 W
WAlethopteris is a prehistoric plant genus of fossil Pteridospermatophyta that developed in the Carboniferous period.
 W
WAnnularia is a form taxon, applied to fossil foliage belonging to extinct plants of the genus Calamites in the order Equisetales.
 W
WArchimedes is a genus of bryozoans belonging to the family Fenestellidae. The first use of the term "Archimedes" in relation to this genus was in 1838.
 W
WAsaphiscus is a genus of trilobite that lived in the Cambrian. Its remains have been found in Australia and North America, especially in Utah.
 W
WAtrypa is a genus of brachiopod with shells round to short egg-shaped, covered with many fine radial ridges, that split further out and growthlines perpendicular to the costae and 2-3 times wider spaced. The pedunculate valve is a little convex, but tends to level out or even become slightly concave toward the anterior margin. The brachial valve is highly convex. There is no interarea in either valve. Atrypa was a cosmopolitan and occurred from the late Lower Silurian (Telychian) to the early Upper Devonian (Frasnian). Other sources expand the range from the Late Ordovician to Carboniferous, approximately from 449 to 336 Ma. A proposed new species, A. harrisi, was found in the trilobite-rich Floresta Formation in Boyacá, Colombia.
 W
WCalamites is a genus of extinct arborescent (tree-like) horsetails to which the modern horsetails are closely related. Unlike their herbaceous modern cousins, these plants were medium-sized trees, growing to heights of 30-50 meters. They were components of the understories of coal swamps of the Carboniferous Period.
 W
WCallipteridium is an extinct genus of pteridospermous seed ferns belonging to the family Cyclopteridaceae. These ferns existed in the Carboniferous period.
 W
WCalymene is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida that are found throughout North America, North Africa, and Europe in primarily Silurian outcrops. Calymene is closely related to Flexicalymene, and both genera are frequently found enrolled. Calymene trilobites are small, typically 2 cm in length. The cephalon is the widest part of the animal and the thorax usually has 13 segments.
 W
WOtodus angustidens is a species of prehistoric megatoothed sharks in the genus Otodus, which lived during the Oligocene and Miocene epochs about 33 to 22 million years ago. This shark is related to another extinct megatoothed shark, Otodus megalodon.
 W
WCincinnetina is an extinct genus of brachiopods which existed in what is now the United States during the Late Ordovician. It was described by Jisuo Jin in 2012, as a new genus for the Orthis species O. multisecta and O. meeki, each of which have been replaced a number of times under other genera, e.g. Dalmanella, Resserella, and Onniella by other authors. A third species, C. minnesotensis, was described from Minnesota, from which its species epithet was derived.
 W
WConstellaria is an extinct genus of bryozoan from the Ordovician.
 W
WCordaites is an important genus of extinct gymnosperms which grew on wet ground similar to the Everglades in Florida. Brackish water mussels and crustacea are found frequently between the roots of these trees. The fossils are found in rock sections from the Upper Carboniferous of the Dutch - Belgian - German coal area. A number of many noteworthy types from this line are:Cordaites principalis Cordaites ludlowi Cordaites hislopii. Found in Paleorrota geopark in Brazil.
 W
WCynthiacetus is an extinct genus of basilosaurid early whale that lived during the Late Eocene Specimens have been found in the southeastern United States and Peru.
 W
WCyrtoceras is an extinct genus of oncoceridan nautiloids that lived from the middle Ordovician to the middle Devonian, in Africa, Europe, North America and South America.
 W
WDalmanitidae is a family of trilobites in the order Phacopida that lived from the Floian (Ordovician) to the Devonian and includes 33 genera.
 W
WDipleura is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida. It was described by Green in 1832, and the type species is Dipleura dekayi. The type locality was in the Hamilton Group in New York.
 W
WElrathia is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite species that lived during the Middle Cambrian of Utah, and possibly British Columbia. E. kingii is one of the most common trilobite fossils in the USA locally found in extremely high concentrations within the Wheeler Formation in the U.S. state of Utah. E. kingii has been considered the most recognizable trilobite. Commercial quarries extract E. kingii in prolific numbers, with just one commercial collector estimating 1.5 million specimens extracted in a 20-year career. 1950 specimens of Elrathia are known from the Greater Phyllopod bed, where they comprise 3.7% of the community."...trilobite occupied the exaerobic zone, at the boundary of anoxic and dysoxic bottom waters. E. kingii consistently occur in settings below the oxygen levels required by other contemporaneous epifaunal and infaunal benthic biota and may have derived energy from a food web that existed independently of phototrophic primary productivity. Although other fossil organisms are known to have preferred such environments, E. kingii is the earliest-known inhabitant of them, extending the documented range of the exaerobic ecological strategy into the Cambrian Period."
 W
WFavosites is an extinct genus of tabulate coral characterized by polygonal closely packed corallites. The walls between corallites are pierced by pores known as mural pores which allowed transfer of nutrients between polyps. Favosites, like many corals, thrived in warm sunlit seas, feeding by filtering microscopic plankton with their stinging tentacles and often forming part of reef complexes. The genus had a worldwide distribution from the Late Ordovician to Late Permian.
 W
WFlexicalymene is a genus of trilobites of the order Phacopida, suborder Calymenina. They are found abundantly in North America. Flexicalymene specimens can be mistaken for Calymene, Gravicalymene, Diacalymene and a few other Calymenina genera. They are used as an index fossil in the Ordovician. Ohio and North America are particularly known for being rich with Flexicalymene fossils. Species include F. meeki and F. retrorsa, F. granulosa, F. senaria and F. croneisi (Ontario).
 W
WHallopora is an extinct genus of bryozoans. They can be found in Ohio, Indiana, and Kentucky of the Midwestern United States, commonly in the Ordovician Kope Formation.
 W
WLeptaena is an extinct genus of mid-sized brachiopod that existes from the Dariwilian epoch to the Emsian epoch, though some specimens have been found in strata as late in age as the Tournasian epoch. Like some other Strophomenids, Lepteana were epifaunal, meaning they lived on top of the seafloor, not buried within it, and were suspension feeders.
 W
WLingula is a genus of brachiopods within the class Lingulata. Lingula or forms very close in appearance have existed possibly since the Cambrian. Like its relatives, it has two unadorned organo-phosphatic valves and a long fleshy stalk. Lingula lives in burrows in barren sandy coastal seafloor and feeds by filtering detritus from the water. It can be detected by a short row of three openings through which it takes in water (sides) and expels it again (middle).
 W
WLyginopteris is a genus of Late Carboniferous seed fern stems with a very distinctive outer cortex of sclereids forming a pattern in cross section like Roman numerals on a clock face, often called a Sparganum cortex. Some Lyginopteris were parasitized by water molds.
 W
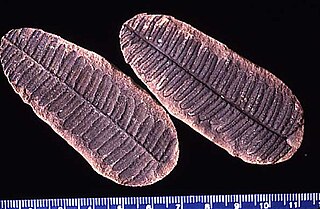
WNeuropteris is an extinct seed fern that existed in the Carboniferous period, known only from fossils.
 W
WPecopteris is a very common form genus of leaves. Most Pecopteris leaves and fronds are associated with the marattialean tree fern Psaronius. However, Pecopteris-type foliage also is borne on several filicalean ferns, and at least one seed fern. Pecopteris first appeared in the Devonian period, but flourished in the Carboniferous, especially the Pennsylvanian. Plants bearing these leaves became extinct in the Permian period.
 W
WPelagiellidae is an extinct family of Paleozoic fossil marine molluscs.
 W
WPentamerus is a prehistoric genus of brachiopods that lived from the Silurian to the Middle Devonian in Asia, Europe, and North America.
 W
WPentremites is an extinct genus of blastoid echinoderm belonging to the family Pentremitidae.
 W
WPeronopsis is a genus of trilobite restricted to the Middle Cambrian. Its remains have been found in Asia, Australia, Europe, and North America.
 W
WPhacops is a genus of trilobites in the order Phacopida, family Phacopidae, that lived in Europe, northwestern Africa, North and South America and China from the Late Ordovician until the very end of the Devonian, with a broader time range described from the Late Ordovician. It was a rounded animal, with a globose head and large eyes, and probably fed on detritus. Phacops is often found rolled up ("volvation"), a biological defense mechanism that is widespread among smaller trilobites but further perfected in this genus.
 W
WPlatycrinites are an extinct genus of Paleozoic stalked crinoids belonging to the family Platycrinitidae.
 W
WPlatystrophia is an extinct genus of brachiopods that lived from the Ordovician to the Silurian in Asia, Europe, North America, and South America. It has a prominent sulcus and fold. It usually lived in marine lime mud and sands.
 W
WPleurodictyum is an extinct genus of tabulate corals, characterized by polygonal corallites. Colonies commonly encrust hard substrates such as rocks, shells and carbonate hardgrounds.
 W
WRafinesquina is an extinct genus of large brachiopod that existed from the Darriwilian to the Ludlow epoch.
 W
WSigillaria is a genus of extinct, spore-bearing, arborescent (tree-like) plants. It was a lycopodiophyte, and is related to the lycopsids, or club-mosses, but even more closely to quillworts, as was its associate Lepidodendron.
 W
WThe extinct Solenoporaceae have traditionally been interpreted as a group of red algae ancestral to the Corallinales.
 W
WSphenophyllum is a genus in the order Sphenophyllales.
 W
WSphenopteris is a genus of seed ferns containing the foliage of various extinct plants, ranging from the Devonian to Late Cretaceous.
 W
WSpirifer is a genus of marine brachiopods belonging to the order Spiriferida and family Spiriferidae. Species belonging to the genus lived from the Middle Ordovician (Sandbian) through to the Middle Triassic (Carnian) with a global distribution. They were stationary epifaunal suspension feeders.
 W
WStigmaria is a form taxon for common fossils found in Carboniferous rocks. They represent the underground rooting structures of coal forest lycopsid trees such as Sigillaria and Lepidodendron. These swamp forest trees grew to 50 meters and were anchored by an extensive network of branching underground structures with "rootlets" attached to them. Analysis of the morphology and anatomy of these stigmarian systems suggests they were shoot-like and so they are called rhizomes or rhizophores. The stigmarian rhizomes are typically covered with a spiral pattern of circular scars where "rootlets" were attached. Since the stigmarian systems are shoot-like, these "rootlets" may be modified leaves, adapted to serve the function of roots. However, some paleontologists argue that the "rootlets" were true roots, with a complex branching structure and root hairs, comparable to the roots of the closest living relative of Lepidodendron, the quillworts.
 W
WStrophomena is a genus of brachiopods belonging to the order Strophomenida family Strophomenidae, named by Rafinesque in 1824. They were stationary epifaunal suspension feeders.
 W
WTricrepicephalus is an extinct genus of ptychopariid trilobites of the family Tricrepicephalidae with species of average size. Its species lived from 501 to 490 million years ago during the Dresbachian faunal stage of the late Cambrian Period. Fossils of Tricrepicephalus are widespread in Late Cambrian deposits in North America, but is also known from one location in South-America. Tricrepicephalus has an inverted egg-shaped exoskeleton, with three characteristic pits in the fold that parallels the margin of the headshield just in front of the central raised area. The articulating middle part of the body has 12 segments and the tailshield carries two long, tubular, curved pygidial spines that are reminiscent of earwig's pincers that rise backwards from the plain of the body at approximately 30°.