 W
WThe 1994 Java earthquake occurred on June 3 at 01:17:37 local time off the coast of Indonesia. The epicenter was off the eastern part of the southern Java coast, near the east end of the Java Trench.
 W
WThe 2009 West Java earthquake occurred on September 2 at 14:55:01 local time in West Java, Indonesia. The magnitude 7.0 earthquake killed at least 79 people, injured over 1,250, and displaced over 210,000. The quake was felt in the capital Jakarta, although damage there was minimal, and it was Indonesia's deadliest earthquake since the 2006 Pangandaran earthquake and tsunami.
 W
WOn 13 December 2014, a landslide in Banjarnegara, Central Java, Indonesia, killing 93 with 23 people missing. The disaster occurred on Jemblung Village in Banjarnegara, Indonesia, at Friday, around 03.00 p.m. At the time, most of the villagers were taking a nap on their houses. The landslides also trapped some vehicles on the road. Amateur video caught the moment when a large piece of the mountain fell to the whole village. Indonesian authority said that at least around 100 people are feared dead and 300 houses were destroyed.
 W
WThe 2017 Java earthquake occurred on 15 December 2017 when a moment magnitude 6.5 earthquake struck the Indonesian island of Java, specifically the city of Tasikmalaya on 23:47:58 West Indonesian Time in West Java, Indonesia. The earthquake struck at a depth of 91 km and was categorized as a strong but deep earthquake. It was initially registered as a 7.3 magnitude earthquake by Indonesian agencies. Widespread damages have been reported across Tasikmalaya, the nearest major city to the epicentre. A tsunami warning was immediately issued by the authorities but was subsequently cancelled. Four people have been confirmed dead.
 W
WOn 23 January 2018, at 13:34:50 Western Indonesian Time, an earthquake struck the Indonesian island of Java near the regency of Lebak. The earthquake, measured 5.9 on the Mww, occurred approximately 40 kilometres south of the village of Binuangeun at a depth of 43.9 kilometres. The earthquake was categorized as a strong and shallow earthquake.
 W
WAirlangga, regnal name Rakai Halu Sri Lokeswara Dharmawangsa Airlangga Anantawikramottunggadewa, was the only raja of the Kingdom of Kahuripan. The Kingdom was built from the territory of the Kingdom of Medang after Medang was sacked by king Wurawari of Lwaram. He gradually gained support, won back the kingdom once ruled by his uncle, and went on to become one of Java's most notable kings. Airlangga literally means "jumping water", thus his name means "he who crossed the water", described his life story; born in the court of Bali and during his youth crossed the Bali Strait to stay in Java and later ruled the kingdom in East Java. He belongs to both Isyana and Warmadewa lineages.
 W
WThe Siege of Batavia was a military campaign led by Sultan Agung of Mataram to capture the Dutch port-settlement of Batavia in Java. The first attempt was launched in 1628, and the second in 1629; both were unsuccessful. Jan Pieterszoon Coen, the Governor-General of the Dutch East Indies, managed to repel the sieges and beat off all of Sultan Agung's attacks.
 W
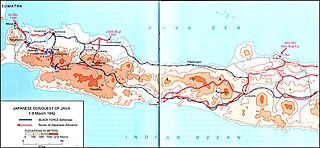
WThe Battle of Java was a battle of the Pacific theatre of World War II. It occurred on the island of Java from 28 February – 12 March 1942. It involved forces from the Empire of Japan, which invaded on 28 February 1942, and Allied personnel. Allied commanders signed a formal surrender at Japanese headquarters at Bandung on 12 March.
 W
WThe Battle of Kalijati was a battle which occurred between 1 and 3 March 1942 during the Dutch East Indies campaign between invading Japanese forces and the Dutch colonial forces. It was fought over control of the Kalijati Airfield in Subang.
 W
WThe Battle of Tjiater Pass was a battle which occurred between 5 and 7 March 1942 during the Dutch East Indies campaign between invading Japanese forces and the Dutch colonial forces, supported by warplanes from the Royal Air Force. It was fought over control of the Tjiater Pass, as part of an attempted defense of the city of Bandung.
 W
WThe 1985 Borobudur bombing occurred on 21 January 1985 when nine bombs detonated at the Borobudur Buddhist temple located in Magelang, Central Java, Indonesia. There were no human casualties in this attack, however nine stupas on upper rounded terraces of Arupadhatu were badly damaged by the bombs.
 W
W"Devarāja" was the religious order of the "god-king", or deified monarch in medieval Southeast Asia.
 W
WPrince Diponegoro, also known as Dipanegara, was a Javanese prince who opposed the Dutch colonial rule. The eldest son of the Yogyakartan Sultan Hamengkubuwono III, he played an important role in the Java War between 1825 and 1830. After his defeat and capture, he was exiled to Makassar, where he died.
 W
WKandjeng Pangeran Aria Adipati Achmad Djajadiningrat was a prominent colonial Indonesian bureaucrat who served as Regent of Serang (1901–1924), and subsequently of Batavia (1924–1929). He was also a member of the Volksraad of the Dutch East Indies.
 W
WThe Indonesian mass killings of 1965–66 were large-scale killings and civil unrest that occurred in Indonesia over several months, targeting Communist Party of Indonesia (PKI) party members, Communist sympathisers, Gerwani women, ethnic Javanese Abangan, ethnic Chinese and alleged leftists, often at the instigation of the armed forces and government. It began as an anti-communist purge following a controversial attempted coup d'état by the 30 September Movement. The most widely published estimates were that 500,000 to more than one million people were killed, with some more recent estimates going as high as two to three million. The purge was a pivotal event in the transition to the "New Order" and the elimination of PKI as a political force, with impacts on the global Cold War. The upheavals led to the fall of President Sukarno and the commencement of Suharto's three-decade authoritarian presidency.
 W
WThe Java War or Diponegoro War was fought in central Java from 1825 – 1830, between the colonial Dutch Empire and native Javanese rebels. The war started as a rebellion led by Prince Diponegoro, a leading member of the Javanese aristocracy who had previously cooperated with the Dutch.
 W
WThe Javanese presence in Australia has been reported by native Southeast Asian and European people over several centuries. The most renowned record is from the itinerary of Chiaymasiouro, king of Demak, and Declaraçam de Malaca e India Meridional com o Cathay by Manuel Godinho de Eredia. Chiaymasiouro describes a land called Luca Antara in Southeast direction of Java, which Eredia coined the term India Meridional. According to Chiaymasiouro's accounts, a subgroup of Javanese people already settled in those lands, but when Eredia's servant went to Luca Antara in 1610, the land had seemingly been abandoned.
 W
WKahuripan later Kediri was an 11th-century Javanese Hindu-Buddhist kingdom with its capital located around the estuarine of Brantas River valley in East Java. The kingdom was short lived only spanned the period between 1019 and 1045 and Airlangga was the only raja of the kingdom, which was built out of the rubble of the Kingdom of Medang after the Srivijaya invasion. Airlangga later in 1045 abdicated in favour of his two sons and divided the kingdom into Janggala and Panjalu (Kadiri). The kingdom's name derived from Old Javanese term hurip with circumfix ka- -an which means "life" or "livelihood". Later in 14th to 15th century, the former kingdom was recognised as one of Majapahit's 12 provinces.
 W
WKediri or Kadiri was a Hindu Javanese Kingdom based in East Java from 1042 to around 1222. Despite the lack of archaeological remains, the age of Kediri saw much development in classical literature. Mpu Sedah's Kakawin Bharatayuddha, Mpu Panuluh's Gatotkacasraya, and Mpu Dharmaja's Smaradhana blossomed in this era. The kingdom's capital is believed to have been established in the western part of the Brantas River valley, somewhere near modern Kediri city and surrounding Kediri Regency.
 W
WThis is a list of campaigns of Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty.
 W
WThe Linggadjati Agreement was a political accord concluded on 15 November 1946 by the Dutch administration and the unilaterally declared Republic of Indonesia in the village of Linggajati, Kuningan Regency, near Cirebon in which the Dutch recognised the republic as exercising de facto authority in Java, Madura and Sumatra.
 W
WThe Sultanate of Mataram was the last major independent Javanese kingdom on Java before the island was colonised by the Dutch. It was the dominant political force radiating from the interior of Central Java from the late 16th century until the beginning of the 18th century.
 W
WMeganthropus is an extinct genus of non-hominin hominid ape, known from the Pleistocene of Indonesia. It is known from a series of large jaw and skull fragments found at the Sangiran site near Surakarta in Central Java, Indonesia, alongside several isolated teeth. The genus has a long and convoluted taxonomic history. The original fossils were ascribed to a new species, Meganthropus palaeojavanicus, and for a long time was considered invalid, with the genus name being used as an informal name for the fossils.
 W
WThe Mongol invasion of Java was a military effort made by Kublai Khan, founder of the Yuan dynasty, to invade Java, an island in modern Indonesia. In 1293, he sent a large invasion fleet to Java with 20,000 to 30,000 soldiers. This was a punitive expedition against King Kertanegara of Singhasari, who had refused to pay tribute to the Yuan and maimed one of its ministers. However, it ended with failure for the Mongols and victory for Singhasari.
 W
WPlered was the location of the palace of Amangkurat I of Mataram. Amangkurat moved the capital there from the nearby Karta in 1647. During the Trunajaya rebellion, the capital was occupied and sacked by the rebels, and Amangkurat died during the retreat from the capital. His son and successor Amangkurat II later moved the capital to Kartasura. It was twice occupied by Diponegoro, during the Java War (1825–1830) between his forces and the Dutch. The Dutch assaulted the walled complex in June 1826, which was Diponegoro's first major defeat in the war.
 W
WThe Shailendra dynasty was the name of a notable Indianised dynasty that emerged in 8th-century Java, whose reign signified a cultural renaissance in the region. The Shailendras were active promoters of Mahayana Buddhism with the glimpses of Hinduism, and covered the Kedu Plain of Central Java with Buddhist monuments, one of which is the colossal stupa of Borobudur, now a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
 W
WSolo Man is a subspecies of Homo erectus, identified based on fossil evidence of 18 specimens discovered between 1931 and 1933 by Gustav Heinrich Ralph von Koenigswald from sites along the Solo River, on the Indonesian island of Java, dated to between 116,000 and 108,000 years old. The remains are also commonly referred to as Ngandong, after the village near where they were first recovered, and older remains located at Bapang.
 W
WSurakarta Sunanate was a Javanese monarchy centred in the city of Surakarta, in the province of Central Java, Indonesia.
 W
WTrunajaya rebellion or Trunajaya War was the ultimately unsuccessful rebellion waged by the Madurese prince Trunajaya and fighters from Makassar against the Mataram Sultanate and its Dutch East India Company (VOC) supporters in Java during the 1670s.
 W
WSri Maharaja Rakai Pangkaja Dyah Wawa Sri Wijayalokanamottungga, better known in Indonesia as Dyah Wawa, was a ruler of the Mataram Kingdom in Central Java, Indonesia. What is known of him is mainly thanks to an inscription engraved on the Minto Stone.
 W
WThe Sultanate of Yogyakarta is a Javanese monarchy in Yogyakarta Special Region, in the Republic of Indonesia. The current head of the Sultanate is Hamengkubuwono X.