 W
WThe first USS Abarenda (AC-13/AG-14) was a collier in the service of the United States Navy during World War I.
 W
WUSS Ajax (AC-14/AG-15) was a collier in the United States Navy. Originally she retained her previous name of Scindia, and was renamed for the mythical Ajax in 1901. In 1921, she became a receiving ship and was redesignated AC-14. She was reclassified as a seaplane tender and given the hull designator AG-15 in 1924.
 W
WUSS Brutus, formerly the steamer Peter Jebsen, was a collier in the United States Navy. She was built in 1894 at South Shields-on-Tyne, England, by John Readhead & Sons and was acquired by the U.S. Navy early in 1898 from L. F. Chapman & Company. She was renamed Brutus and commissioned at the Mare Island Navy Yard on 27 May 1898, with Lieutenant Vincendon L. Cottman, commanding officer and Lieutenant Randolph H. Miner, executive officer.
 W
WUSS Caesar (AC-16) was a collier built in 1896 by Ropner and Sons, Stockton-on-Tees, England, as Kingtor; purchased by the United States Navy on 21 April 1898; fitted out by New York Navy Yard; and commissioned on 13 May 1898, Lieutenant Commander A. B. Speyers in command.
 W
WUSS Cyclops (AC-4) was the second of four Proteus-class colliers built for the United States Navy several years before World War I. Named for the Cyclops, a primordial race of giants from Greek mythology, she was the second U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name. The loss of the ship and 306 crew and passengers without a trace within the area known as the Bermuda Triangle some time after 4 March 1918 remains the single largest loss of life in U.S. Naval history not directly involving combat. As it was wartime, she was thought to have been captured or sunk by a German raider or submarine, because she was carrying 10,800 long tons (11,000 t) of manganese ore used to produce munitions, but German authorities at the time, and subsequently, denied any knowledge of the vessel. The Naval History & Heritage Command has stated she "probably sank in an unexpected storm", but the ultimate cause of the ship's loss is not known.
 W
WUSS Fahkee (1862) was a steamer purchased by the Union Navy during the American Civil War. She was built in 1862 at Williamsburg, New York, purchased by the Navy on 15 July 1863; and commissioned on 24 September 1863 with Acting Master F. R. Webb in command.
 W
WUSS Hannibal (AG-1), a converted steamer, was built as Joseph Holland by J. Blumer & Company at Sunderland, England, in 1898. She was purchased by the United States Navy on 16 April 1898 and renamed Hannibal. She was one of the very few ships to serve in the U.S. Navy in the Spanish–American War, World War I and World War II. She was commissioned on 7 June 1898 with Commander Harrison Gray Otis Colby in command.
 W
WUSS Hector (AC-7) was a collier acquired by the United States Navy prior to World War I. She carried coal to those ships still burning coal to build up steam for their engines, and continued that service until her wrecking and sinking in 1916. She was the sister of USS Mars.
 W
WUSS Iris was a ship of the United States Navy which served in the Pacific in a variety of roles from 1899 until 1916. Originally fitted out as a distilling ship, she served as a general utility ship, then as a collier, before being refitted as a torpedo boat tender.
 W
WUSS J. B. Walker was an old schooner hulk acquired by the U.S. Navy during World War I. Because of her age, condition and relatively large cargo capacity, she was used as a collier, carrying coal where needed. She was not self-propelled, and required to be towed from one port to another. Post-war, J. B. Walker was sold.
 W
WThe first Jason was a collier of the United States Navy. She was laid down 26 March 1912 and launched 16 November 1912 by Maryland Steel Company, Sparrows Point, Maryland.
 W
WUSS Langley (CV-1/AV-3) was the United States Navy's first aircraft carrier, converted in 1920 from the collier USS Jupiter (AC-3), and also the US Navy's first turbo-electric-powered ship. Conversion of another collier was planned but canceled when the Washington Naval Treaty required the cancellation of the partially built Lexington-class battlecruisers Lexington and Saratoga, freeing up their hulls for conversion to the aircraft carriers Lexington and Saratoga. Langley was named after Samuel Pierpont Langley, an American aviation pioneer. Following another conversion to a seaplane tender, Langley fought in World War II. On 27 February 1942, she was attacked by nine twin-engine Japanese bombers of the Japanese 21st and 23rd Naval Air Flotillas and so badly damaged that she had to be scuttled by her escorts.
 W
WUSS Justin (1891) was a steamship acquired by the United States Navy for use as a collier. Her task was to carry coal and to provide it to ships and stations. Her task was one that was being phased out, as the navies of the world were shifting from coal to oil to drive their ships.
 W
WUSS Lebanon (AG-2) was a 3,285-long-ton (3,338-metric-ton) collier, which the United States Navy acquired in 1898 from the Philadelphia and Reading RR. Company to provide coal for Navy warships during the Spanish–American War. When the need for her coal was no longer a necessity, Lebanon was assigned various duty such as transporting stores as well as target repair and towing operations.
 W
WUSS Leonidas (AD-7) was a destroyer tender, the lone ship in her class, named for Leonidas I, and the second United States naval vessel to bear the name.
 W
WUSS Marcellus was an iron schooner-rigged collier United States Navy Auxiliary ship in service with the United States Navy from 1898 to 1910. She participated in the U.S. Navy's first efforts in coaling warships while underway at sea. She was rammed by a commercial steamer in the early morning hours of 9 August 1910 and sank that afternoon without loss of life.
 W
WThe second USS Mars (AC-6) was a collier of the United States Navy. The ship was laid down by the Maryland Steel Co., Sparrows Point, Maryland on 5 October 1908, launched on 10 April 1909, sponsored by Miss Juliana Keyser, and commissioned at Norfolk on 26 August 1909, Master A. B. Randall, Naval Auxiliary Service, in command. She was the sister of the USS Hector (AC-7).
 W
WUSS Nanshan (AG-3) was a collier in the service of the United States Navy.
 W
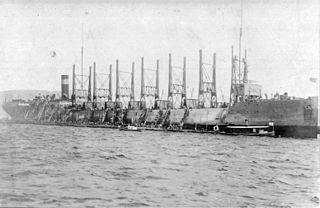
WThe third USS Neptune (AC–8), a collier of the U.S. Navy, was laid down by the Maryland Steel Co., Sparrows Point, Md. 23 March 1910; launched 21 January 1911; and placed in service with a merchant crew at Norfolk Navy Yard 20 September 1911, Master F. E. Horton, Naval Auxiliary Service, in command.
 W
WUSS Nereus (AC-10) was one of four Proteus-class colliers built for the United States Navy before World War I. Named for Nereus, an aquatic deity from Greek mythology, she was the second U.S. Naval vessel to bear the name. Nereus was laid down on 4 December 1911, and launched on 26 April 1913 by the Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, Newport News, Virginia, and commissioned on 10 September 1913.
 W
WUSS Nero (AC–17), a steel steam collier, was built in 1895 as the steamer Whitgift by J.L. Thompson and Sons, Sunderland, England. The vessel was purchased on 30 June 1898 from McCondray and Co. at San Francisco and commissioned on 8 June 1898, Commander Charles Belknap in command.
 W
WUSS Nightingale (1851) was originally the tea clipper and slave ship Nightingale, launched in 1851. USS Saratoga captured her off Africa in 1861; the United States Navy then purchased her.
 W
WUSS Orion (AC–11) was a collier of the United States Navy. The ship was laid down by the Maryland Steel Co., Sparrows Point, Maryland, on 6 October 1911, launched on 23 March 1912, and commissioned at Norfolk on 29 July 1912.
 W
WThe collier USS Proteus (AC-9) was laid down on 31 October 1911, by the Newport News Shipbuilding and Dry Dock Company, and launched on 14 September 1912. She was the lead ship of her class of four colliers. She was commissioned on 9 July 1913, to the United States Navy, Master Robert J. Easton, Naval Auxiliary Service, in command.
 W
WThe first USS Saturn (AG-4) was an iron collier in the United States Navy.
 W
WUSS Sioux (ID-1766) was a cargo ship in the United States Navy.
 W
WUSS Southery, a steamer built in 1889 by R. Thompson Sons & Co. at Sunderland, England, was purchased by the United States Navy on 16 April 1898. She was converted to a collier at the Boston Navy Yard and commissioned there on 2 May 1898, Commander Walton Goodwin in command.
 W
WUnited States Navy Auxiliary ship Sterling was an iron, schooner-rigged collier in service with the United States Navy from 1898 to 1919. Originally purchased to transport coal for United States Navy ships during the Spanish–American War, she served in that role until sold in 1919. While serving as the Chilean flagged steamer, Llai Llai, she was rammed by a Chilean warship on 11 March 1920 and sank near Iquique, Chile.
 W
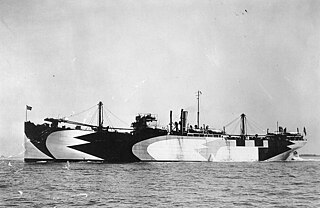
WUSS Vestal (AR-4) was a repair ship in service with the United States Navy from 1913 to 1946. Before her conversion to a repair ship, she had served as a collier since 1909. Vestal served in both World Wars. She was damaged during the Japanese attack on Pearl Harbor and received two battle stars for her World War II service.
 W
WThe second USS Volunteer (ID-3242) was a United States Navy collier in commission from 1918 to 1919.
 W
WUSS Vulcan was a collier of the United States Navy.
 W
WUSS Zafiro was a collier, a bulk cargo ship, that served in the United States Navy from 1898 until 1904.