 W
WEarthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. Earthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, applied physics, etc. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering, nuclear engineering, and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics, and finance.
 W
WSeismology is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other planet-like bodies. The field also includes studies of earthquake environmental effects such as tsunamis as well as diverse seismic sources such as volcanic, tectonic, glacial, fluvial, oceanic, atmospheric, and artificial processes such as explosions. A related field that uses geology to infer information regarding past earthquakes is paleoseismology. A recording of Earth motion as a function of time is called a seismogram. A seismologist is a scientist who does research in seismology.
 W
WActive vibration control is the active application of force in an equal and opposite fashion to the forces imposed by external vibration. With this application, a precision industrial process can be maintained on a platform essentially vibration-free.
 W
WSeismic base isolation, also known as base isolation, or base isolation system, is one of the most popular means of protecting a structure against earthquake forces. It is a collection of structural elements which should substantially decouple a superstructure from its substructure that is in turn resting on the shaking ground, thus protecting a building or non-building structure's integrity.
 W
WA column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column is a compression member. The term column applies especially to a large round support with a capital and a base or pedestal, which is made of stone, or appearing to be so. A small wooden or metal support is typically called a post, and supports with a rectangular or other non-round section are usually called piers.
 W
WC. (Carl) Allin Cornell was a civil engineer, a researcher, and a professor who made important contributions to reliability theory and earthquake engineering and, along with Dr. Luis Esteva, developed the field of Probabilistic Seismic Hazard Analysis in 1968.
 W
WDamage to infrastructure in the 2010 Haiti earthquake was extensive and affected areas included Port-au-Prince, Petit-Goâve, Léogâne, Jacmel and other settlements in southwestern Haiti. In February Prime Minister Jean-Max Bellerive estimated that 250,000 residences and 30,000 commercial buildings had collapsed or were severely damaged. The deputy mayor of Léogâne, which was at the epicenter of the earthquake, reported that 90% percent of the buildings in that city had been destroyed and Léogâne had "to be totally rebuilt." Many notable landmark buildings were significantly damaged or destroyed, including the Presidential Palace, the National Assembly building, the Port-au-Prince Cathedral, and the main jail. The Ministry of Education estimated that half the nation's 15,000 primary schools and 1,500 secondary schools were severely damaged, cracked or destroyed. In addition, the three main universities in Port-au-Prince were also severely damaged. Other affected infrastructure included telephone networks, radio station, factories, and museums. Poor infrastructure before the earthquake only made the aftermath worse. It would take half a day to make a trip of a few miles. The roads would also crisscross haphazardly due to disorganized construction.
 W
WEarthquake Baroque is a style of Baroque architecture found in the Philippines, which suffered destructive earthquakes during the 17th century and 18th century, where large public buildings, such as churches, were rebuilt in a Baroque style during the Spanish Colonial period in the country.
 W
WThe Earthquake Engineering Research Institute (EERI) is a leading technical society in dissemination of earthquake risk and earthquake engineering research both in the U.S. and globally. EERI members include researchers, geologists, geotechnical engineers, educators, government officials, and building code regulators. Their mission, as stated in their 5-year plan published in 2006, has three points: "Advancing the science and practice of earthquake engineering; Improving understanding of the impact of earthquakes on the physical, social, economic, political, and cultural environment; and Advocating comprehensive and realistic measures for reducing the harmful effects of earthquakes".
 W
WEarthquake-resistant or aseismic structures are designed to protect buildings to some or greater extent from earthquakes. While no structure can be entirely immune to damage from earthquakes, the goal of earthquake-resistant construction is to erect structures that fare better during Seismic activity than their conventional counterparts. According to building codes, earthquake-resistant structures are intended to withstand the largest earthquake of a certain probability that is likely to occur at their location. This means the loss of life should be minimized by preventing collapse of the buildings for rare earthquakes while the loss of the functionality should be limited for more frequent ones.
 W
WEarthquake environmental effects are the effects caused by an earthquake, including surface faulting, tsunamis, soil liquefactions, ground resonance, landslides and ground failure, either directly linked to the earthquake source or provoked by the ground shaking. These are common features produced both in the near and far fields, routinely recorded and surveyed in recent events, very often remembered in historical accounts and preserved in the stratigraphic record (paleoearthquakes). Both surface deformation and faulting and shaking-related geological effects not only leave permanent imprints in the environment, but also dramatically affect human structures. Moreover, underwater fault ruptures and seismically-triggered landslides can generate tsunami waves.
 W
WEarthquake insurance is a form of property insurance that pays the policyholder in the event of an earthquake that causes damage to the property. Most ordinary homeowners insurance policies do not cover earthquake damage.
 W
WEarthquake simulation applies a real or simulated vibrational input to a structure that possesses the essential features of a real seismic event. Earthquake simulations are generally performed to study the effects of earthquakes on man-made engineered structures, or on natural features which may present a hazard during an earthquake.
 W
WA gaiola pombalina is a masonry building reinforced with an internal wooden cage, developed as an anti-seismic construction system in Portugal after the 1755 Lisbon earthquake and implemented during the reconstruction of Lisbon Baixa (Lisbon downtown).
 W
WMedhat Haroun was an Egyptian-American expert on earthquake engineering. He wrote more than 300 technical papers and received the Charles Martin Duke Lifeline Earthquake Engineering Award (2006) and the Walter Huber Civil Engineering Research Prize (1992) from the American Society of Civil Engineers.
 W
WYanosuke Hirai was a Japanese civil engineer and corporate executive in the electric power industry. He developed electric power generation in the Tohoku region during the Shōwa era with unusual foresight and a deep sense of responsibility. 25 years after his death, Hirai’s foresight protected lives and environment from the March 11, 2011 Tohoku earthquake and tsunami. The Onagawa Nuclear Power Plant, designed and built under his watch, was the sole plant in the region that fully resisted the disaster of March 11, 2011: all of its three reactors successfully withstood the seismic event and subsequent tsunami, shutting down safely as designed and virtually without any incident. The site of the plant even ended up providing a refuge for three months to more than 300 neighboring people who had lost their homes.
 W
WICEARRAY is an abbreviation for Icelandic Strong-motion Array. The ICEARRAY network is a seismic array of 14 strong-motion stations located within the South Iceland Seismic Zone. Each station consists of a seismograph situated in a protective housing. The stations are spread across a geographical area of approximately 3 km² in the town of Hveragerdi in south-western Iceland. Most of the units are located in the basements of residential buildings in Hveragerdi town centre, which is approximately 35 km southeast of Iceland's capital, Reykjavík. The ICEARRAY project is supported by the 6th Framework of the European Commission through the Marie Curie International Re-integration Grant, the Iceland Centre for Research and the University of Iceland Earthquake Engineering Research Centre.
 W
WInsulating concrete form or insulated concrete form (ICF) is a system of formwork for reinforced concrete usually made with a rigid thermal insulation that stays in place as a permanent interior and exterior substrate for walls, floors, and roofs. The forms are interlocking modular units that are dry-stacked and filled with concrete. The units lock together somewhat like Lego bricks and create a form for the structural walls or floors of a building. ICF construction has become commonplace for both low rise commercial and high performance residential construction as more stringent energy efficiency and natural disaster resistant building codes are adopted.
 W
WThe Kashiwazaki-Kariwa Nuclear Power Plant is a large, modern nuclear power plant on a 4.2-square-kilometer (1,000-acre) site including land in the towns of Kashiwazaki and Kariwa in Niigata Prefecture, Japan on the coast of the Sea of Japan, from where it gets cooling water. The plant is owned and operated by Tokyo Electric Power Company (TEPCO).
 W
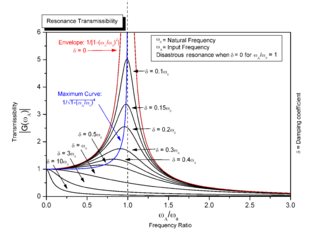
WMechanical resonance is the tendency of a mechanical system to respond at greater amplitude when the frequency of its oscillations matches the system's natural frequency of vibration than it does at other frequencies. It may cause violent swaying motions and even catastrophic failure in improperly constructed structures including bridges, buildings and airplanes. This is a phenomenon known as resonance disaster.
 W
WGiuseppe Mercalli was an Italian volcanologist and Catholic priest. He is known best for the Mercalli intensity scale for measuring earthquake intensity.
 W
WModal analysis is the study of the dynamic properties of systems in the frequency domain. Examples would include measuring the vibration of a car's body when it is attached to a shaker, or the noise pattern in a room when excited by a loudspeaker.
 W
WThe HurriQuake nail is a construction nail designed by Ed Sutt for Bostitch, a division of Stanley Works, and patented in 2004. The features of the nail are designed primarily to provide more structural integrity for a building, especially against the forces of hurricanes and earthquakes.
 W
WNational Center for Research on Earthquake Engineering is an organisation found in Taipei, Taiwan. Since Taiwan is located on the ridge of the Eurasian and Philippine tectonic plates, it is highly seismic. The biggest earthquake in Taiwan in more than a century was 21 September 1999, also known as the Chi-Chi earthquake which measured 7.3 on the Richter scale.
 W
WThe National Society for Earthquake Technology - Nepal (NSET) is a Nepali non-governmental organisation working on reducing earthquake risk and increasing earthquake preparedness in Nepal as well as other earthquake-prone countries.
 W
WNathan Mortimore Newmark was an American structural engineer and academic, who is widely considered as one of the founding fathers of Earthquake Engineering. He was awarded the National Medal of Science for engineering.
 W
WOscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. The term vibration is precisely used to describe mechanical oscillation. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum and alternating current.
 W
WPopp & Asociații is a professional services company based in Bucharest, Romania. It provides structural design & assessment, consultancy, retrofitting design, and project management services for all aspects of the built environment either existing or new, including infrastructure works design.
 W
WEarthquake engineering is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that designs and analyzes structures, such as buildings and bridges, with earthquakes in mind. Its overall goal is to make such structures more resistant to earthquakes. An earthquake engineer aims to construct structures that will not be damaged in minor shaking and will avoid serious damage or collapse in a major earthquake. Earthquake engineering is the scientific field concerned with protecting society, the natural environment, and the man-made environment from earthquakes by limiting the seismic risk to socio-economically acceptable levels. Traditionally, it has been narrowly defined as the study of the behavior of structures and geo-structures subject to seismic loading; it is considered as a subset of structural engineering, geotechnical engineering, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, applied physics, etc. However, the tremendous costs experienced in recent earthquakes have led to an expansion of its scope to encompass disciplines from the wider field of civil engineering, mechanical engineering, nuclear engineering, and from the social sciences, especially sociology, political science, economics, and finance.
 W
WA response spectrum is a plot of the peak or steady-state response of a series of oscillators of varying natural frequency, that are forced into motion by the same base vibration or shock. The resulting plot can then be used to pick off the response of any linear system, given its natural frequency of oscillation. One such use is in assessing the peak response of buildings to earthquakes. The science of strong ground motion may use some values from the ground response spectrum for correlation with seismic damage.
 W
WSeismic analysis is a subset of structural analysis and is the calculation of the response of a building structure to earthquakes. It is part of the process of structural design, earthquake engineering or structural assessment and retrofit in regions where earthquakes are prevalent.
 W
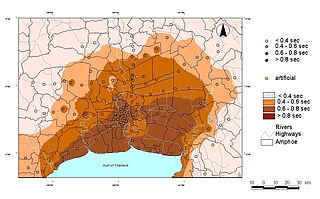
WSeismic microzonation is defined as the process of subdividing a potential seismic or earthquake prone area into zones with respect to some geological and geophysical characteristics of the sites such as ground shaking, liquefaction susceptibility, landslide and rock fall hazard, earthquake-related flooding, so that seismic hazards at different locations within the area can correctly be identified. Microzonation provides the basis for site-specific risk analysis, which can assist in the mitigation of earthquake damage. In most general terms, seismic microzonation is the process of estimating the response of soil layers under earthquake excitations and thus the variation of earthquake characteristics on the ground surface.
 W
WSeismic retrofitting is the modification of existing structures to make them more resistant to seismic activity, ground motion, or soil failure due to earthquakes. With better understanding of seismic demand on structures and with our recent experiences with large earthquakes near urban centers, the need of seismic retrofitting is well acknowledged. Prior to the introduction of modern seismic codes in the late 1960s for developed countries and late 1970s for many other parts of the world, many structures were designed without adequate detailing and reinforcement for seismic protection. In view of the imminent problem, various research work has been carried out. State-of-the-art technical guidelines for seismic assessment, retrofit and rehabilitation have been published around the world – such as the ASCE-SEI 41 and the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering (NZSEE)'s guidelines. These codes must be regularly updated; the 1994 Northridge earthquake brought to light the brittleness of welded steel frames, for example.
 W
WShakeAlert is an earthquake early warning system (EEW) for the West Coast of the United States and the Pacific Northwest sponsored by the United States Geological Survey (USGS).
 W
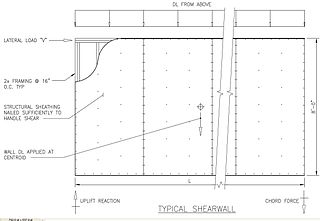
WIn structural engineering, a shear wall is a vertical element of a seismic force resisting system that is designed to resist in-plane lateral forces, typically wind and seismic loads. In many jurisdictions, the International Building Code and International Residential Code govern the design of shear walls.
 W
WThe shinbashira refers to a central pillar at the core of a pagoda or similar structure.
 W
WA soft story building is a multi-story building in which one or more floors have windows, wide doors, large unobstructed commercial spaces, or other openings in places where a shear wall would normally be required for stability as a matter of earthquake engineering design. A typical soft story building is an apartment building of three or more stories located over a ground level with large openings, such as a parking garage or series of retail businesses with large windows.
 W
WSoil liquefaction occurs when a saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses strength and stiffness in response to an applied stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other sudden change in stress condition, in which material that is ordinarily a solid behaves like a liquid. In soil mechanics, the term "liquefied" was first used by Allen Hazen in reference to the 1918 failure of the Calaveras Dam in California. He described the mechanism of flow liquefaction of the embankment dam as:If the pressure of the water in the pores is great enough to carry all the load, it will have the effect of holding the particles apart and of producing a condition that is practically equivalent to that of quicksand… the initial movement of some part of the material might result in accumulating pressure, first on one point, and then on another, successively, as the early points of concentration were liquefied.
 W
WSpectral acceleration (SA) is a unit measured in g that describes the maximum acceleration in an earthquake on an object – specifically a damped, harmonic oscillator moving in one physical dimension. This can be measured at different oscillation frequencies and with different degrees of damping, although 5% damping is commonly applied. The SA at different frequencies may be plotted to form a response spectrum.
 W
WA steel plate shear wall (SPSW) consists of steel infill plates bounded by boundary elements.
 W
WStilts are poles, posts or pillars used to allow a structure or building to stand at a distance above the ground. In flood plains, and on beaches or unstable ground, buildings are often constructed on stilts to protect them from damage by water, waves or shifting soil or sand.
 W
WStructural mechanics or Mechanics of structures is the computation of deformations, deflections, and internal forces or stresses within structures, either for design or for performance evaluation of existing structures. It is one subset of structural analysis. Structural mechanics analysis needs input data such as structural loads, the structure's geometric representation and support conditions, and the materials' properties. Output quantities may include support reactions, stresses and displacements. Advanced structural mechanics may include the effects of stability and non-linear behaviors.
 W
WIn earthquake engineering, vibration control is a set of technical means aimed to mitigate seismic impacts in building and non-building structures.