 W
WOrganothiophosphates or organophosphorothioates are a subclass of organophosphorus compounds. Many of these compounds are used as pesticides, some have medical applications, and some are used as oil additives. They generally have the chemical formula (RO)3PS, [(RO)2P(S)O]−, R(RO)2PS, etc.
 W
WAmmonium diethyl dithiophosphate or more systematically ammonium O,O′-diethyl dithiophosphate, is the ammonium salt of diethyl dithiophosphoric acid. It is used as a source of the (C2H5O)2PS2− ligand in coordination chemistry and in analytical chemistry for determination of various ions. It can be obtained by the reaction of phosphorus pentasulfide with ethanol and ammonia. In crystal structure of this compound the ammonium cation is connected by four charge-assisted N—H···S hydrogen bonds to four tetrahedral diethyl dithiophosphate anions.
 W
WAzamethiphos is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is a veterinary drug used in Atlantic salmon fish farming to control parasites.
 W
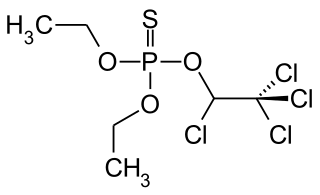
WCarbophenothion also known as Stauffer R 1303 as for the manufacturer, Stauffer Chemical, is an organophosphorus chemical compound. It was used as a pesticide for citrus fruits under the name of Trithion. Carbophenothion was used as an insecticide and acaricide. Although not used anymore it is still a restricted use pesticide in the United States. The chemical is identified in the US as an extremely hazardous substance according to the Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act.
 W
WChlorethoxyfos is an organophosphate acetylcholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide. It is registered for the control of corn rootworms, wireworms, cutworms, seed corn maggot, white grubs and symphylans on corn. The insecticide is sold under the trade name Fortress by E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Company.
 W
WChlormephos (chemical formula: C5H12ClO2PS2) is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act (42 U.S.C. 11002), and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
 W
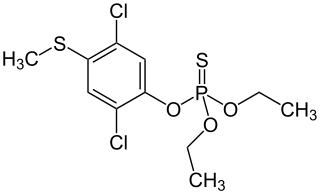
WChlorpyrifos (CPS) is an organophosphate pesticide used on crops, animals, and buildings, and in other settings, to kill a number of pests, including insects and worms. It acts on the nervous systems of insects by inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme. Chlorpyrifos was patented in 1966 by Dow Chemical Company.
 W
WChlorthiophos is an organophosphorus pesticide. It is a mixture of isomers:
 W
WCoumaphos is a nonvolatile, fat-soluble phosphorothioate with ectoparasiticide properties: it kills insects and mites. It is well known by a variety of brand names as a dip or wash, used on farm and domestic animals to control ticks, mites, flies and fleas.
 W
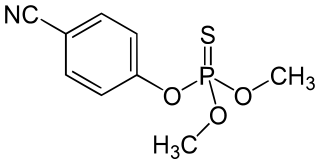
WCyanophos is a cholinesterase inhibitor used as an insecticide and avicide; for example, against rice stem borers and house flies. It is part of the chemical class of organophosphorus compounds, and is a yellow to reddish-yellow transparent liquid.
 W
WDemeton was a phosphorothioate insecticide with the chemical formula C8H19O3PS2. While it was previously used as an insecticide, it is now largely obsolete due to its relatively high toxicity to humans. The chemical structure of demeton is closely related to military nerve agents such as VX, and a derivative with one of the ethoxy groups replaced by methyl was investigated by both the US and Soviet chemical weapons programs under the names "V.sub.X" and "GD-7".
 W
WDiazinon, a colorless to dark brown liquid, is a thiophosphoric acid ester developed in 1952 by Ciba-Geigy, a Swiss chemical company. It is a nonsystemic organophosphate insecticide formerly used to control cockroaches, silverfish, ants, and fleas in residential, non-food buildings. Diazinon was heavily used during the 1970s and early 1980s for general-purpose gardening use and indoor pest control. A bait form was used to control scavenger wasps in the western U.S. Diazinon is used in flea collars for domestic pets in Australia and New Zealand. Residential uses of diazinon were outlawed in the U.S. in 2004 because of human health risks but it is still approved for agricultural uses. An emergency antidote is atropine.
 W
WDichlofenthion is a phosphorothioate which is primarily used as a pesticide and nematicide.
 W
WDiethyl dithiophosphoric acid, sometimes mistakenly called diethyl dithiophosphate, is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (C2H5O)2PS2H. It is the processor for production of the organophosphate insecticide Terbufos. Although samples can appear dark, it is a colorless liquid.
 W
WDimethyl dithiophosphoric acid is the organophosphorus compound with the formula (CH3O)2PS2H. It is the processor for production of the organothiophosphate insecticide Malathion. Although samples can appear dark, the compound is a colorless, distillable liquid.
 W
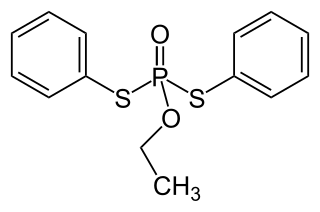
WEchothiophate (Phospholine) is an irreversible acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
 W
WEdifenphos is a systemic fungicide that inhibits phosphatidylcholine biosynthesis. It was introduced in 1966 by Bayer to combat blast fungus and Pellicularia sasakii in rice cultivation. It was never authorized for use in the EU.
 W
WFenitrothion is a phosphorothioate (organophosphate) insecticide that is inexpensive and widely used worldwide. Trade names include Sumithion, a 94.2% solution of fenitrothion.
 W
WFenthion is an organothiophosphate insecticide, avicide, and acaricide. Like most other organophosphates, its mode of action is via cholinesterase inhibition. Due to its relatively low toxicity towards humans and mammals, fenthion is listed as moderately toxic compound in U.S. Environmental Protection Agency and World Health Organization toxicity class.
 W
WIsoxathion is a molecular chemical with the molecular formula C13H16NO4PS. It is an insecticide, specifically an isoxazole organothiophosphate insecticide.
 W
WMalaoxon (Liromat, Malation oxon, Malthon oxon) is a chemical compound with the formula C10H19O7PS. More specifically, it is a phosphorothioate. It is a breakdown product of, and more toxic than, malathion.
 W
WML-154 (NCGC-84) is a drug which acts as a selective, non-peptide antagonist at the neuropeptide S receptor NPSR. In animal studies it decreases self-administration of alcohol in addicted rats, and lowers motivation for alcohol rewards, suggesting a potential application for NPS antagonists in the treatment of alcoholism.
 W
WOmethoate (C5H12NO4PS) is a systemic organophosphorous insecticide and acaricide available as a soluble concentrate. It is used to control insects and mites in horticulture and agriculture, as well as in the home garden.
 W
WOxydemeton-methyl is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is primarily used to control aphids, mites, and thrips.
 W
WParathion, also called parathion-ethyl or diethyl parathion and locally known as "Folidol", is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide. It was originally developed by IG Farben in the 1940s. It is highly toxic to non-target organisms, including humans, so its use has been banned or restricted in most countries. The basic structure is shared by parathion methyl.
 W
WParathion methyl, or methyl parathion, is an organophosphate insecticide, possessing an organothiophosphate group. It is structurally very similar to parathion-ethyl. It is not allowed for sale and import in nearly all countries around the world, while a few allow it under subject to specified conditions only.
 W
WParathion S is an organophosphate related to the organophosphate insecticide paraoxon and parathion. It's the structural isomer of parathion. Parathion S is a potent acetylcholinesterase inhibitor.
 W
WPhenthoate is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is used against Lepidoptera, jassids, aphids, soft scales, mosquitoes, blowflies, houseflies, and ked.
 W
WPhoxim is an organophosphate insecticide that is produced by the Bayer corporation. It is an analogous dimethyl ester and an organothiophosphate acaricide. It is allowed for use in limited applications in the European Union. It is banned for use on crops in the European Union since 22 December 2007.
 W
WPirimiphos-methyl, marketed as Actellic, and Sybol is a phosphorothioate used as an insecticide. It was originally developed by Imperial Chemical Industries Ltd., now Syngenta, at their Jealott's Hill site and first marketed in 1977, ten years after its discovery.
 W
WSodium dithiophosphate is the salt with the formula Na3PS2O2. It is usually supplied as the hydrated solid or as an aqueous solution together with other thiophosphates such as sodium monothiophosphate and sodium trithiophosphate. It is a colorless compound, but commercial samples can appear dark owing to the presence of impurities. It is used to facilitate the isolation of molybdenum from its ores.
 W
WSodium monothiophosphate, or sodium phosphorothioate, is an inorganic compound with the molecular formula Na3PO3S(H2O)x. All are white solids. The anhydrous material (x = 0) decomposes without melting at 120-125 °C. More common is the dodecahydrate. A nonahydrate is also known.
 W
WSulfotep (also known as tetraethyldithiopyrophosphate and TEDP) is a pesticide commonly used in greenhouses as a fumigant. The substance is also known as Dithione, Dithiophos, and many other names. Sulfotep has the molecular formula C8H20O5P2S2 and belongs to the organophosphate class of chemicals. It has a cholinergic effect, involving depression of the cholinesterase activity of the peripheral and central nervous system of insects. The transduction of signals is disturbed at the synapses that make use of acetylcholine. Sulfotep is a mobile oil that is pale yellow-colored and smells like garlic. It is primarily used as an insecticide.
 W
WTBPS (tert-butylbicyclophosphorothionate) is a bicyclic phosphate convulsant. It is an extremely potent GABA receptor antagonist.
 W
WTebupirimfos, also known as phostebupirim, is an organothiophosphate insecticide. It is used on corn crops, including popcorn.
 W
WTemefos or temephos is an organophosphate larvicide used to treat water infested with disease-carrying insects including mosquitoes, midges, and black fly larvae.
 W
WThionazin is a chemical compound used in nematicides.
 W
WThiophosphoric acid is a chemical compound. Structurally, it is the acid derived from phosphoric acid with one extra sulfur atom, although it cannot be prepared from phosphoric acid. It is a colorless compound that is rarely isolated in pure form, but rather as a solution. The structure of the compound has not been reported, but two tautomers are reasonable: SP(OH)3 and OP(OH)2SH.
 W
WTransition metal dithiophosphate complexes are coordination compounds containing dithiophosphate ligands, i.e. ligands of the formula (RO)2PS−2. The homoleptic complexes have formulas M[S2P(OR)2]2 and M[S2P(OR)2]3. These neutral complexes tend to be soluble in organic solvents, especially when R is branched.
 W
WVG is a "V-series" nerve agent chemically similar to the better-known VX nerve agent. Tetram is the common Russian name for the substance. Amiton was the trade name for the substance when it was marketed as an insecticide by ICI in the mid-1950s.
 W
WZinc dialkyldithiophosphates are a family of coordination compounds developed in the 1940s that feature zinc bound to the anion of a dialkyldithiophosphoric acid. These uncharged compounds are not salts. They are soluble in nonpolar solvents, and the longer-chain derivatives easily dissolve in mineral and synthetic oils used as lubricants. They come under CAS number 68649-42-3. In aftermarket oil additives, the percentage of ZDDP ranges approximately between 2 and 15%. Zinc dithiophosphates have many names, including ZDDP, ZnDTP, and ZDP.