 W
W1,4-Oxathiane is a heterocyclic compound containing with one oxygen atom and one sulfur atom at opposite corners of a saturated six-membered ring. By systematic numbering, the oxygen atom is position number 1, sulfur is number 4, and positions 1, 3, 5, and 6 are carbon atoms.
 W
W4,5-Dichloro-1,2,3-dithiazolium chloride is an organosulfur compound. It is the chloride salt of the 4,5-dichloro-1,2,3-dithiazolium cation. It is a green solid that is poorly soluble in organic solvents.
 W
W6-APA is an abbreviation used for the name of the chemical compound (+)-6-aminopenicillanic acid. In 1958, Beecham scientists found a way to obtain 6-APA from penicillin. Other β-lactam antibiotics could then be synthesized by attaching various side-chains to the nucleus. The other antibiotics are used in place of penicillin G or penicillin V.
 W
W7-ACA is the core chemical structure for the synthesis of cephalosporin antibiotics and intermediates. It can be obtained by chemoenzymatic hydrolysis of cephalosporin C.
 W
WBaloxavir marboxil (BXM), sold under the brand name Xofluza, is an antiviral medication for treatment of influenza A and influenza B flu. It was approved for medical use both in Japan and in the United States in 2018, and is taken as a single dose by mouth. It may reduce the duration of flu symptoms by about a day, but is prone to selection of resistant mutants that render it ineffectual.
 W
WBiotin sulfoxide is the substance that is formed when biotin is exposed to ultraviolet light in the presence of oxygen.
 W
WBromo(tetrahydrothiophene)gold(I) is a coordination complex of gold. It is related to the more commonly used chloro(tetrahydrothiophene)gold(I). Similarly, the tetrahydrothiophene ligand is labile and is readily substituted with other stronger ligands, to give linear gold bromide complexes.
 W
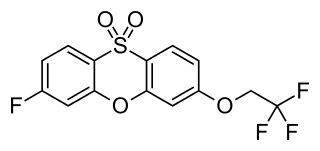
WCX157 is a selective and reversible inhibitor of MAO-A (RIMA). As of 2007 it was in phase II clinical trials for the treatment of depression. In 2013, work on the drug was terminated.
 W
WDihydrothiophenes are heterocyclic organosulfur compounds. Two isomers are possible for the parent C4H6S:2,3-Dihydrothiophene, a vinyl thioether. CAS RN = 1120-59-8. 2,5-Dihydrothiophene, an allylic thioether. A well-known derivative is 2,5-dihydrothiophene 1,1-dioxide. CAS RN = 1708-32-3.
 W
W2,3-Dihydrothiophene is a heterocyclic compound and an organosulfur compound with the formula SC4H6. It is isomeric with the more symmetrical 2,5-dihydrothiophene. Both isomers of dihydrothiophene are colorless liquids with a thioether-like odor. In terms of their reactivity, both isomers exhibit characteristics of alkenes and thioethers, undergoing addition reactions at carbon and oxidation at sulfur. In contrast, thiophene engages in neither reaction.
 W
W1,5-Dithiacyclooctane (DTCO) is an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2CH2)CH2S)2. This cyclic dithioether is a colorless oil that is soluble in polar solvents. It forms a variety of transition metal thioether complexes.
 W
WIn chemistry, dithiadiazoles are a family of heterocyclic compounds with the formula RCN2S2. Although several isomers are possible, the 1,2,3,5-dithiadiazoles have received greater attention. The neutral compounds are radicals with 7 π electrons. Oxidation affords the dithiadiazolium cations.
 W
WDithiete is an unsaturated heterocyclic compound that contains two adjacent sulfur atoms and two sp2-hybridized carbon centers. Derivatives are known collectively as dithietes or 1,2-dithietes. With 6 π electrons, 1,2-dithietes are examples of aromatic organosulfur compounds. A few 1,2-dithietes have been isolated.
 W
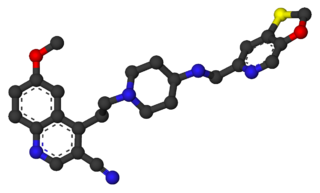
WFananserin (RP-62203) is a drug which acts as a potent antagonist at both the 5HT2A receptor, and the Dopamine D4 receptor, but without blocking other dopamine receptors such as D2. It has sedative and antipsychotic effects, and has been researched for the treatment of schizophrenia, although efficacy was less than expected and results were disappointing.
 W
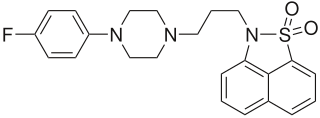
WGSK 299423 or GlaxoSmithKline 299423 is an antibiotic chemical compound that has been identified as potentially effective in treating patients infected with bacteria expressing the New Delhi metallo-beta-lactamase. The antibiotic inhibits the enzyme topoisomerase, which bacteria need to replicate.
 W
WImidazothiazoles are a class of chemical compounds containing a bicyclic heterocycle consisting of an imidazole ring fused to a thiazole ring. The structure contains three heteroatoms: two nitrogen atoms and one sulfur atom. Imidazothiazole derivatives show a broad spectrum of physiological activity such as anticancer, antipsychotic, antimicrobial, antifungal, and anthelmintic.
 W
WLawesson's reagent, or LR, is a chemical compound used in organic synthesis as a thiation agent. Lawesson's reagent was first made popular by Sven-Olov Lawesson, who did not, however, invent it. Lawesson's reagent was first made in 1956 during a systematic study of the reactions of arenes with P4S10.
 W
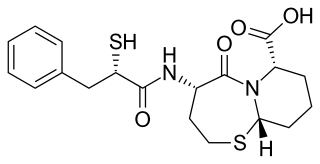
WOmapatrilat is an experimental antihypertensive agent that was never marketed. It inhibits both neprilysin and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). NEP inhibition results in elevated natriuretic peptide levels, promoting natriuresis, diuresis, vasodilation, and reductions in preload and ventricular remodeling.
 W
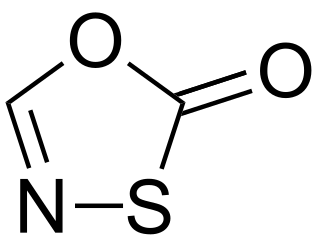
WThe oxathiazolones are a family of heterocyclic compounds in which the parent derivative has the molecular formula C2HNO2S and for which multiple isomers are known. The two known isomers with the highest profile in the literature are 1,3,4-oxathiazol-2-one and 1,4,2-oxathiazol-5-one.
 W
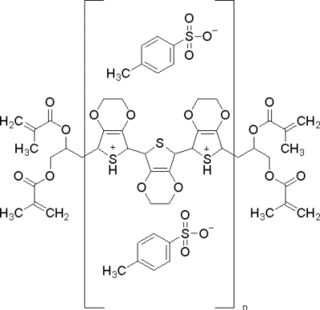
WPoly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene)-tetramethacrylate or PEDOT-TMA is a p-type conducting polymer based on 3,4-ethylenedioxylthiophene or the EDOT monomer. It is a modification of the PEDOT structure. Advantages of this polymer relative to PEDOT are that it is dispersible in organic solvents, and it is non-corrosive. PEDOT-TMA was developed under a contract with the National Science Foundation, and it was first announced publicly on April 12, 2004. The trade name for PEDOT-TMA is Oligotron. PEDOT-TMA was featured in an article entitled "Next Stretch for Plastic Electronics" that appeared in Scientific American in 2004. The U.S. Patent office issued a patent protecting PEDOT-TMA on April 22, 2008.
 W
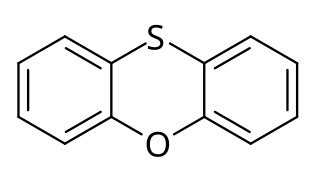
WPhenoxathiin (dibenzooxathiane) C12H8OS is a heterocyclic compound of molecular weight 200.25632 g/mol with the CAS Registry Number 262-20-4.
 W
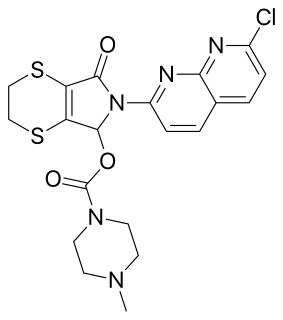
WPrulifloxacin is an older synthetic antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class undergoing clinical trials prior to a possible NDA submission to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is a prodrug which is metabolized in the body to the active compound ulifloxacin. It was developed over two decades ago by Nippon Shinyaku Co. and was patented in Japan in 1987 and in the United States in 1989.
 W
WSuriclone (Suril) is a sedative and anxiolytic drug in the cyclopyrrolone family of drugs. Other cyclopyrrolone drugs include zopiclone and pagoclone.
 W
WTemocapril is an ACE inhibitor. It was not approved for use in the US.
 W
WTetramethylenedisulfotetramine (TETS) is an organic compound that is used as a rodenticide. It is an odorless, tasteless white powder that is slightly soluble in water, DMSO and acetone, and insoluble in methanol and ethanol. TETS is a sulfamide derivative. It can be synthesized by reacting sulfamide with formaldehyde under acidic condition. When crystallized from acetone, it forms cubic crystals with a melting point of 255–260 °C.
 W
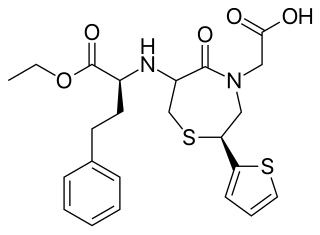
WThiane is a heterocyclic compound and an organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2)5S. It is a saturated six-membered ring with five carbon atoms and one sulfur atom. The compound is a colorless liquid. It can be prepared by the reaction of 1,5-dibromopentane with sodium sulfide:Br-(CH2)5-Br + Na2S → (CH2)5S + 2NaBr
 W
WThienothiophene usually refers to any of three structurally related derivatives of thiophene with the formula C6H4S2. In order of importance, they are: thieno(3,2-b)thiophene, thieno(2,3-b)thiophene, and thieno(3,4-b)thiophene. Other isomers feature S(IV) and are less stable. Thieno[2,3-b]thiophene was the first member of the series to be isolated. It was obtained in very low yield upon heating citric acid, a source of a six-carbon linear chain, with P4S10. More efficient syntheses of this and the other two stable thienothiophenes involve cyclization reactions of substituted thiophenes.
 W
WThiepane is the organosulfur compound with the formula (CH2)6S. Thiepanes are seven-membered ring heterocycles that contains sulfide. The parent thiepane has seldom been studied.
 W
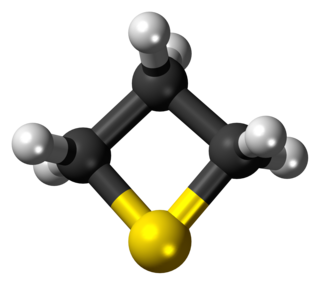
WThietane is a heterocyclic compound containing a saturated four-membered ring with three carbon atoms and one sulfur atom.
 W
WThiopyran is a heterocyclic compound with the chemical formula C5H6S. There are two isomers, 2H-thiopyran and 4H-thiopyran, which differ by the location of double bonds. Thiopyrans are analogous to pyrans in which the oxygen atoms have been replaced by sulfur atoms.
 W
WTinabinol is a synthetic cannabinoid drug and analogue of dronabinol which was patented as an antihypertensive but was never marketed.
 W
W1,4,7-Trithiacyclononane, also called 9-ane-S3, is the heterocyclic compound with the formula (CH2CH2S)3. This cyclic thioether is most often encountered as a tridentate ligand in coordination chemistry.
 W
W1,3,5-Trithiane is the chemical compound with the formula (CH2S)3. This heterocycle is the cyclic trimer of the otherwise unstable species thioformaldehyde. It consists of a six-membered ring with alternating methylene bridges and thioether groups. It is prepared by treatment of formaldehyde with hydrogen sulfide.
 W
WTrithiapentalene is an organic bicyclic molecule containing two sulfur heterocycles. Its 10-π aromatic structure is similar to naphthalene. There has been a literature dispute about whether the connectivity among the three sulfur atoms is a case of rapid tautomerization between two valence tautomers or a 3-center 4-electron bond.
 W
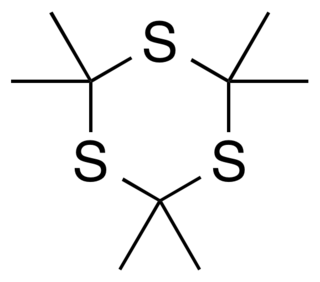
WTrithioacetone (2,2,4,4,6,6-hexamethyl-1,3,5-trithiane) is an organic chemical with formula C9H18S3. Its covalent structure is [–C(CH3)2–S–]3, that is, a six-membered ring of alternating carbon and sulfur atoms, with two methyl groups attached to each carbon. It can be viewed as a derivative of 1,3,5-trithiane, with methyl-group substituents for all of the hydrogen atoms in that parent structure.
 W
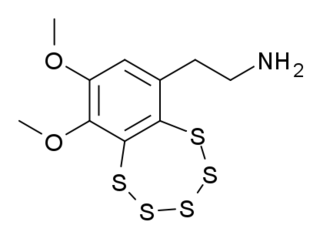
WVaracin is a bicyclic organosulfur compound originally found in marine Ascidiacea from the Polycitor genus. It contains an unusual pentathiepin ring which reacts with DNA, and varacin and synthetic analogues have been investigated for their antimicrobial and antitumour properties. Because of its potent biological activity and unusual and challenging ring system, it has been a popular target of efforts toward its total synthesis.
 W
WY-23684 is an anxiolytic drug with a novel chemical structure, which is used in scientific research. It has similar effects to benzodiazepine drugs, but is structurally distinct and so is classed as a nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytic.