 W
WThe Abrolhos Archipelago are a group of 5 small islands with coral reefs off the southern coast of Bahia state in the northeast of Brazil, between 17º25’—18º09’ S and 38º33’—39º05’ W. Caravelas is the nearest town. Their name comes from the Portuguese: abrolho, a rock awash or submerged sandbank that is a danger to ships. There is a conspicuous shipwreck in the group.
 W
WThe Aurora Islands was a group of three phantom islands first reported in 1762 by the Spanish merchant ship Aurora while sailing from Lima to Cádiz. The Aurora's officers reported sighting them again in 1774. The Spanish ship San Miguel fixed their location at 52°37'S, 47°49'W. On 20 February 1794, they were sighted again by a Spanish survey ship, the corvette Atrevida, which as part of the Alejandro Malaspina circumnavigation had been sent to confirm them. Their reported location was approximately halfway between the Falkland Islands and South Georgia at 53°S 48°W. The latitude is considered perfect, the longitude was based on the meridian of the astronomical observatory, San Fernando, Cádiz. The islands were last reportedly sighted in 1856, but continued to appear on maps of the South Atlantic until the 1870s.
 W
WThe Bahamas, known officially as the Commonwealth of The Bahamas, is a country within the Lucayan Archipelago of the West Indies in the Atlantic. It takes up 97% of the Lucayan Archipelago's land area and is home to 88% of the archipelago's population. The archipelagic state consists of more than 700 islands, cays, and islets in the Atlantic Ocean, and is located north of Cuba and northwest of the island of Hispaniola and the Turks and Caicos Islands, southeast of the US state of Florida, and east of the Florida Keys. The capital is Nassau on the island of New Providence. The Royal Bahamas Defence Force describes The Bahamas' territory as encompassing 470,000 km2 (180,000 sq mi) of ocean space.
 W
WBermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. It is approximately 1,035 km (643 mi) east-southeast of Cape Hatteras, North Carolina ; 1,236 km (768 mi) south of Cape Sable Island, Nova Scotia; 1,759 km (1,093 mi) northeast of Cuba, and 1,538 km (956 mi) due north of the British Virgin Islands. Though it is typically referred to in the singular, Bermuda consists of 181 islands; the largest of these islands is known as Main Island. The capital city of Bermuda is Hamilton. Bermuda is internally self-governing, with its own constitution and cabinet of ministers selected from the elected Members of the lower house of a Parliament that enacts local laws. As the national government, the Government of the United Kingdom is ultimately responsible for ensuring good governance within British Overseas Territories, and retains responsibility for defence and foreign relations. As of July 2018, it has a population of 71,176, making it the most populous of the British overseas territories. Bermuda's largest industries are offshore insurance, reinsurance, and tourism. Bermuda had one of the world's highest GDP per capita for most of the 20th century.
 W
WChausey is a group of small islands, islets and rocks off the coast of Normandy, in the English Channel. It lies 17 kilometres (11 mi) from Granville and forms a quartier of the Granville commune in the Manche département. Chausey forms part of the Channel Islands from a geographical point of view, but, because it is under French jurisdiction, it is almost never mentioned in the context of the other Channel Islands. There are no scheduled transport links between Chausey and the other Channel Islands, although between two and four daily shuttles link Chausey to mainland France through Granville, depending on the season.
 W
WThe Cíes Islands are an archipelago off the coast of Pontevedra in Galicia (Spain), in the mouth of the Ria de Vigo. They belong to the parish of San Francisco de Afora, in the municipality of Vigo. They were declared a Nature Reserve in 1980 and are included in the Atlantic Islands of Galicia National Park created in 2002.
 W
WThe Ons Island is the main island of a small archipelago in the coast of Pontevedra in Galicia, Spain. Ons belongs administratively to the municipality of Bueu, which has a regular ferry boat connection to the island, as have the mainland towns of Portonovo, Sanxenxo, Marín and Aldán. In 2020, lightning due to Subtropical Storm Alpha started a forest fire.
 W
WFernando de Noronha is an archipelago in the Atlantic Ocean, part of the State of Pernambuco, Brazil, and located 354 km (220 mi) offshore from the Brazilian coast. It consists of 21 islands and islets, extending over an area of 26 km2 (10 sq mi). Only the homonymous main island is inhabited; it has an area of 18.4 km2 (7.1 sq mi) and a population estimated at 2,718 in 2012.
 W
WÎles de Los are an island group lying off Conakry in Guinea, on the west coast of Africa. Their name is derived from the Portuguese: Ilhas dos Ídolos, "Islands of the Idols". They are located about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) off the headland limiting the southern side of Sangareya Bay.
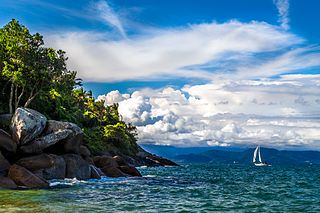 W
WIlhabela is an archipelago and city situated in the Atlantic Ocean four miles off the coast of São Paulo state in Brazil. The city is 205 km (127 mi) from the city of São Paulo and 340 km (210 mi) from the city of Rio de Janeiro. The largest island, although commonly called Ilhabela, is officially named Ilha de São Sebastião. It, the other islands and the islets make up the municipality of Ilhabela.
 W
WThe Ilhas Cagarras are an uninhabited archipelago located 5 km off Ipanema, a major beach of the southern coast of the city of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. They have been designated a federal natural monument since 2010.
 W
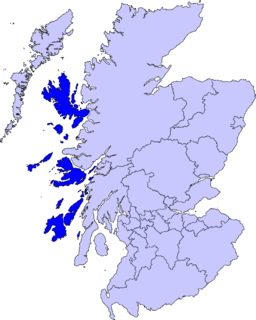
WThe Inner Hebrides is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, which experience a mild oceanic climate. The Inner Hebrides comprise 35 inhabited islands as well as 44 uninhabited islands with an area greater than 30 hectares. Skye, Islay and Mull are the three largest, and also have the highest populations. The main commercial activities are tourism, crofting, fishing and whisky distilling. In modern times the Inner Hebrides have formed part of two separate local government jurisdictions, one to the north and the other to the south. Together, the islands have an area of about 4,130 km2 (1,594 sq mi), and had a population of 18,948 in 2011. The population density is therefore about 4.6 inhabitants per square kilometre.
 W
WThe Islands of the Firth of Clyde are the fifth largest of the major Scottish island groups after the Inner and Outer Hebrides, Orkney and Shetland. They are situated in the Firth of Clyde between Ayrshire and Argyll and Bute. There are about forty islands and skerries, of which only four are inhabited and only nine larger than 40 hectares. The largest and most populous are Arran and Bute, and Great Cumbrae and Holy Island are also served by dedicated ferry routes. Unlike the four larger Scottish archipelagos, none of the isles in this group are connected to one another or to the mainland by bridges.
 W
WThe Lucayan Archipelago, also known as the Bahama Archipelago, is an island group comprising the Commonwealth of The Bahamas and the British Overseas Territory of the Turks and Caicos Islands. The archipelago is in the western North Atlantic Ocean, north of Cuba along with the other Antilles, and east and southeast of Florida.
 W
WMadre de Deus is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil. The municipality is located on a small archipelago in the Bay of All Saints; it both the smallest municipality by land mass in Bahia and the Northeastern region of Brazil. Madre de Deus is spread across two islands, the Ilha de Madre de Deus and the much smaller Ilha de Maria Guarda. It sits in close proximity to two others islands, the Ilha do Bom Jesus dos Passos and Ilha dos Frades, both part of the city of Salvador. The Ilha de Madre de Deus is further subdivided into the neighborhoods of Centro, Suape, Cação, Marezinha, Mirim, Alto do Paraíso, Apicum, Nova Madre de Deus e Quitéria, Alto da Matriz, Alto do Santo Antônio, Alto da Boa Vista, Cururupeba, Malvinas, and Nova Brasília.
 W
WThe Magdalen Islands are a small archipelago in the Gulf of Saint Lawrence with a land area of 205.53 square kilometres (79.36 sq mi). Administratively, the islands are part of the Gaspésie–Îles-de-la-Madeleine region in the Canadian province of Quebec, but geographically, they are closer to the Maritime provinces than to the Gaspé Peninsula, on the Quebec mainland.
 W
WThe Mingan Archipelago is an archipelago located east of Quebec, Canada. It consists of a chain of about 40 islands.
 W
WThe Molde Archipelago is a chain of about 50 tree-clad islands and islets, about 2 kilometres (1.2 mi) south the town of Molde in Molde Municipality, Møre og Romsdal county, Norway. The islands lie across the Moldefjorden from the town of Molde. The archipelago is public, protected land, and a recreational resort. The main island, Hjertøya, hosts the Museum of Fisheries, a collection of maritime culture from the 17th-19th centuries, and is serviced by water taxi from Molde.
 W
WThe Northern Isles are a pair of archipelagos off the north coast of mainland Scotland, comprising Orkney and Shetland. The climate is cool and temperate and much influenced by the surrounding seas. There are a total of 26 inhabited islands with landscapes of the fertile agricultural islands of Orkney contrasting with the more rugged Shetland islands to the north, where the economy is more dependent on fishing and the oil wealth of the surrounding seas. Both have a developing renewable energy industry. They also share a common Pictish and Norse history. Both island groups were absorbed into the Kingdom of Scotland in the 15th century and remained part of the country following the formation of the Kingdom of Great Britain in 1707, and later the United Kingdom after 1801. The islands played a significant naval role during the world wars of the 20th century.
 W
WOrkney, also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, Mainland, is often referred to as "the Mainland", and has an area of 523 square kilometres (202 sq mi), making it the sixth-largest Scottish island and the tenth-largest island in the British Isles. The largest settlement and administrative centre is Kirkwall.
 W
WThe Outer Hebrides or Western Isles, sometimes known as Innse Gall or the Long Isle/Long Island, is an island chain off the west coast of mainland Scotland. The islands are geographically coextensive with Comhairle nan Eilean Siar, one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. They form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides by the waters of the Minch, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. Scottish Gaelic is the predominant spoken language, although in a few areas English speakers form a majority.
 W
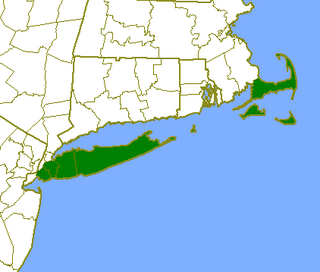
WThe Outer Lands is the prominent terminal moraine archipelagic region off the southern coast of New England in the United States. This eight-county region of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and New York, comprises the peninsula of Cape Cod and the islands of Martha's Vineyard, the Elizabeth Islands, Nantucket, Block Island, the Narragansett Bay Islands, Staten Island, and Long Island, as well as surrounding islands and islets.
 W
WSabana-Camagüey is an archipelago that lines Cuba's north-central Atlantic coast. It is located off the northern coast of the provinces of Matanzas, Villa Clara, Sancti Spíritus, Ciego de Ávila and Camagüey, and is bounded to the north by the Atlantic Ocean, specifically by the Nicholas Channel and Old Bahama Channel.
 W
WThe Saint Peter and Saint Paul Archipelago is a group of 15 small islets and rocks in the central equatorial Atlantic Ocean held by Brazil. It lies in the Intertropical Convergence Zone, a region of the Atlantic characterized by low average winds punctuated with local thunderstorms. It lies approximately 510 nmi from the nearest point of mainland South America ; 625 km (388 mi) northeast of the archipelago of Fernando de Noronha; 990 km (620 mi) from the city of Natal; and 1,824 km (1,133 mi) from the west coast of Africa. Administratively, the archipelago belongs to Brazil and is part of the special "state district" of Fernando de Noronha, in the state of Pernambuco, in spite of the very large distance between the two island groups and the even larger distance to the state mainland.
 W
WThe Scalloway Islands are in Shetland opposite Scalloway on south west of the Mainland. They form a mini-archipelago and include:Burra East Burra West Burra South Havra Little Havra Papa - belongs to Civil parish of Lerwick West Head of Papa (tidal)
 W
WShetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated in the Northern Atlantic, between Great Britain, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost part of Scotland and the wider United Kingdom.
 W
WThe Thimble Islands is an archipelago consisting of small islands in Long Island Sound, located in and around the harbor of Stony Creek in the southeast corner of Branford, Connecticut. The islands are under the jurisdiction of the United States with security provided by the town of Branford police and the US Coast Guard.
 W
WTrindade and Martin Vaz is an archipelago located in the South Atlantic Ocean about 1,100 kilometres east of the coast of the Brazilian state of Espírito Santo, of which it forms a part. The archipelago has a total area of 10.4 square kilometres and a population of 32. The archipelago consists of five islands and several rocks and stacks; Trindade is the largest island, with an area of 10.1 square kilometres ; about 49 kilometres east of it are the tiny Martin Vaz islets, with a total area of 0.3 square kilometres.
 W
WVikna is a former municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. The municipality existed from 1869 until its dissolution in 2020 when it joined Nærøysund Municipality. It was part of the Namdalen region. The administrative centre of the municipality was the village of Rørvik. Other villages in Vikna included Austafjord, Garstad, and Valøya.
 W
WVitória Island is an archipelago and island in Espírito Santo state, Brazil. Vitória, the capital of Espírito Santo, is situated on the main island. The main island has an area of 89 km² and a population of 358,875, according to 2015 estimates.