 W
WA gold standard is a monetary system in which the standard economic unit of account is based on a fixed quantity of gold. The gold standard was widely used in the 19th and early part of the 20th century. Most nations abandoned the gold standard as the basis of their monetary systems at some point in the 20th century, although many still hold substantial gold reserves.
 W
W9–9–9: An Army of Davids, written by Herman Cain and Rich Lowrie, was released on May 1, 2012. The book details the 9–9–9 Plan and traces its history along with Cain and other politicians' promotion of the tax policy during the 2012 United States presidential election. The text also advocates for the gold standard.
 W
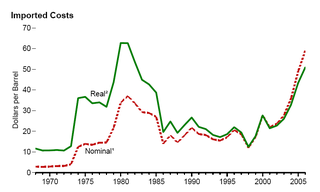
WThe 1970s energy crisis occurred when the Western world, particularly the United States, Canada, Western Europe, Australia, and New Zealand, faced substantial petroleum shortages, real and perceived, as well as elevated prices. The two worst crises of this period were the 1973 oil crisis and the 1979 energy crisis, when the Yom Kippur War and the Iranian Revolution triggered interruptions in Middle Eastern oil exports.
 W
WThe Almoravid dinar was a gold dinar coin minted under the Almoravid dynasty in the Maghreb and Iberia. The mints that produced them were supplied by the West African gold mines south of the Sahara dessert. The Almoravid dinars circulated widely beyond the reach of the empire; the Christian kingdoms of Iberia called them "marabotins" and "maravedís".
 W
WThe bancor was a supranational currency that John Maynard Keynes and E. F. Schumacher conceptualised in the years 1940–1942 and which the United Kingdom proposed to introduce after World War II. The name was inspired by the French banque or. This newly created supranational currency would then be used in international trade as a unit of account within a multilateral clearing system—the International Clearing Union—which would also have to be founded.
 W
WThe Belle Époque or La Belle Époque is the term often given to a period of French history, usually dated to between 1880 and the outbreak of World War I in 1914. Occurring during the era of the French Third Republic, it was a period characterised by optimism, regional peace, economic prosperity, colonial expansion, and technological, scientific, and cultural innovations. In this era of France’s cultural and artistic climate, the arts markedly flourished, with numerous masterpieces of literature, music, theatre, and visual art gaining extensive recognition.
 W
WThe Black Friday gold panic of September 24, 1869 was caused by a conspiracy between two investors, Jay Gould and his partner James Fisk, and Abel Corbin, a small time speculator who had married Virginia (Jennie) Grant, the younger sister of President Grant. They formed the Gold Ring to corner the gold market and force up the price of that metal on the New York Gold Exchange. The scandal took place during the Presidency of Ulysses S. Grant, whose policy was to sell Treasury gold at weekly intervals to pay off the national debt, stabilize the dollar, and boost the economy. The country had gone through tremendous upheaval during the Civil War and was not yet fully restored.
 W
WThe Bretton Woods Conference, formally known as the United Nations Monetary and Financial Conference, was the gathering of 730 delegates from all 44 Allied nations at the Mount Washington Hotel, situated in Bretton Woods, New Hampshire, United States, to regulate the international monetary and financial order after the conclusion of World War II.
 W
WThe British Empire Economic Conference was a 1932 conference of British colonies and the autonomous dominions held to discuss the Great Depression. It was held between 21 July and 20 August in Ottawa.
 W
WCoin's Financial School was an 1894 pamphlet written by lawyer, politician and resort founder William Hope Harvey (1851–1936). It advocated a return to bimetallism, where the value of a monetary unit is defined as a certain amount of two different kinds of metals, often gold and silver. In the book, Harvey charged that the demonetization of silver caused by the Coinage Act of 1873 led to the Panic of 1893 by halving the supply of available redemption money in the economy. This lowered the prices of goods throughout the country and hurt farmers and small business owners, according to Harvey. Harvey argued that by returning silver to the same monetary status as gold, the American economy would benefit from stabilized prices, resulting in higher revenue, and ease of repayment of debts. The pamphlet sold about 1 million copies, which helped popularized the free silver movement to the public. Harvey would go on to aid Democratic candidate William Jennings Bryan’s presidential campaign in 1896, which ran on the platform of free coinage of silver. The issue of bimetallism remained controversial throughout the remainder of the 19th century.
 W
WThe Coinage Act 1816, also known as Liverpool's Act, defined the value of the pound sterling relative to gold. One troy pound of standard (22-carat) gold was defined as equivalent to £46 14s 6d., i.e. 44½ guineas, the guinea having been fixed in December 1717 at £1 1s exactly. According to its preamble, the purposes of the Act were to:prohibit the use of silver coins, for transactions larger than 40s establish a single gold standard for transactions of all sizes.
 W
WThe Cross of Gold speech was delivered by William Jennings Bryan, a former United States Representative from Nebraska, at the Democratic National Convention in Chicago on July 9, 1896. In the address, Bryan supported bimetallism or "free silver", which he believed would bring the nation prosperity. He decried the gold standard, concluding the speech, "you shall not crucify mankind upon a cross of gold". Bryan's address helped catapult him to the Democratic Party's presidential nomination; it is considered one of the greatest political speeches in American history.
 W
WThe Genoa Economic and Financial Conference was a formal conclave of 34 nations held in Genoa, Italy from 10 April to 19 May 1922. It was planned by British prime minister David Lloyd George to resolve the major economic and political issues facing Europe, and to deal with the pariah states of Germany and Russia, both of which had been excluded from the Paris Peace Conference of 1919. The conference was particularly interested in developing a strategy to rebuild a defeated Germany, as well as central and eastern European states, and to negotiate a relationship between European capitalist economies and the new Bolshevik regime in Soviet Russia. However, Russia and Germany signed a separate agreement at Rapallo and the result at Genoa was a fiasco with few positive results. The conference did come up with a proposal for resuming the gold standard that was largely put in place by major countries.
 W
WIn United States history, the Gilded Age was an era that occurred during the late 19th century, from the 1870s to about 1900. The Gilded Age was an era of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern United States and the Western United States. As American wages grew much higher than those in Europe, especially for skilled workers, the period saw an influx of millions of European immigrants. The rapid expansion of industrialization led to a real wage growth of 60%, between 1860 and 1890, and spread across the ever-increasing labor force. The average annual wage per industrial worker rose from $380 in 1880, to $564 in 1890, a gain of 48%. Conversely, the Gilded Age was also an era of abject poverty and inequality, as millions of immigrants—many from impoverished regions—poured into the United States, and the high concentration of wealth became more visible and contentious.
 W
WThe Gold (Control) Act, 1968 is a repealed Act of the Parliament of India which was enacted to control sale and holding of gold in personal possession. However excessive demand for gold in India with negligible indigenous production is met with gold imports leading to drastic devaluation of Indian rupee and depletion of foreign exchange reserves to alarming levels. Devaluation of Indian rupee is also leading to steep rise in food commodity prices due to costlier petroleum products imports. In these circumstances, the gold import policy of India aims at curbing the gold imports to manageable level time to time by imposing taxes and legal restrictions.
 W
WThe gold holdings of Norway, also known as Norway's gold reserves, were a formally defined entity related to Norges Bank's foreign-exchange reserves as well as the physical quantity of gold owned by the same central bank. During the eras of the gold standard, the national currency was in theory redeemable by a specific quantity of the state's gold holdings.
 W
WGold repatriation refers to plans of various governments to bring home their gold stored outside the home country.
 W
WGold holdings are the quantities of gold held by individuals, private corporations, or public entities as a store of value, an investment vehicle, or perceived as protection against hyperinflation and against financial and/or political upheavals.
 W
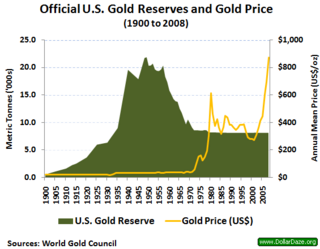
WA gold reserve was the gold held by a national central bank, intended mainly as a guarantee to redeem promises to pay depositors, note holders, or trading peers, during the eras of the gold standard, and also as a store of value, or to support the value of the national currency.
 W
WThe Gold Standard issue or Small Head issue was the first definitive series of postage stamps issued by the Soviet Union between 1923 and 1927. The stamps were designed by Ivan Shadr.
 W
WThe National Democratic Party, also known as Gold Democrats, was a short-lived political party of Bourbon Democrats who opposed the regular party nominee William Jennings Bryan in the 1896 presidential election.
 W
WThe Nixon shock was a series of economic measures undertaken by United States President Richard Nixon in 1971, in response to increasing inflation, the most significant of which were wage and price freezes, surcharges on imports, and the unilateral cancellation of the direct international convertibility of the United States dollar to gold.
 W
WThe post–World War II economic expansion, also known as the postwar economic boom or the Golden Age of Capitalism, was a broad period of worldwide economic expansion beginning after World War II and ending with the 1973–1975 recession. The United States, Soviet Union, Western European and East Asian countries in particular experienced unusually high and sustained growth, together with full employment. Contrary to early predictions, this high growth also included many countries that had been devastated by the war, such as Japan, West Germany and Austria (Wirtschaftswunder), South Korea, Belgium, France, Italy and Greece. Even countries that were relatively unaffected by the war such as Sweden experienced considerable economic growth.
 W
WThe Scandinavian Monetary Union was a monetary union formed by Denmark and the Swedish part of the Union between Sweden and Norway on 5 May 1873, by fixing their currencies against gold at par to each other. After the dissolution of the Swedish-Norwegian union, in 1905, Norway continued to be a part of this monetary union. The union ended with the outbreak of World War I.
 W
WThe Utah Legal Tender Act, which was passed March 10, 2011, recognizes gold and silver coins as legal tender in the state of Utah. This includes allowing the state of Utah to pay off debts in gold and silver and allowing individuals to transact in gold and silver coins without paying state capital gains tax, among other provisions. The bill was introduced as HB317 by State Representative Brad J. Galvez.
 W
WIn 1896, William Jennings Bryan ran unsuccessfully for President of the United States. Bryan, a former Democratic congressman from Nebraska, gained his party's presidential nomination in July of that year after electrifying the Democratic National Convention with his Cross of Gold speech. He was defeated in the general election by the Republican candidate, former Ohio governor William McKinley.
 W
WIn 1896, William McKinley was elected President of the United States. McKinley, a Republican and former Governor of Ohio, defeated the joint Democratic and Populist nominee, William Jennings Bryan, as well as minor-party candidates. McKinley's decisive victory in what is sometimes seen as a realigning election ended a period of close presidential contests, and ushered in an era of dominance for the Republican Party.
 W
WYamashita's gold, also referred to as the Yamashita treasure, is the name given to the alleged war loot stolen in Southeast Asia by Imperial Japanese forces during World War II and hidden in caves, tunnels, underground complexes, or just underground in the Philippines. It is named after the Japanese general Tomoyuki Yamashita, nicknamed "The Tiger of Malaya". Though accounts that the treasure remains hidden in the Philippines have lured treasure hunters from around the world for over fifty years, its existence is dismissed by most experts. The rumored treasure was the subject of a complex lawsuit that was filed in a Hawaiian state court in 1988 involving a Filipino treasure hunter, Rogelio Roxas, and the former Philippine president, Ferdinand Marcos.