 W
WAgathaeromys is an extinct genus of oryzomyine rodents from the Pleistocene of Bonaire, Netherlands Antilles. Two species are known, which differ in size and some details of tooth morphology. The larger A. donovani, the type species, is known from hundreds of teeth, found in four localities that are probably 900,000 to 540,000 years old. A. praeuniversitatis, the smaller species, is known from 35 teeth found in a single fossil site, which is probably 540,000 to 230,000 years old.
 W
WAmerhippus is an extinct subgenus of Equus which includes several species of horses that lived in South America. They were one of two groups of equines in South America alongside Hippidion. Fossils have been recovered from the Tarija Formation of Bolivia, the Serranía del Perijá in Venezuela, the Chiu-Chiu Formation of Chile, the Sabana Formation of the Bogotá savanna in Colombia, and from various locations in Ecuador. The subgenus lived from 2.588 to 0.012 Mya. It measured roughly 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and weighed approximately 400 kg (880 lb). While they have formerly been referred to as belonging to 5 separate species, this has been revised down into three, and more recently a single, morphologically variable species Equus neogeus. Equus first appeared in South America during the late Early Pleistocene around 1 Ma. A 2008 study of mitochondrial DNA fragments of a specimen of E. neogeus found it to be nested within mitochondrial lineages of E. caballus. A close relationship to caballine horses was also supported by a 2019 morphological analysis study.
 W
WArctotherium is an extinct genus of Pleistocene South American short-faced bears within Ursidae. Their ancestors migrated from North America to South America during the Great American Interchange, following the formation of the Isthmus of Panama during the late Pliocene. The oldest dated confirmed remains are those of A. angustidens from Buenos Aires, Argentina, dating to the Ensenadan epoch, 1.76 to 0.98 Ma old, within the Early to Middle Pleistocene, with a tooth possibly belonging to Arctotherium dating about 2.588 Mya. They are genetically closer to the spectacled bear, than to Arctodus of North America, implying the two extinct forms evolved large size in a convergent manner, perhaps to facilitate dominating other carnivores in the competition for the biggest carcasses. The northernmost species, A. wingei, known from Venezuela in South America, apparently invaded Central America and reached as far north as the Yucatán.
 W
WCarletonomys cailoi is an extinct rodent from the Pleistocene (Ensenadan) of Buenos Aires Province, Argentina. Although known only from a single maxilla with the first molar, its features are so distinctive that it is placed in its own genus, Carletonomys. Discovered in 1998 and formally described in 2008, it is part of a well-defined group of oryzomyine rodents that also includes Holochilus, Noronhomys, Lundomys, and Pseudoryzomys. This group is characterized by progressive semiaquatic specializations and a reduction in the complexity of molar morphology.
 W
WCatonyx is an extinct genus of ground sloth of the family Scelidotheriidae, endemic to South America during the Pleistocene epoch. It lived from 2.5 Ma to about 10,000 years ago, existing for approximately 2.49 million years . The most recent date obtained is about 9600 B.P.
 W
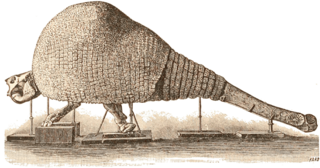
WCuvieronius is an extinct New World genus of gomphotheres and is named after the French naturalist Georges Cuvier. Alive, specimens typically stood about 2.3 m (7.5 ft) tall at the shoulder, weighed about 3.5 t and would have superficially resembled a modern elephant with spiral-shaped tusks.
 W
WDoedicurus, or Dædicurus, is an extinct genus of glyptodont from South America containing one species, D. clavicaudatus. Glyptodonts are a member of the family Chlamyphoridae, which also includes some modern armadillo species, and they are classified in the order Xenarthra alongside sloths and anteaters. Being a glyptodont, it was a rotund animal with heavy armor and a carapace. Averaging at an approximate 1,400 kg (3,100 lb), it was one of the largest glyptodonts to have ever lived. Though glyptodonts were quadrupeds, large ones like Doedicurus may have been able to stand on two legs like other xenarthrans. It notably sported a spiked tail club, which may have weighed 40 or 65 kg in life, and it may have swung this in defense against predators or in fights with other Doedicurus at speeds of perhaps 11 m/s.
 W
WEutatus is an extinct genus of large armadillos of the family Dasypodidae. It was endemic to South America from the Early Miocene to Late Pleistocene, living from 17.5 Ma-11,000 years ago, with possible survival into the early Holocene and existing for approximately 17.49 million years . Based on carbon isotope ratios, it is thought to have been an herbivore that fed on grasses.
 W
WGlossotherium was a genus of ground sloth. It was a heavily built animal with a length of about 4 metres (13 ft) snout to tail-tip, a weight estimated at 1,000 kg (2,200 lb), and could potentially assume a slight bipedal stance.
 W
WGryposuchus is an extinct genus of gavialoid crocodilian. It is the type genus of the subfamily Gryposuchinae. Fossils have been found from Argentina, Colombia, Venezuela, Brazil and the Peruvian Amazon. The genus existed during the Miocene epoch. One recently described species, G. croizati, grew to an estimated length of 10 metres (33 ft).
 W
WHemiauchenia, synonym Tanupolama, is a genus of lamine camelids that evolved in North America in the Miocene period about 10 million years ago. This genus diversified and moved to South America in the Early Pleistocene, as part of the Great American Biotic Interchange, giving rise to modern lamines. The genus became extinct at the end of the Pleistocene.
 W
WHippidion is an extinct genus of horse that lived in South America from the Late Pliocene to the end of the Late Pleistocene (Lujanian), between two million and 11,000 years ago. They were one of two lineages of equines native to South America during the Pleistocene epoch alongside those of the Equus subgenus Amerhippus.
 W
WHolmesina is a genus of pampathere, an extinct group of armadillo-like creatures that were distantly related to extant armadillos. Like armadillos, and unlike the other extinct branch of megafaunal cingulates, the glyptodonts, the shell was made up of flexible plates which allowed the animal to move more easily. Holmesina species were herbivores that grazed on coarse vegetation; armadillos are mostly insectivorous or omnivorous.
 W
WThe Jama Formation is a Pliocene to Early Pleistocene geologic formation in Ecuador. The claystones and sandstones were deposited in an coastal environment. The age of the Jama Formation is constrained by 40Ar/39Ar dating of tephra beds. The formation is correlated to the Charco Azul Formation of western Panama and southeastern Costa Rica.
 W
WLestodon is an extinct genus of megafaunal ground sloth from South America during the Pliocene to Pleistocene periods. Its fossil remains have been found in Argentina, Paraguay, Uruguay, Venezuela, Bolivia, and Brazil. Measuring approximately 4.6 metres (15 ft) from snout to tail tip, it is estimated to have weighed 2,590 kilograms. It was a herbivore and primarily fed on the grasses on the South American plains and is thought to perhaps have used its semi-bipedal stance to obtain foliage from trees. Lestodon is placed as member of the Mylodontidae as indicated by the lobed form of the last tooth in the dentition.
 W
WMacrauchenia was a large, long-necked and long-limbed, three-toed native South American mammal in the order Litopterna. The genus gives its name to its family, the Macraucheniidae or "robust litopterns". Like other litopterns, it is not closely related to any living mammal, being most closely related to the group containing horses, rhinos and tapirs, from which litopterns diverged approximately 66 million years ago. The oldest fossils in the genus date to the late Miocene, around seven million years ago, and M. patachonica disappears from the fossil record during the late Pleistocene, around 20,000-10,000 years ago. M. patachonica is one of the last and best known member of the family and is known primarily from the Luján Formation in Argentina, but is known from localities across southern South America. Another genus of macraucheniid Xenorhinotherium was present in northeast Brazil and Venezuela during the Late Pleistocene. The type specimen was discovered by Charles Darwin during the voyage of the Beagle. In life, Macrauchenia may have resembled a humpless camel, though the two taxa are not closely related. It fed on plants in a variety of environments across what is now South America. Among the species described, M. patachonica and M. ullomensis are considered valid; M. boliviensis is considered a nomen dubium; and M. antiqua has been moved to the genus Promacrauchenia.
 W
WMesotherium, synonym, "Typotherium," is the type genus of Mesotheriidae, a long-lasting family of superficially rodent-like, burrowing notoungulates from South America. It was first named by Étienne Serres in 1867, and through further finds now contains four species, M. cristatum, M. hystatum, M. maendrum, and M. pachygnathum. Fossils have been found in the Miramar and Vorohué Formations of Argentina.
 W
WMixotoxodon is an extinct genus of notoungulate of the family Toxodontidae inhabiting South America, Central America and parts of southern North America during the Pleistocene, from 1,800,000—12,000 years ago.
 W
WNeolicaphrium is an extinct genus of ungulate mammal belonging to the extinct order Litopterna. This animal lived from the Late Pliocene (Chapadmalalan) to the Late Pleistocene (Lujanian) in southern South America, being the last survivor of the family Proterotheriidae.
 W
WNeosclerocalyptus was an extinct genus of glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in northeastern Argentina.
 W
WNothrotherium is an extinct genus of medium-sized ground sloth from South America. It differs from Nothrotheriops in smaller size and differences in skull and hind leg bones, but both genera can be traced back to Hapalops, the genus which both evolved from in different ecological conditions.
 W
WPanochthus is an extinct genus of glyptodont, which lived in the Gran Chaco-Pampean region of Argentina, Brazil, Bolivia, Paraguay and Uruguay during the Pleistocene epoch.
 W
WPlatygonus is an extinct genus of herbivorous peccaries of the family Tayassuidae, endemic to North and South America from the Miocene through Pleistocene epochs, existing for about 10.289 million years .
 W
WScelidodon is an extinct genus of South American ground sloths. Its remains have been found in the Yupoí and Uspara Formations of Argentina, the Ulloma, Umala, Ñuapua and Tarija Formations of Bolivia, in Brazil, in Chile and in Peru. The youngest fossils have been dated to as recently as 9000 B.P.
 W
WSclerocalyptus was a glyptodont that lived during the Pleistocene in Argentina. Four species are described from the Ensenadan, S. pseudornatus, S. ornatus, S. perfectus and S. cordubensis, and two Lujanian taxa S. heusseri and S. evidens.
 W
WTheriodictis is an extinct genus of small hypercarnivorous fox-like canid endemic to South America during the Pleistocene, living from 1.2 Ma- 500,000 years ago and existing for approximately 0.7 million years .
 W
WThylamys is a genus of opossums in the family Didelphidae. The premaxillae are rounded rather than pointed. The females lack a pouch. The females' nipples are arranged in two symmetrical rows on the abdomen. All species but T. macrurus store fat in their tails., although this is not necessarily true for all species in the genus. Fossils belonging to the genus date back to the Miocene, with the oldest specimens being found in the Cerro Azul Formation of Argentina and the Honda Group of Colombia. Genetic studies indicate that the genus may have originated around 14 million years ago.
 W
WToxodon is an extinct genus of South American mammals from the Late Miocene to early Holocene epochs. It is a member of Notoungulata, one of several now extinct orders of hoofed mammals indigenous to South America. It was among the largest and last members of its order, and was probably the most common large hoofed mammal in South America of its time.
 W
WXenorhinotherium is an extinct genus of macraucheniids, closely related to Macrauchenia of Patagonia. The type species is X. bahiense.