from 1,300 to 2,230 metres. At almost 14 cm (5.5 in), its prehensile tail is longer than its 11 cm (4.3 in) combined head and body length. Its diet consists of insects, fleshy fruits, nuts, nectar and seeds. Its body is covered in a thick coat of fine grey fur except for its stomach, which is cream coloured; its tail is hairless. On the underside of the female's body is a pouch containing four teats. This possum is the only extant species in the genus Burramys. It is also the only Australian mammal restricted to alpine habitat.
 W
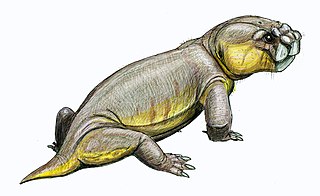
WPelanomodon is an extinct genus of dicynodont therapsids that lived in the Late Permian period. Fossil evidence of this genus is principally found in the Karoo Basin of South Africa, in the Dicynodon Assemblage Zone. Lack of fossil record after the Late Permian epoch suggests that Pelanomodon fell victim to the Permian-Triassic extinction event.
 W
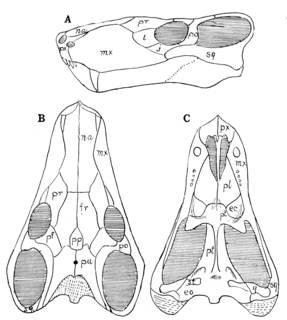
WProcynosuchus is an extinct genus of cynodonts from the Late Permian. It is considered to be one of the earliest and most basal cynodonts. It was 60 cm (2 ft) long and seems to have been adapted to a semi-aquatic lifestyle.
 W
WScylacops is an extinct genus of Gorgonopsia. It was first named by Broom in 1913, and contains two species, S. bigendens, and S. capensis. Its fossils have been found in South Africa and Zambia. It is believed to be closely related to the Gorgonopsian Sauroctonus progressus. Scylacops was a moderately sized Gorgonopsid.
 W
WScylacosaurus is an extinct genus of therocephalian therapsids.
 W
WScymnosaurus is now considered a nomen dubium.
 W
WSmilesaurus is an extinct genus of gorgonopsian known from Africa. It lived during the Late Permian. It contains the single species S. ferox.
 W
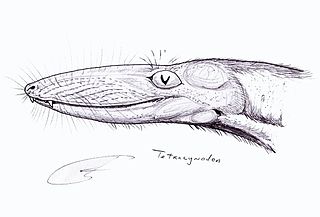
WTetracynodon is an extinct genus of therocephalian. Fossils of Tetracynodon have been found in the Karoo Basin of South Africa. Two species are known: the type species T. tenuis from the Late Permian and the species T. darti from the Early Triassic. Both species were small-bodied and probably fed on insects and small vertebrates. Although Tetracynodon is more closely related to mammals than it is to reptiles, its braincase is very primitive and shares more in common with modern amphibians and reptiles than it does with mammals.
 W
WTherapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals and their ancestors. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more underneath the body, as opposed to the sprawling posture of many reptiles and salamanders. The earliest fossil attributed to Therapsida is Tetraceratops insignis from the Lower Permian.
 W
WYoungina is an extinct genus of diapsid reptile from the Late Permian Beaufort Group of the Karoo Red Beds of South Africa. This, and a few related forms, make up the family Younginidae, within the Order Eosuchia. Eosuchia, having become a wastebasket taxon for many probably distantly-related primitive diapsid reptiles ranging from the Late Carboniferous to the Eocene, Romer proposed that it be replaced by Younginiformes.