 W
WAnthelmintics or antihelminthics are a group of antiparasitic drugs that expel parasitic worms (helminths) and other internal parasites from the body by either stunning or killing them and without causing significant damage to the host. They may also be called vermifuges or vermicides. Anthelmintics are used to treat people who are infected by helminths, a condition called helminthiasis. These drugs are also used to treat infected animals.
 W
WAlbendazole, also known as albendazolum, is a medication used for the treatment of a variety of parasitic worm infestations. It is useful for giardiasis, trichuriasis, filariasis, neurocysticercosis, hydatid disease, pinworm disease, and ascariasis, among other diseases It is taken by mouth.
 W
WAmoscanate (INN), also known as nithiocyamine, is an experimental anthelmintic agent of the arylisothiocyanate class which was found to be highly effective in animals against the four major species of schistosomes which infect humans, and is also highly active against hookworm infection. However, significant liver toxicity was seen in lab animals at higher doses. The ether analogue of amoscanate, nitroscanate, is used in veterinary medicine as an anthelmintic.
 W
WBefuraline (DIV-154) is a psychoactive drug and member of the piperazine chemical class which was developed in Germany in the 1970s. Befuraline has stimulant and antidepressant effects and has seen some use in Germany and France, although it has never become widely used. Befuraline's active metabolite benzylpiperazine is responsible for its effects.
 W
WBitoscanate is an organic chemical compound used in the treatment of hookworms. It is classified as an extremely hazardous substance in the United States as defined in Section 302 of the U.S. Emergency Planning and Community Right-to-Know Act, and is subject to strict reporting requirements by facilities which produce, store, or use it in significant quantities.
 W
WBromofenofos is an anthelminthic agent used in veterinary medicine. It is used to treat common liver fluke infections in cattle and sheep.
 W
WCiclobendazole is an anthelmintic.
 W
WDesaspidin is an anthelmintic. Desapidin may occur in natural form within some plants such as Coastal woodfern, Dryopteris arguta. Since the 1950s the inhibition effects of desapidins upon phosphorylation in chloroplasts has been noted and studied.
 W
WDiatrizoate, also known as amidotrizoate, is a contrast agent used during X-rays. This includes when visualizing veins, the urinary system, spleen, and joints, as well as during computer tomography. It is given by mouth, injection into a vein, injection into the bladder, through a nasogastric tube, or rectally.
 W
WDithiazanine iodide is a chemical compound. It is used as a veterinary anthelmintic for dogs. It is a highly toxic chemical, with a lethal dose for humans of about 4–16 mg/kg by oral ingestion. The mechanism of toxicity is not well known but it is believed that this chemical interferes with cells' absorption of glucose, which is essential to obtain energy through cell respiration.
 W
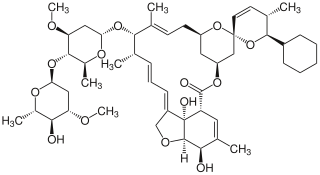
WDoramectin (Dectomax) is a veterinary drug approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of parasites such as gastrointestinal roundworms, lungworms, eyeworms, grubs, sucking lice and mange mites in cattle.
 W
WEmodepside is an anthelmintic drug that is effective against a number of gastrointestinal nematodes, is licensed for use in cats and belongs to the class of drugs known as the octadepsipeptides, a relatively new class of anthelmintic, which are suspected to achieve their anti-parasitic effect by a novel mechanism of action due to their ability to kill nematodes resistant to other anthelmintics.
 W
WEpsiprantel is a veterinary drug which is used as an anthelmintic against tapeworms such as Echinococcus granulosus.
 W
WFenbendazole is a broad spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic used against gastrointestinal parasites including: giardia, roundworms, hookworms, whipworms, the tapeworm genus Taenia, pinworms, aelurostrongylus, paragonimiasis, strongyles, and strongyloides that can be administered to sheep, cattle, horses, fish, dogs, cats, rabbits, and seals.
 W
WFlubendazole is an anthelmintic. Its brand name is Flutelmium which is a paste manufactured by Janssen Pharmaceutica N.V. used by veterinarians for protection against internal parasites and worms in dogs and cats. Other brand names are Flubenol, Biovermin, and Flumoxal.
 W
WHaloxon is an anthelminthic agent used in veterinary medicine to treat infection in cattle. It is considered the safest of the organophosphate class of anthelmintics for use in ruminants.
 W
WHexylresorcinol is an organic compound with local anaesthetic, antiseptic, and anthelmintic properties.
 W
WLevamisole, sold under the brand name Ergamisol among others, is a medication used to treat parasitic worm infections. Specifically it is used for ascariasis and hookworm infections. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WMebendazole (MBZ) is a medication used to treat a number of parasitic worm infestations. This includes ascariasis, pinworm disease, hookworm infections, guinea worm infections, hydatid disease, and giardia, among others. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WMilbemycin oxime is a veterinary drug from the group of milbemycins, used as a broad spectrum antiparasitic. It is active against worms (anthelmintic) and mites (miticide).
 W
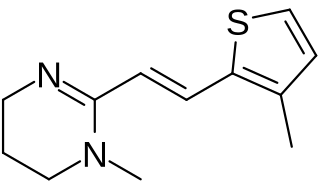
WMorantel is an anthelmintic drug used for the removal of parasitic worms in livestock. It affects the nervous system of worms given the drug is an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase.
 W
WMoxidectin is an anthelmintic drug used in animals to prevent or control parasitic worms (helminths), such as heartworm and intestinal worms, in dogs, cats, horses, cattle and sheep. Moxidectin kills some of the most common internal and external parasites by selectively binding to a parasite's glutamate-gated chloride ion channels. These channels are vital to the function of invertebrate nerve and muscle cells; when moxidectin binds to the channels, it disrupts neurotransmission, resulting in paralysis and death of the parasite.
 W
WNiclosamide, sold under the brand name Niclocide among others, is a medication used to treat tapeworm infestations. This includes diphyllobothriasis, hymenolepiasis, and taeniasis. It is not effective against other worms such as pinworms or roundworms. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WNitroscanate is an anthelmintic drug used in veterinary medicine to treat Toxocara canis, Toxascaris leonina, Ancylostoma caninum, Uncinaria stenocephala, Taenia, and Dipylidium caninum.
 W
WOxfendazole is a broad spectrum benzimidazole anthelmintic. Its main use is for protecting livestock against roundworm, strongyles and pinworms. Oxfendazole is the sulfoxide metabolite of fenbendazole.
 W
WOxyclozanide is a salicylanilide anthelmintic. It is used in the treatment and control of fascioliasis in ruminants mainly domestic animals such as cattle, sheep, and goats. It mainly acts by uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in flukes. Along with niclosamide, another tapeworm drug, it has been recently found to display "strong in vivo and in vitro activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)".
 W
WPeganum harmala, commonly called wild rue, Syrian rue, African rue, esfand, or harmel,, is a perennial, herbaceous plant, with a woody underground root-stock, of the family Nitrariaceae, usually growing in saline soils in temperate desert and Mediterranean regions. Its common English-language name came about because of a resemblance to rue. Because eating it can cause livestock to sicken or die, it is considered a noxious weed in a number of countries. It has become an invasive species in some regions of the western United States. The plant is popular in Middle Eastern and north African folk medicine. The alkaloids contained in the plant, including the seeds, are hallucinogenic, possibly due to a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, thus it is sold in the West for recreational drug use.
 W
WPiperazine is an organic compound that consists of a six-membered ring containing two nitrogen atoms at opposite positions in the ring. Piperazine exists as small alkaline deliquescent crystals with a saline taste.
 W
WPraziquantel (PZQ), sold under the brandname Biltricide among others, is a medication used to treat a number of types of parasitic worm infections. Specifically, it is used for schistosomiasis, clonorchiasis, opisthorchiasis, tapeworm infections, cysticercosis, hydatid disease, and other fluke infections. It should not be used for worm infections of the eye. It is taken by mouth.
 W
WPyrvinium (Viprynium) is an anthelmintic effective for pinworms. Several forms of pyrvinium have been prepared with variable counter anions, such as halides, tosylate, triflate and pamoate.
 W
WRafoxanide is a salicylanilide used as an anthelmintic. It is most commonly used in ruminant animals to treat adult liver flukes of the species Fasciola hepatica and Fasciola gigantica.
 W
WSuramin is a medication used to treat African sleeping sickness and river blindness. It is the treatment of choice for sleeping sickness without central nervous system involvement. It is given by injection into a vein.
 W
WTribendimidine is a broad-spectrum anthelmintic agent developed in China, at the National Institute of Parasitic Diseases in Shanghai. It is a derivative of amidantel.
 W
WTriclabendazole, sold under the brand name Egaten among others, is a medication used to treat fascioliasis and paragonimiasis. It is very effective for both conditions. Treatment in hospital may be required. It is taken by mouth with typically one or two doses being required.