 W
WAbel is an ancient lunar impact crater that lies near the southeast limb of the Moon's near side. It is located to the south of the crater Barnard, at the northwest edge of the Mare Australe.
 W
WAdams is a lunar impact crater that is located in the rugged southeastern section of the Moon, near the lunar limb. It lies just to the southwest of the crater Legendre. To the northwest are the craters Hase and Petavius, and to the southwest is Furnerius. To the southwest of Adams is a system of rilles designated the Rimae Hase. The longest of these rilles follows a course to the southeast.
 W
WAnuchin is a lunar impact crater that lies on the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It is located to the south of the larger crater Lamb, and to the north-northwest of Kugler.
 W
WBjerknes is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the rugged far side of the Moon. The crater lies behind the southeastern limb, and beyond the region that is sometimes brought into sight through libration. Thus this crater can not be viewed from Earth, and has only been seen from orbit. Nearby named craters are Clark to the east, and Pogson to the south-southwest.
 W
WBrisbane is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southeastern part of the Moon, to the south of the crater Peirescius. To the northwest lie the craters Vega and Reimarus, and farther to the east is the walled plain Lyot. Due to its proximity to the limb, foreshortening of this crater causes it to appear somewhat elliptical in shape, even though it is actually circular.
 W
WCassegrain is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, beyond the southeastern limb. It lies to the southeast of the larger crater Lebedev, and to the northeast of the comparably-sized Priestley.
 W
WChamberlin is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon, just past the southeastern limb. It lies to the southeast of the crater Jeans, and Moulton is attached to the southeastern rim of Chamberlin. This crater is located in a part of the lunar surface that has undergone resurfacing of crater interiors, producing dark-hued crater floors.
 W
WClark is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere of the Moon's far side. It is located midway between the larger walled plain Van der Waals to the south and the similar-sized crater Pizzetti to the north. It is named for American astronomer and telescope maker Alvan Clark and his son Alvan Graham Clark.
 W
WDonner is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located just to the northeast of the Mare Australe, behind the southeastern limb of the Moon. During favorable librations this part of the lunar surface can be brought into view of the Earth, but the site is viewed from the edge and so not much detail can be seen.
 W
WFurnerius is a large lunar impact crater located in the southeast part of the Moon, in the area close to the southeastern limb of the nearside or visible Moon. Because of its location, the crater appears oval in shape due to foreshortening but is actually nearly circular. Notable nearby craters include Stevinus to the northwest and Fraunhofer to the south-southwest. Farther to the northwest is the crater Snellius and the Vallis Snellius crater valley.
 W
WGernsback is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located in the northeastern part of the uneven Mare Australe, just behind the southeastern limb. During periods of favorable libration this feature can be brought into view of the Earth, but it is seen from the side and not much detail can be observed. It is located about a crater diameter north of the larger crater Lamb, and southwest of Parkhurst.
 W
WGill is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southeastern limb of the Moon. Due to its proximity to the edge of the Moon as seen from the Earth, this crater is viewed nearly from the side and it can become hidden from sight due to libration. The crater lies to the southwest of the irregular Mare Australe, and southeast of the prominent crater Pontécoulant. To the southwest of Gill is the crater Helmholtz.
 W
WGum is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southeastern limb of the Moon, and is viewed nearly from the side from Earth. It lies along the western edge of the irregular Mare Australe, to the northeast of the crater Hamilton. To the north-northwest is the larger Abel, and to the east-southeast on the far side of the Moon is Jenner.
 W
WHamilton is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southeastern limb of the Moon. From the Earth this crater is viewed nearly from the edge, limiting the amount of detail that can be observed. It can also become hidden from sight due to libration, or brought into a more favorably viewing position.
 W
WHanno is a lunar impact crater that lies near the southeastern limb of the Moon, along the western edge of the Mare Australe. About a crater diameter to the southwest is the prominent crater Pontécoulant.
 W
WJeans is a lunar impact crater, on the southeastern limb of the Moon, with its majority lying on the far side. A favorable libration can bring the entire crater into view, but even then the details observable from Earth are very limited as the crater is viewed rather "edge-on".
 W
WJenner is a lunar crater that is located within the Mare Australe. It lies just past the southeastern limb, on the far side of the Moon, and can be viewed from the Earth during periods of favorable libration and lighting. Nearly attached to the eastern outer rim of Jenner is the larger, flooded crater Lamb.
 W
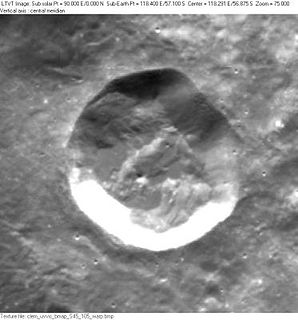
WKimura is a small impact crater that is located on the Moon's far side, beyond the southeastern limb. It lies to the west-northwest of the crater Fechner, along the northeastern rim of an unnamed basin in the surface.
 W
WKugler is a lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It is located just past the southeast limb of the Moon's surface, in the proximity of the libration zone that is occasionally brought into sight. The crater lies in the midpoint between the craters Anuchin to the north-northwest and Priestley to the south-southeast.
 W
WLamb is a lunar crater that lies beyond the southeastern limb on the Moon's far side. It is located in an irregular lunar mare region named Mare Australe, just to the east of the crater Jenner.
 W
WLebedev is a crater on the far side of the Moon. It is located at the eastern edge of the irregular feature known as Mare Australe. The crater lies to the southeast of the larger, flooded Lamb, and to the east-northeast of Anuchin. To the southeast of Lebedev lies the smaller crater Cassegrain.
 W
WLyot is a large lunar impact crater that is located along the southeastern limb of the Moon. It lies within the irregular and patchy lunar mare named Mare Australe, and to the south of the crater Hamilton. Due to its location, this formation is viewed at a low angle from the Earth, and its visibility is affected by libration.
 W
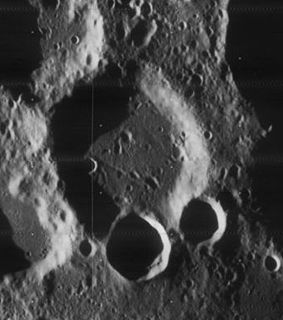
WMare Australe is a lunar mare located in the southeastern hemisphere of the Moon. It is 997 kilometers in diameter, overlapping the near and far sides of the Moon. Smooth, dark volcanic basalt lines the bottom of the mare. The Australe basin was formed in the Pre-Nectarian epoch, while the mare material inside formed in the Upper Imbrian epoch. The basin was almost completely destroyed by impacts prior to the appearance of the mare.
 W
WMarinus is a lunar impact crater that is located near the southeastern limb of the Moon. At this location it is viewed at an oblique angle from the Earth, limiting the amount of detail that can be observed. It lies due north of the slightly larger and dark-floored crater Oken. To the east is the northern part of the Mare Australe.
 W
WThe Mendel-Ryberg Basin is a Nectarian impact basin on the southwestern limb of the moon. It is named after the crater Mendel on the west margin and the smaller crater Rydberg north of the center of the basin. The basin is due south of the larger, younger Orientale basin, and ejecta and other geomorphological effects from the younger basin have overprinted the older one.
 W
WMilne is a large lunar crater that is located in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon, named after the British mathematician and astrophysicist Edward Arthur Milne. It lies to the northeast of the Mare Australe, and southeast of Lacus Solitudinis.
 W
WMoulton is a crater on the Moon's far side, just beyond the south-southwestern limb as seen from the Earth. The crater is attached to the southern edge of Chamberlin, and it lies at the northern terminus of the Vallis Schrödinger. There is a cleft in the shared rim between Chamberlin and Moulton.
 W
WOken is a lunar impact crater near the southeastern limb of the Moon. It is normally visible from the Earth, but is foreshortened and within the region of the surface that is subject to libration. To the south and east of this feature is the broad, uneven Mare Australe, which extends to the far side of the Moon.
 W
WParkhurst is a heavily degraded lunar impact crater to the northeast of the Mare Australe on the far side of the Moon. To the north-northeast of Parkhurst is the crater Scaliger and to the southwest lies the dark-floored Gernsback. The small lunar mare named Lacus Solitudinis lies due north of Parkhurst.
 W
WPeirescius is a lunar impact crater that is located in the southeastern part of the Moon. It is close enough to the limb that it appears significantly foreshortened when viewed from the Earth, even though it is nearly circular in shape. To the west-northwest of Peirescius is the crater Vega, and less than one crater diameter to the south is Brisbane. Farther to the east is the Mare Australe.
 W
WPetropavlovsky is a crater on the far side of the Moon. It is attached to the southern rim of the slightly larger crater Razumov, intruding slightly into the interior. Just to the west is the crater Frost, along the southern rim of the walled plain Landau.
 W
WPetrov is an impact crater along the southeastern limb of the Moon. The crater is difficult to observe in this location, and visibility of this feature is affected by libration. The nearest crater of note is Chamberlin, just on the far side to the northeast. Somewhat farther to the west-southwest of Petrov is Gill.
 W
WPilâtre is a lunar impact crater near the southwestern limb of the Moon. It is located just to the north-northwest of the much larger walled plain Hausen. The satellite crater Pingré S is attached to the eastern rim, with Pingré itself located farther to the northeast. Just to the west-southwest is Chappe, a formation of similar dimension to Pilâtre.
 W
WPizzetti is a partly eroded lunar impact crater that lies in the southern hemisphere on the far side of the Moon. It is located due north of the similar-dimensioned Clark, and to the southeast of the large walled plain Milne. Nearly attached to the western rim is the small Tyndall. The crater is named for the Italian astronomer and geodesist Paolo Pizzetti (1860-1918).
 W
WPogson is a lunar impact crater on the Moon's far side, behind the southeastern limb. It is located midway between the flooded crater Lebedev to the southwest and Bjerknes to the northeast. Farther west of Pogson is the uneven Mare Australe.
 W
WPontécoulant is a prominent lunar impact crater that is located in the southeastern part of the Moon. Due to its position, the crater appears foreshortened from the Earth and it is difficult to observe much detail. Nearby craters include Hanno just to the northeast, and the comparably sized Helmholtz due south.
 W
WPriestley is a lunar impact crater that is located on the far side of the Moon from the Earth, in the low southern latitudes. It lies to the southeast of the flooded crater Kugler.
 W
WReimarus is a lunar impact crater, located in the southeastern part of the Moon's near side. The eroded southeastern end of the long Vallis Rheita passes just to the west. To the northeast is the larger and heavily worn crater Vega.
 W
WTyndall is a relatively small lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon, behind the southeastern limb. It is located very near the western outer rim of the larger crater Pizzetti, and the two are separated only by a few kilometers. To the southwest of Tyndall is the crater Bjerknes, and to the south lies Clark.
 W
WVan der Waals is a lunar impact crater on the far side of the Moon. It is a heavily eroded feature with an irregular outer rim. The edge is lowest along the southern side where it is little more than a circular crest along the ground. It is more developed along the northern side, but the rim is notched and rugged. The satellite crater Van der Waals W is attached to the exterior of the northeast, and Van der Waals H intrudes into the rim along the southeast. The interior floor is relatively even and featureless, with only a few tiny craterlets to mark the surface.
 W
WVega is an eroded lunar impact crater that is located in the southeastern part of the Moon. It lies on the near side and so can be viewed from the Earth. Less than one crater diameter to the east-southeast is the slightly smaller Peirescius. About one and a half crater diameters to the west is the long Vallis Rheita.