 W
WAnatolia is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It makes up the majority of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe.
 W
WAnatolia is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It makes up the majority of modern-day Turkey. The region is bounded by the Turkish Straits to the northwest, the Black Sea to the north, the Armenian Highlands to the east, the Mediterranean Sea to the south, and the Aegean Sea to the west. The Sea of Marmara forms a connection between the Black and Aegean seas through the Bosporus and Dardanelles straits and separates Anatolia from Thrace on the Balkan peninsula of Southeast Europe.
 W
WThe history of Anatolia can be roughly subdivided into prehistory, Ancient Near East, Classical Anatolia, Hellenistic Anatolia, Byzantine Anatolia, followed by the gradual Seljuk/Ottoman conquest in the 13th to 14th centuries, Ottoman Anatolia and the modern history of the Republic of Turkey.
 W
WThe history of Turkey, understood as the history of the region now forming the territory of the Republic of Turkey, includes the history of both Anatolia and Eastern Thrace. These two previously politically distinct regions came under control of the Roman Empire in the second century BCE, eventually becoming the core of the Roman Byzantine Empire.
 W
WThe prehistory of Anatolia stretches from the Paleolithic era through to the appearance of classical civilisation in the middle of the 1st millennium BC. It is generally regarded as being divided into three ages reflecting the dominant materials used for the making of domestic implements and weapons: Stone Age, Bronze Age and Iron Age. The term Copper Age (Chalcolithic) is used to denote the period straddling the stone and Bronze Ages.
 W
WPolyommatus myrrha is a species of butterfly in the family Lycaenidae. It was first described as Lycaena myrrha by Gottlieb August Wilhelm Herrich-Schäffer in 1851 in the six volume Systematische Bearbeitung der Schmetterlinge von Europa. This rare species has been found in Anatolia area of Turkey. and in the Zangezur Mountains, which is inhabited by subspecies P. m. cinyraea Nekrutenko & Effendi, 1979.
 W
WThe Aegean and Western Turkey sclerophyllous and mixed forests is an ecoregion in the lands around the Aegean Sea. The ecoregion covers most of mainland Greece, the Greek Aegean Islands, the western coast of Turkey, the southern Vardar and Struma river valleys in North Macedonia, and the extreme south-western corner of Bulgaria.
 W
WAfyonkarahisar is a city in western Turkey, the capital of Afyon Province. Afyon is in mountainous countryside inland from the Aegean coast, 250 km (155 mi) south-west of Ankara along the Akarçay River. In Turkey, Afyonkarahisar stands out as a capital city of thermal and spa, an important junction of railway, highway and air traffic in West-Turkey, and the grounds where independence had been won. In addition, Afyonkarahisar is one of the top leading provinces in agriculture, globally renowned for its marble and globally largest producer of pharmaceutical opium.
 W
WThe Anatolian conifer and deciduous mixed forests is an ecoregion in is located in southwestern Anatolia, Turkey. It has a Mediterranean climate, and is part of the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome.
 W
WBelbaşı is a cave and a late Paleolithic/Mesolithic site in southern Turkey, located southwest of Antalya.
 W
WThe Black Sea Region is a geographical region of Turkey.
 W
WBryges or Briges is the historical name given to a people of the ancient Balkans. They are generally considered to have been related to the Phrygians, who during classical antiquity lived in western Anatolia. Both names, Bryges and Phrygians, are assumed to be variants of the same root. Based on archaeological evidence, some scholars such as Nicholas Hammond and Eugene N. Borza argue that the Bryges/Phrygians were members of the Lusatian culture that migrated into the southern Balkans during the Late Bronze Age.
 W
WThe Büyük Menderes River, is a river in southwestern Turkey. It rises in west central Turkey near Dinar before flowing west through the Büyük Menderes graben until reaching the Aegean Sea in the proximity of the ancient Ionian city Miletus. The word "meander" is used to describe a winding pattern, after the river.
 W
WÇatalhöyük was a very large Neolithic and Chalcolithic proto-city settlement in southern Anatolia, which existed from approximately 7100 BC to 5700 BC, and flourished around 7000 BC. In July 2012, it was inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WThe Central Anatolian deciduous forests, also known as the Central Anatolian woodlands and steppe, is a Palearctic ecoregion of the Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest biome. It is located in Central Anatolia, Asian Turkey.
 W
WThe Central Anatolian steppe is a Palearctic ecoregion in the temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands biome. It covers an area of 24,934 km2.
 W
WThe Central East Anatolia Region (TRB) is a statistical region in Turkey.
 W
WCilicia is a geo-cultural region in southern Turkey, extending inland from the northeastern coasts of the Mediterranean Sea. Cilicia has a population of over six million, concentrated mostly at the Cilicia plain. The region includes the provinces of Mersin, Adana, Osmaniye, and Hatay.
 W
WThe Çineköy inscription is a Hieroglyphic Luwian-Phoenician bilingual inscription, uncovered in 1997 near Çine, Yüreğir, Adana Province, Turkey. The village of Çine lies 30 km south of Adana.
 W
WThe Eastern Anatolian deciduous forests ecoregion is located in the mountains of eastern Turkey. It is a Palearctic ecoregion in the temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biome.
 W
WThe Eastern Anatolian montane steppe is a temperate grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion. It is located in high plateau of Eastern Anatolia, covering parts of eastern Turkey, Armenia, Azerbaijan, southern Georgia, and northwestern Iran.
 W
WHattusa was the capital of the Hittite Empire in the late Bronze Age. Its ruins lie near modern Boğazkale, Turkey, within the great loop of the Kızılırmak River.
 W
WCilicia was one of the most important regions of the Middle East throughout history and hosted the Hittite, Hellenistic, Roman, Armenian, and Islamic civilizations. Historically many people considered it as a part of the Levant, and during what is called the Rashidun Caliphate, much of the area was called "Ath-Thugur As-Shamiyya" meaning the Levantine outskirts.
 W
Wİnandıktepe is an archaeological site located in Cankiri Province, Turkey, about 50 miles northeast of Ankara. In 1965 workers found there potsherds of the famous İnandık-vase. Thereafter excavations took place.
 W
WThe Karamanlides, or simply Karamanlis, are a Greek Orthodox, Turkish-speaking people native to the Karaman and Cappadocia regions of Anatolia. Today, a majority of the population live in Greece, though there is a sizeable diaspora in Western Europe and North America.
 W
WThe Kızıl Kule is a historical tower in the Turkish city of Alanya. The building is considered to be the symbol of the city, and is even used on the city's flag.
 W
WLabraunda is an ancient archaeological site five kilometers west of Ortaköy, Muğla Province, Turkey, in the mountains near the coast of Caria. In ancient times, it was held sacred by Carians and Mysians alike. The site amid its sacred plane trees was enriched in the Hellenistic style by the Hecatomnid dynasty of Mausolus, satrap of Persian Caria, and also later by his successor and brother Idrieus; Labranda was the dynasty's ancestral sacred shrine. The prosperity of a rapidly hellenised Caria occurred in the during the 4th century BCE. Remains of Hellenistic houses and streets can still be traced, and there are numerous inscriptions. The cult icon here was a local Zeus Labrandeus, a standing Zeus with the tall lotus-tipped scepter upright in his left hand and the double-headed axe, the labrys, over his right shoulder. The cult statue was the gift of the founder of the dynasty, Hecatomnus himself, recorded in a surviving inscription.
 W
WMyra was an ancient Greek, then Roman Greek, then Byzantine Greek, then Ottoman Greek town in Lycia, which became the small Turkish town of Kale, renamed Demre in 2005, in the present-day Antalya Province of Turkey. In 1923 its Greek inhabitants had been required to leave by the Population exchange between Greece and Turkey, at which time its church was finally abandoned. It was founded on the river Myros, in the fertile alluvial plain between Alaca Dağ, the Massikytos range and the Aegean Sea.
 W
WThe Northern Anatolian conifer and deciduous forests is a temperate coniferous forests ecoregion located in northern Anatolia, Turkey.
 W
WThe name Pelasgians was used by classical Greek writers to refer either to the ancestors or forerunners of the Greeks, or to all inhabitants of Greece before the emergence or arrival of Greeks aware of their Greekness. In general, "Pelasgian" has come to mean more broadly all the indigenous inhabitants of the Aegean Sea region and their cultures, "a hold-all term for any ancient, primitive and presumably indigenous people in the Greek world".
 W
WScamander, Skamandros, Xanthos (Ξάνθος), was the name of a river god in Greek mythology.
 W
WThe Southern Anatolian montane conifer and deciduous forests ecoregion, in the Mediterranean forests, woodlands, and scrub biome, is in the eastern Mediterranean Basin.
 W
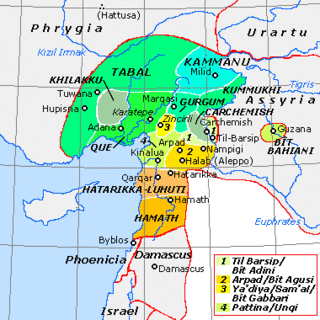
WTabal was a Luwian speaking Neo-Hittite kingdom of South Central Anatolia. According to archaeologist Kurt Bittel, the kingdom of Tabal first appeared after the collapse of the Hittite Empire.
 W
WYazılıkaya was a sanctuary of Hattusa, the capital city of the Hittite Empire, today in the Çorum Province, Turkey. Rock reliefs are a prominent aspect of Hittite art, and these are generally regarded as the most important group.
 W
WThe Zagros Mountains are a long mountain range in Iran, Iraq and southeastern Turkey. This mountain range has a total length of 1,600 km (990 mi). The Zagros mountain range begins in northwestern Iran and roughly follows Iran's western border, while covering much of southeastern Turkey and northeastern Iraq. From this border region, the range roughly follows Iran's coast on the Persian Gulf. It spans the whole length of the western and southwestern Iranian plateau, ending at the Strait of Hormuz. The highest point is Mount Dena, at 4,409 metres (14,465 ft).
 W
WThe Zydretae were an ancient people of Colchis recorded by the Classical accounts as dwelling on the coast of the Pontus Euxinus, on the southern side of the Apsarus river, and between the Machelonoi and the Lazi tribes. The early 2nd century Roman author Arrian lists several neighboring and probably ethnically related tribes on a west to east orientation: the Sannoi (Sanigs), Drilae, Machelonoi, Heniochoi, Zudreitai, and Lazoi. The anonymous Periplus Ponti Euxini places them further south between the Akamosis and Archabis rivers. Little is known about the Zydretae’s social and political life, but at that time when Arrian described them, they seem to have been subjected to the king of Iberia in eastern Georgia.