 W
WAcheroraptor is an extinct genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur known from the latest Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation of Montana, United States. It contains a single species, Acheroraptor temertyorum. A. temertyorum is one of the two geologically youngest known species of dromaeosaurids, the other being Dakotaraptor, which is also known from Hell Creek. A basal cousin of Velociraptor, Acheroraptor is known from upper and lower jaw material.
 W
WAdocus is an extinct genus of aquatic turtles belonging to the family Adocidae. Adocus was once considered a genus belonging to the family Dermatemyidae.
 W
WAlphadon was a genus of small, primitive mammal that was a member of the metatherians, a group of mammals that includes modern-day marsupials. Its fossils were first discovered in Henan, China, and named by George Gaylord Simpson in 1929.
 W
WAnkylosaurus is a genus of armored dinosaur. Its fossils have been found in geological formations dating to the very end of the Cretaceous Period, about 68–66 million years ago, in western North America, making it among the last of the non-avian dinosaurs. It was named by Barnum Brown in 1908; the only species in the genus is A. magniventris. The genus name means "fused lizard", and the specific name means "great belly". A handful of specimens have been excavated to date, but a complete skeleton has not been discovered. Though other members of Ankylosauria are represented by more extensive fossil material, Ankylosaurus is often considered the archetypal member of its group, despite having some unusual features.
 W
WAnzu is a genus of caenagnathine dinosaur from the late Cretaceous of North Dakota and South Dakota, US. The type species is Anzu wyliei.
 W
WAvisaurus is a genus of enantiornithine bird from the Late Cretaceous of North America.
 W
WAxestemys is an extinct genus of softshell turtle that lived from the Late Cretaceous to the Eocene in western North America and Europe.
 W
WBasilemys is a large, terrestrial trionychoid turtle that was from the Upper Cretaceous time period. In Greek, the "Basil (name)" means royal or kingly and the word "Emys" means turtle. Therefore, Basilemys means King Turtle. The stratigraphic subdivisions of the Upper Cretaceous include Cenomanian, Turonian, Coniacian, Santonian, Campanian, and Maastrichtian. Basilemys was mostly from the Campanian and Maastrichtian subdivisions of the Cretaceous time period and is considered to be the largest terrestrial turtle of its time. This extinct genus of land turtles belongs to the family Nanhsiungchelyidae. Occurrences of Basilemys have largely been reported in the North America region. It is interesting to note that the family Nanhsiungchelyidae made its first appearance in the Lower Cretaceous in Asia and we know from Basilemys that this family appeared in the Upper Cretaceous in North America. The North American populations of Basilemys are considered to be immigrants from Asia through the Beringia during the Upper Cretaceous. In an analysis made by Sukhanov et al. on a new Nansiunghelyid turtle from the Upper Cretaceous of Mongolia, it was demonstrated that Asian nanhsiungchelyids gave rise to the North American nanhsiungchelyids. One genus from the family Nanhsiungchelyidae, Zangerlia, is similar to Basilemys in terms of skull proportions. However, Basilemys has a more complex triturating surface that includes well-defined pockets on the dentary. Basilemys also has tooth-like projections on the triturating surface of the maxilla.
 W
WBorealosuchus is an extinct genus of crocodylians that lived from the Late Cretaceous to the Eocene in North America. It was named by Chris Brochu in 1997 for several species that had been assigned to Leidyosuchus. The species assigned to it are: B. sternbergii, the type species, from the Maastrichtian of Colorado, Montana, North Dakota, South Dakota, and Wyoming; B. acutidentatus, from the Paleocene of Saskatchewan; B. formidabilis, from the Paleocene of North Dakota; B. griffithi, from the Paleocene of Alberta; and B. wilsoni, from the Eocene of Wyoming. B. formidabilis is particularly well-known, represented by the remains of many individuals from the Wannagan Creek site in North Dakota.
 W
WBrachychampsa is an extinct genus of alligatoroid. Specimens have been found from New Mexico, Colorado, Wyoming, Montana, North and South Dakota, New Jersey, and Saskatchewan. One specimen has been found from the Darbasa Formation of Kazakhstan, although the species status is indeterminant for the fossil. The genus first appeared during the late Campanian stage of the Late Cretaceous and became extinct during the early Danian stage of the Paleocene, a few million years after the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Brachychampsa is distinguished by an enlarged fourth maxillary tooth in the upper jaw.
 W
WCedrobaena is an extinct genus of turtle which existed in the Tiffanian Cedar Point Quarry, Wyoming and in the latest Maastrichtian Hell Creek Formation, United States. It was first named by Tyler R. Lyson and Walter G. Joyce in 2009 and the type species is Cedrobaena putorius.
 W
WCimexomys is an extinct North American mammal that lived from the Upper Cretaceous to the Paleocene. For a while, it shared the world with dinosaurs, but outlived them. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata and lies within the suborder Cimolodonta. It is perhaps a member of the Paracimexomys group, though it is not certain.
 W
WCimolomys is a mammal genus from the Upper Cretaceous of North America. It was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
 W
WDakotaraptor is a potentially chimaeric genus of large dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur that lived in North America during the Late Cretaceous period. The remains have been found in the Maastrichtian stage of the Hell Creek Formation, dated to the very end of the Mesozoic era, making Dakotaraptor one of the last surviving dromaeosaurids. The remains of D. steini were discovered in a multi-species bonebed. Elements of the holotype and referred specimens were later found to belong to trionychid turtles, and further analysis of potential non-dromaeosaurid affinities of the holotype and referred material have not yet been conducted. Phylogenetic analyses of D. steini place it in a variety of positions in the Dromaeosauridae.
 W
WDenversaurus is a genus of herbivorous nodosaurid ankylosaurian dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous of western North America. Although at one point treated as a junior synonym of Edmontonia by some taxonomists, current research indicates that it is a distinct nodosaurid genus.
 W
WDidelphodon is a genus of stagodont metatherians from the Late Cretaceous of North America.
 W
WDiscoscaphites is an extinct genus of ammonite.
 W
WEdmontosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid (duck-billed) dinosaur. It contains two known species: Edmontosaurus regalis and Edmontosaurus annectens. Fossils of E. regalis have been found in rocks of western North America that date from the late Campanian stage of the Cretaceous Period 73 million years ago, while those of E. annectens were found in the same geographic region but in rocks dated to the end of the Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous, 66 million years ago. Edmontosaurus was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs, and lived alongside dinosaurs like Triceratops, Tyrannosaurus, Albertosaurus and Pachycephalosaurus shortly before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
 W
WEdmontosaurus annectens is a species of flat-headed and duck-billed (hadrosaurid) dinosaur from the very end of the Cretaceous Period, in what is now North America. Remains of E. annectens have been preserved in the Frenchman, Hell Creek, and Lance Formations. All of these formations are dated to the late Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous Period, representing the last three million years before the extinction of the dinosaurs. Also, E. annectens is also from the Laramie Formation, and magnetostratigraphy suggests an age of 69-68 Ma for the Laramie Formation. Edmontosaurus annectens is known from numerous specimens, including at least twenty partial to complete skulls, discovered in the U.S. states of Montana, South Dakota, North Dakota, Wyoming and Colorado and the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It was a large animal, up to approximately 12 metres (39 ft), potentially up to 15 m (49 ft) in length, with an extremely long and low skull. E. annectens exhibits one of the most striking examples of the "duckbill" snout common to hadrosaurs. It has a long taxonomic history, and specimens have at times been classified in the genera Diclonius, Trachodon, Hadrosaurus, Claosaurus, Thespesius, Anatosaurus and Anatotitan, before being grouped together in Edmontosaurus.
 W
WLeptoceratops, is a genus of primitive ceratopsian dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous Period of what is now Western North America. Their skulls have been found in Alberta, Canada and Wyoming.
 W
WLeptorhynchos is an extinct genus of caenagnathid dinosaurs known from the Late Cretaceous Aguja Formations of west Texas United States. It lived about 80.5–72 million years ago. It is distinguished from its relatives Chirostenotes and Anzu by its smaller size, and by a more strongly upturned mandible, similar to that of oviraptorids. The specializations of the beak in Leptorhynchos and other caenagnathids suggest that they were herbivores. The species L. elegans has since been transferred to the genus Citipes.
 W
WMeniscoessus is a genus of extinct mammal from the Upper Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. It lived toward the end of the "age of the dinosaurs" and was a member of the extinct order Multituberculata. It lies within the suborder Cimolodonta and family Cimolomyidae.
 W
WMyledaphus is a genus of Late Cretaceous cartilaginous fish whose fossils are known from Canada, the Midwest of the United States, Olmos Formation of the Difunta Group of Mexico, and the Beshtyubin and Bissekty Formations of Uzbekistan. It was a freshwater guitarfish that probably reached a length of 3 feet (91 cm), and had teeth adapted for a durophagous diet of animals such as clams. Most taxonomic authories place the genus in the Rhinobatidae, with a few placing it with prehistoric sharks (Anacoracidae), although the latter may be incorrect. Two species are known: Myledaphus bipartitus, the type species, and Myledaphus araucanus, named in 2019.
 W
WOrnithomimus is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. Ornithomimus was a swift bipedal theropod which fossil evidence indicates was covered in feathers, equipped with a small toothless beak that may indicate an omnivorous diet. It is usually classified into two species: the type species, Ornithomimus velox, and a referred species, Ornithomimus edmontonicus. O. velox was named in 1890 by Othniel Charles Marsh on the basis of a foot and partial hand from the late Maastrichtian-age Denver Formation of Colorado, United States. Another seventeen species have been named since, though most of them have subsequently been assigned to new genera or shown to be not directly related to Ornithomimus velox. The best material of species still considered part of the genus has been found in Alberta, Canada, representing the species O. edmontonicus, known from several skeletons from the early Maastrichtian Horseshoe Canyon Formation. Additional species and specimens from other formations are sometimes classified as Ornithomimus, such as Ornithomimus samueli from the earlier, Campanian-age Dinosaur Park Formation of Alberta.
 W
WPachycephalosaurus is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaurs. The type species, P. wyomingensis, is the only known species. It lived during the Late Cretaceous Period of what is now North America. Remains have been excavated in Montana, South Dakota, Wyoming and Alberta. It was a herbivorous creature which is primarily known from a single skull and a few extremely thick skull roofs, though more complete fossils have been found in recent years. Pachycephalosaurus was one of the last non-avian dinosaurs before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event. Another dinosaur, Tylosteus of western North America, has been synonymized with Pachycephalosaurus, as have the genera Stygimoloch and Dracorex in recent studies.
 W
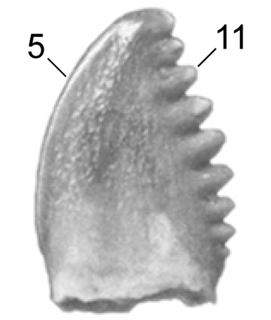
WPectinodon is a genus of bird like dinosaurs from the Late Cretaceous period (66 mya). It currently contains a single valid species, Pectinodon bakkeri, known only from teeth.
 W
WProtungulatum is an extinct genus of mammal first found in the Bug Creek Anthills in northeastern Montana. The Bug Creek Anthills were initially believed to be Late Cretaceous because of the presence of the remains of non-avian dinosaurs and common Cretaceous mammals, but these were later shown to have been reworked from Late Cretaceous strata, and consequently the Bug Creek Anthills are currently believed to be Early Paleocene (Puercan) in age. Remains from the Ravenscrag Formation of Saskatchewan, Canada have been assigned to P. donnae. These remains may also be Cretaceous in age, but the age of the Ravenscrag Formation is not entirely certain. In 2011, remains of a new species of Protungulatum, P. coombsi, from the Hell Creek Formation, which is definitely Late Cretaceous (Maastrichtian) in age, proved that Protungulatum was present in both the Cretaceous and the Paleocene. It was initially assigned to the order condylarthra, a group of archaic "ungulates", that is now known to be polyphyletic. According to Archibald et al. (2011), Protungulatum is not even definitely a placental mammal. Some studies have found it to be close to Cetartiodactyla, but the most recent analysis holds it to be a non-placental eutherian.
 W
WPurgatorius is a genus of four extinct eutherian species typically believed to be the earliest example of a primate or a proto-primate, a primatomorph precursor to the Plesiadapiformes, dating to as old as 66 million years ago. The first remains were reported in 1965, from what is now eastern Montana's Tullock Formation, specifically at Purgatory Hill in deposits believed to be about 63 million years old, and at Harbicht Hill in the late Cretaceous and lower Paleocene Hell Creek Formation. Both locations are in McCone County.
 W
WSphaerotholus is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Upper Cretaceous of the western United States and Canada. To date, three species have been described: the type species, S. goodwini, from the Den-na-zin Member of the Kirtland Formation of San Juan County, New Mexico, USA; S. buchholtzae, from the Hell Creek Formation of western Carter County, Montana, USA and the Frenchman Formation of Saskatchewan, Canada; and S. edmontonensis, from the Horseshoe Canyon Formation of Alberta, Canada.
 W
WSphenodiscus is an extinct genus of acanthoceratacean ammonite. The genus has been found from many continents and is thought to have had a large global distribution during the Maastrichtian stage of the Late Cretaceous. It was one of the last ammonoids to have evolved before the entire subclass became extinct at the end of the period during the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.
 W
WStruthiomimus is a genus of ornithomimid dinosaurs from the late Cretaceous of North America. Ornithomimids were long-legged, bipedal, ostrich-like dinosaurs with toothless beaks. The type species, Struthiomimus altus, is one of the more common small dinosaurs found in Dinosaur Provincial Park; its abundance suggests that these animals were herbivores or omnivores rather than pure carnivores.
 W
WTatankaceratops is a controversial genus of herbivorous ceratopsian dinosaur. It is a small chasmosaurine ceratopsian which lived during the Late Cretaceous period in what is now South Dakota. It is known from a single partial skull which was collected from the Hell Creek Formation, dating to 66 million years ago. Tatankaceratops was described by Christopher J. Ott and Peter L. Larson in 2010 and the type species is Tatankaceratops sacrisonorum. Tatankaceratops is known from one specimen housed at the Black Hills Institute, BHI 6226.
 W
WThescelosaurus was a genus of small ornithopod dinosaur that appeared at the very end of the Late Cretaceous period in North America. It was a member of the last dinosaurian fauna before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event around 66 million years ago. The preservation and completeness of many of its specimens indicate that it may have preferred to live near streams.
 W
WThoracosaurus is an extinct genus of eusuchian crocodylomorph which existed during the Late Cretaceous and early Paleocene. The animal is usually regarded as a gavialoid crocodilian, though the phylogenetic study published by Lee & Yates (2018) suggests that it might have been a non-crocodylian eusuchian. The genus contains the species Thoracosaurus neocesariensis in North America and what is either Thoracosaurus isorhynchus or T. macrorhynchus; a recent review argues that T. macrorhynchus is a junior synonym of T. isorhynchus, but it is unclear whether the type of T. isorhynchus allows differentiation of European and North American Thoracosaurus; if not, then T. isorhynchus would be a nomen dubium. A number of species have been referred to this genus, but most are dubious.
 W
WTorosaurus is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that lived during the late Maastrichtian stage of the Cretaceous period, between 68 and 66 million years ago, though it is possible that the species range might extend to as far as 69 million years ago. Fossils have been discovered across the Western Interior of North America, from Saskatchewan to southern Texas.
 W
WTriceratops is a genus of herbivorous ceratopsid dinosaur that first appeared during the late Maastrichtian stage of the late Cretaceous period, about 68 million years ago (mya) in what is now North America. It is one of the last-known non-avian dinosaur genera, and became extinct in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event 66 million years ago. The name Triceratops, which literally means "three-horned face", is derived from the Ancient Greek words τρί- (tri-) meaning "three", κέρας (kéras) meaning "horn", and ὤψ (ōps) meaning "face".
 W
WTrionyx is a genus of softshell turtles belonging to the family Trionychidae. In the past many species in the family were classified in this genus, but today T. triunguis, the African or Nile softshell turtle, is the only extant softshell still classified as Trionyx. The other species still assigned to this genus are only known from fossils. T. triunguis is a relatively large, aquatic piscivore.
 W
WTyrannosaurus is a genus of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaur. The species Tyrannosaurus rex, often called T. rex or colloquially T-Rex, is one of the most well-represented of the large theropods. Tyrannosaurus lived throughout what is now western North America, on what was then an island continent known as Laramidia. Tyrannosaurus had a much wider range than other tyrannosaurids. Fossils are found in a variety of rock formations dating to the Maastrichtian age of the upper Cretaceous period, 68 to 66 million years ago. It was the last known member of the tyrannosaurids, and among the last non-avian dinosaurs to exist before the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event.