 W
WAn ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of the Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and greenhouse periods, during which there are no glaciers on the planet. Earth is currently in the Quaternary glaciation, known in popular terminology as the Ice Age. Individual pulses of cold climate within an ice age are termed glacial periods, and intermittent warm periods within an ice age are called interglacials or interstadials.
 W
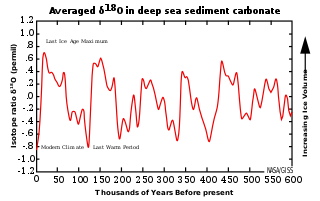
WThe 100,000-year problem of the Milankovitch theory of orbital forcing refers to a discrepancy between the reconstructed geologic temperature record and the reconstructed amount of incoming solar radiation, or insolation over the past 800,000 years. Due to variations in the Earth's orbit, the amount of insolation varies with periods of around 21,000, 40,000, 100,000, and 400,000 years. Variations in the amount of incident solar energy drive changes in the climate of the Earth, and are recognised as a key factor in the timing of initiation and termination of glaciations.
 W
WThe Anglian Stage is the name used in the British Isles for a middle Pleistocene glaciation. It precedes the Hoxnian Stage and follows the Cromerian Stage in the British Isles. The Anglian Stage is correlated to Marine Isotope Stage 12, which started about 478,000 years ago and ended about 424,000 years ago.
 W
WBeringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of the Kamchatka Peninsula. It includes the Chukchi Sea, the Bering Sea, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi and Kamchatka Peninsulas in Russia as well as Alaska in the United States.
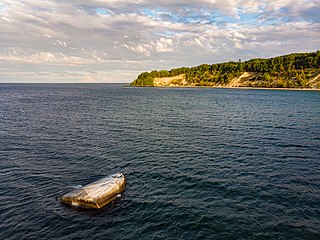 W
WThe Buskam, also Buhskam or Buskamen is a large glacial erratic boulder, 325 metres off the coast of Göhren, Rügen, northern Germany. Erratics have been scattered all over northern Germany by the glaciers of the Ice Age, but are usually much smaller. The Buskam has a volume of about 600 m3, a circumference of about 40 metres, and weights about 1,600 tons. A third of it (206 m3) lies above the water surface.
 W
WThe Cordilleran ice sheet was a major ice sheet that periodically covered large parts of North America during glacial periods over the last ~2.6 million years. This included the following areas:Western Montana The Idaho Panhandle Northern Washington state down to about Olympia and Spokane All of British Columbia The southwestern third or so of Yukon Territory All of the Alaska Panhandle South Central Alaska The Alaska Peninsula Almost all of the continental shelf north of the Strait of Juan de Fuca
 W
WThe Cryogenian is a geologic period that lasted from 720 to 635 million years ago. It forms the second geologic period of the Neoproterozoic Era, preceded by the Tonian Period and followed by the Ediacaran.
 W
WDoggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the southern North Sea, that connected Great Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BC. Geological surveys have suggested that it stretched from where Great Britain's east coast now is to the present-day Netherlands, western coast of Germany, and peninsula of Jutland. It was probably a rich habitat with human habitation in the Mesolithic period, although rising sea levels gradually reduced it to low-lying islands before its final submergence, possibly following a tsunami caused by the Storegga Slide.
 W
WThe Don Glaciation, also known as the Donian Glaciation and the Donian Stage, was the major glaciation of the East European Plain, 0.5–0.8 million years ago, during the Cromerian Stage of the Middle Pleistocene. It is correlated to Marine Isotope Stage 16, approximately 650,000 years ago, which globally contained one of the largest glacial volumes of the Quaternary.
 W
WThe Elster glaciation or, less commonly, the Elsterian glaciation, in the older and popular scientific literature also called the Elster Ice Age (Elster-Eiszeit), is the oldest known ice age that resulted in the large-scale glaciation of North Germany. It took place 500,000–300,000 years ago. It succeeded a long period of rather warmer average temperatures, the Cromerian Complex. The Elster was followed by the Holstein interglacial and the Saale glaciation. The glacial period is named after the White Elster, a right tributary of the Saale.
 W
WAccording to the northern cryptic glacial refugial hypothesis, during the last ice age cold tolerant plant and animal species persisted in ice-free microrefugia north of the Alps in Europe. The alternative hypothesis of no persistence and postglacial immigration of plants and animals from southern refugia in Europe is sometimes also called the tabula rasa hypothesis.
 W
WThe Ice Age Centre is a museum dedicated to the understanding of ice ages, located in Äksi village,Tartu county, Estonia
 W
WThe Ice Age Floods National Geologic Trail or Ice Age Floods Trail is designated as the first National Geologic Trail in the United States. It will consist of a network of routes connecting facilities that will provide interpretation of the geological consequences of the Glacial Lake Missoula floods of the last glacial period that began about 110,000 years ago.
 W
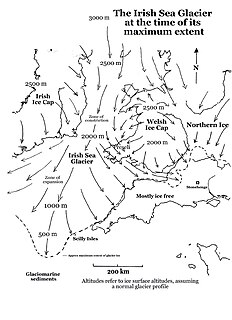
WThe Irish Sea Glacier was a huge glacier during the Pleistocene Ice Age that, probably on more than one occasion, flowed southwards from its source areas in Scotland and Ireland and across the Isle of Man, Anglesey and Pembrokeshire. It probably reached its maximum extent during the Anglian Glaciation, and it was also extensive during the Late Devensian Glaciation.
 W
WThe Last Glacial Maximum (LGM), also referred to as the Late Glacial Maximum, was the most recent time during the Last Glacial Period that ice sheets were at their greatest extent. Ice sheets covered much of North America, Northern Europe, and Asia and profoundly affected Earth's climate by causing drought, desertification, and a large drop in sea levels. According to Clark et al., growth of ice sheets commenced 33,000 years ago and maximum coverage was between 26,500 years and 19–20,000 years ago, when deglaciation commenced in the Northern Hemisphere, causing an abrupt rise in sea level. Decline of the West Antarctica ice sheet occurred between 14,000 and 15,000 years ago, consistent with evidence for another abrupt rise in the sea level about 14,500 years ago.
 W
WLast Glacial Maximum refugia were places in which humans and other species survived during the Last Glacial Period in the Northern Hemisphere, around 25,000 to 20,000 years ago.
 W
WThe Last Glacial Period (LGP) occurred from the end of the Eemian to the end of the Younger Dryas, encompassing the period c. 115,000 – c. 11,700 years ago. The LGP is part of a larger sequence of glacial and interglacial periods known as the Quaternary glaciation which started around 2,588,000 years ago and is ongoing. The definition of the Quaternary as beginning 2.58 million years ago is based on the formation of the Arctic ice cap. The Antarctic ice sheet began to form earlier, at about 34 Ma, in the mid-Cenozoic. The term Late Cenozoic Ice Age is used to include this early phase.
 W
WThe Late Cenozoic Ice Age, or Antarctic Glaciation began 33.9 million years ago at the Eocene-Oligocene Boundary and is ongoing. It is Earth's current ice age or icehouse period. Its beginning is marked by the formation of the Antarctic ice sheets. The Late Cenozoic Ice Age gets its name due to the fact that it covers roughly the last half of Cenozoic era so far.
 W
WThe late Paleozoic icehouse, formerly known as the Karoo ice age, was between 360–260 million years ago (Mya) during which large land-based ice-sheets were present on Earth's surface. It was the second major glacial period of the Phanerozoic. It is named after the tillite found in the Karoo Basin of South Africa, where evidence for this ice age was first clearly identified in the 19th century.
 W
WThe Laurentide Ice Sheet was a massive sheet of ice that covered millions of square kilometers, including most of Canada and a large portion of the Northern United States, multiple times during the Quaternary glacial epochs, from 2.588 ± 0.005 million years ago to the present.
 W
WThe Mid-Pleistocene Transition (MPT), also known as the Mid-Pleistocene Revolution (MPR), is a fundamental change in the behaviour of glacial cycles during the Quaternary glaciations. The transition happened approximately 1.25–0.7 million years ago, in the Pleistocene epoch. Before the MPT, the glacial cycles were dominated by a 41,000 year periodicity with low-amplitude, thin ice sheets and a linear relationship to the Milankovitch forcing from axial tilt. After the MPT there have been strongly asymmetric cycles with long-duration cooling of the climate and build-up of thick ice sheets, followed by a fast change from extreme glacial conditions to a warm interglacial. The cycle lengths have varied, with an average length of approximately 100,000 years.
 W
WMilankovitch cycles describe the collective effects of changes in the Earth's movements on its climate over thousands of years. The term is named for Serbian geophysicist and astronomer Milutin Milanković. In the 1920s, he hypothesized that variations in eccentricity, axial tilt, and precession resulted in cyclical variation in the solar radiation reaching the Earth, and that this orbital forcing strongly influenced the Earth's climatic patterns.
 W
WThe Mindel glaciation is the third youngest glacial stage in the Alps. Its name was coined by Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner, who named it after the Swabian river, the Mindel. The Mindel glacial occurred in the Middle Pleistocene; it was preceded by the Haslach-Mindel interglacial and succeeded by the Mindel-Riss interglacial.
 W
WThe Oldest Dryas is a biostratigraphic subdivision layer corresponding to an abrupt cooling event, or stadial, which occurred during the last glacial retreat. The time period to which the layer corresponds varies between regions, but it is generally dated as starting at 18.5-17 ka BP and ending 15-14 ka BP. As with the Younger and Older Dryas events, the stratigraphic layer is marked by abundance of the pollen and other remains of Dryas octopetala, an indicator species that colonizes arctic-alpine regions.
 W
WThe Quaternary glaciation, also known as the Pleistocene glaciation, is an alternating series of glacial and interglacial periods during the Quaternary period that began 2.58 Ma, and is ongoing. Although geologists describe the entire time period as an "ice age", in popular culture the term "ice age" is usually associated with just the most recent glacial period during the Pleistocene. Since planet Earth still has ice sheets, geologists consider the Quaternary glaciation to be ongoing, with the Earth now experiencing an interglacial period.
 W
WThe Riss glaciation, Riss Glaciation, Riss ice age, Riss Ice Age, Riss glacial or Riss Glacial is the second youngest glaciation of the Pleistocene epoch in the traditional, quadripartite glacial classification of the Alps. The literature variously dates it to between about 300,000 to 130,000 years ago and 347,000 to 128,000 years ago. It coincides with the Saale glaciation of North Germany. The name goes back to Albrecht Penck and Eduard Brückner who named this cold period after the river Riss in Upper Swabia in their three-volume work Die Alpen im Eiszeitalter published between 1901 and 1909.
 W
WThe Saale glaciation or Saale Glaciation, sometimes referred to as the Saalian glaciation, Saale cold period, Saale complex (Saale-Komplex) or Saale glacial stage, covers the middle of the three large glaciations in Northern Europe and the northern parts of Eastern, Central and Western Europe by the Scandinavian Inland Ice Sheet between the older Elster glaciation and the younger Weichselian glaciation.
 W
WDuring the Last Glacial Maximum, the mammoth steppe was the Earth’s most extensive biome. It spanned from Spain eastward across Eurasia to Canada and from the arctic islands southward to China. It had a cold, dry climate; the vegetation was dominated by palatable high-productivity grasses, herbs and willow shrubs, and the animal biomass was dominated by bison, horses, and woolly mammoth. This ecosystem covered wide areas of the northern part of the globe, thrived for approximately 100,000 years without major changes, and then suddenly became all but extinct about 12,000 years ago.
 W
WThere have been five or six major ice ages in the history of Earth over the past 3 billion years. The Late Cenozoic Ice Age began 34 million years ago, its latest phase being the Quaternary glaciation, in progress since 2.58 million years ago.
 W
WThe Vashon Glaciation, Vashon Stadial or Vashon Stade is a local term for the most recent period of very cold climate in which during its peak, glaciers covered the entire Salish Sea as well as present day Seattle, Tacoma, Olympia and other surrounding areas in the western part of present-day Washington (state) of the United States of America. This occurred during a cold period around the world known as the last glacial period. This was the most recent cold period of the Quaternary glaciation, the time period in which the arctic ice sheets have existed. The Quaternary Glaciation is part of the Late Cenozoic Ice Age, which began 33.9 million years ago and is ongoing. It is the time period in which the Antarctic ice cap has existed.
 W
WThe Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cordillera; the Innuitian ice sheet, which extended across the Canadian Arctic Archipelago; the Greenland ice sheet; and the massive Laurentide Ice Sheet, which covered the high latitudes of central and eastern North America. This advance was synchronous with global glaciation during the last glacial period, including the North American alpine glacier advance, known as the Pinedale glaciation. The Wisconsin glaciation extended from approximately 75,000 to 11,000 years ago, between the Sangamonian Stage and the current interglacial, the Holocene. The maximum ice extent occurred approximately 25,000–21,000 years ago during the last glacial maximum, also known as the Late Wisconsin in North America.
 W
WThe World in Winter is a 1962 post-apocalyptic science fiction novel by British writer John Christopher. It deals with a new ice age caused by a reduction in the output of the Sun.
 W
WThe Würm glaciation or Würm stage, in the literature usually just referred to as the Würm, often spelt "Wurm", was the last glacial period in the Alpine region. It is the youngest of the major glaciations of the region that extended beyond the Alps themselves. It is, like most of the other ice ages of the Pleistocene epoch, named after a river, the Würm in Bavaria, a tributary of the Amper. The Würm ice age can be dated to the time about 115,000 to 11,700 years ago, the sources differing depending on whether the long transition phases between the glacials and interglacials are allocated to one or other of these periods. The average annual temperatures during the Würm ice age in the Alpine Foreland were below −3 °C. This has been determined from changes in the vegetation as well as differences in the facies.