 W
WBraden R. Allenby is an American environmental scientist, environmental attorney and Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering, and of Law, at Arizona State University.
 W
WRobert Underwood Ayres is an American-born physicist and economist. His career has focused on the application of physical ideas, especially the laws of thermodynamics, to economics; a long-standing pioneering interest in material flows and transformations —a concept which he originated. His most recent work challenges the widely held economic theory of growth.
 W
WBiomimetics or biomimicry is the emulation of the models, systems, and elements of nature for the purpose of solving complex human problems. The terms "biomimetics" and "biomimicry" are derived from Ancient Greek: βίος (bios), life, and μίμησις (mīmēsis), imitation, from μιμεῖσθαι (mīmeisthai), to imitate, from μῖμος (mimos), actor. A closely related field is bionics.
 W
WCradle-to-cradle design is a biomimetic approach to the design of products and systems that models human industry on nature's processes, where materials are viewed as nutrients circulating in healthy, safe metabolisms. The term itself is a play on the popular corporate phrase "cradle to grave", implying that the C2C model is sustainable and considerate of life and future generations—from the birth, or "cradle", of one generation to the next generation, versus from birth to death, or "grave", within the same generation.
 W
WDPSIR is a causal framework for describing the interactions between society and the environment: Human impact on the environment and vice versa because of the interdependence of the components.
 W
WEco-costs are the costs of the environmental burden of a product on the basis of prevention of that burden. They are the costs which should be made to reduce the environmental pollution and materials depletion in our world to a level which is in line with the carrying capacity of our earth.
 W
WAn eco-industrial park (EIP) is an industrial park in which businesses cooperate with each other and with the local community in an attempt to reduce waste and pollution, efficiently share resources, and help achieve sustainable development, with the intention of increasing economic gains and improving environmental quality. An EIP may also be planned, designed, and built in such a way that it makes it easier for businesses to co-operate, and that results in a more financially sound, environmentally friendly project for the developer.
 W
WEcological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, or eco-economics, is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital.
 W
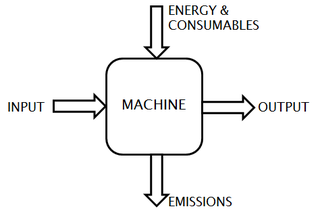
WEcomechatronics is an engineering approach to developing and applying mechatronical technology in order to reduce the ecological impact and total cost of ownership of machines. It builds upon the integrative approach of mechatronics, but not with the aim of only improving the functionality of a machine. Mechatronics is the multidisciplinary field of science and engineering that merges mechanics, electronics, control theory, and computer science to improve and optimize product design and manufacturing. In ecomechatronics, additionally, functionality should go hand in hand with an efficient use and limited impact on resources. Machine improvements are targeted in 3 key areas: energy efficiency, performance and user comfort.
 W
WEfficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a building allows it to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a thermal comfort. Installing light-emitting diode bulbs, fluorescent lighting, or natural skylight windows reduces the amount of energy required to attain the same level of illumination compared to using traditional incandescent light bulbs. Improvements in energy efficiency are generally achieved by adopting a more efficient technology or production process or by application of commonly accepted methods to reduce energy losses.
 W
WEnergy quality is a measure of the ease at which a form of energy can be converted to useful work or to another form of energy. A high quality form of energy is easily converted to work or to a lower quality form of energy, whereas converting low quality forms of energy to work or a higher quality form may be inefficient, difficult or impossible. The concept of energy quality is also used in ecology, where it is used to track the flow of energy between different trophic levels in a food chain and in thermoeconomics, where it is used as a measure of economic output per unit of energy. Methods of evaluating energy quality often involve developing a ranking of energy qualities in hierarchical order.
 W
WIn the field of waste management, extended producer responsibility (EPR) is a strategy to add all of the environmental costs associated with a product throughout the product life cycle to the market price of that product. Extended producer responsibility legislation is a driving force behind the adoption of remanufacturing initiatives because it "focuses on the end-of-use treatment of consumer products and has the primary aim to increase the amount and degree of product recovery and to minimize the environmental impact of waste materials".
 W
WThe helix of sustainability is a concept coined to help manufacturing industry move to more sustainable practices by mapping its models of raw material use and reuse onto those of nature.The environmental benefits of the use crop origin sustainable materials have been assumed to be self-evident, but as the debate on food vs fuel shows, the whole product life cycle must be examined in the light of social and environmental effects in addition to technical suitability and profitability.
 W
WIndustrial symbiosis a subset of industrial ecology. It describes how a network of diverse organizations can foster eco-innovation and long-term culture change, create and share mutually profitable transactions—and improve business and technical processes.
 W
WThe ISASMELT process is an energy-efficient smelting process that was jointly developed from the 1970s to the 1990s by Mount Isa Mines Limited and the Australian government’s Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation ("CSIRO"). It has relatively low capital and operating costs for a smelting process.
 W
WIn economics, the Jevons paradox occurs when technological progress or government policy increases the efficiency with which a resource is used, but the rate of consumption of that resource rises due to increasing demand. The Jevons paradox is perhaps the most widely known paradox in environmental economics. However, governments and environmentalists generally assume that efficiency gains will lower resource consumption, ignoring the possibility of the paradox arising.
 W
WKalundborg Eco-Industrial Park is an industrial symbiosis network located in Kalundborg, Denmark, in which companies in the region collaborate to use each other's by-products and otherwise share resources.
 W
WLife-cycle assessment or life cycle assessment is a methodology for assessing environmental impacts associated with all the stages of the life-cycle of a commercial product, process, or service. For instance, in the case of a manufactured product, environmental impacts are assessed from raw material extraction and processing (cradle), through the product's manufacture, distribution and use, to the recycling or final disposal of the materials composing it (grave).
 W
WLife-cycle engineering (LCE) is a sustainability-oriented engineering methodology that takes into account the comprehensive technical, environmental, and economic impacts of decisions within the product life cycle. Alternatively it can be defined as “sustainability-oriented product development activities within the scope of one to several product life cycles.” LCE requires analysis to quantify sustainability, setting appropriate targets for environmental impact. The application of complementary methodologies and technologies enables engineers to apply LCE to fulfill environmental objectives.
 W
WMaterial criticality is the determination of which materials that flow through an industry or economy are most important to the production process. It is a sub-category within the field of material flow analysis (MFA), which is a method to quantitatively analyze the flows of materials used for industrial production in an industry or economy. MFA is a useful tool to assess what impacts materials used in the industrial process have and how efficiently a given process uses them.
 W
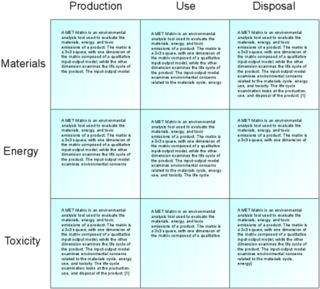
WA MET Matrix is an analysis tool used to evaluate various environmental impacts of a product over its life cycle. The tool takes the form of a 3x3 matrix with descriptive text in each of its cells. One dimension of the matrix is composed of a qualitative input-output model that examines environmental concerns related to the product's materials use, energy use, and toxicity. The other dimension looks at the life cycle of the product through its production, use, and disposal phase. The text in each cell corresponds to the intersection of two particular aspects. For example, this means that by looking at certain cells, one can examine aspects such as energy use during the production phase, or levels of toxicity that may be a concern during the disposal phase.
 W
WIn environmental law, the polluter pays principle is enacted to make the party responsible for producing pollution responsible for paying for the damage done to the natural environment. It is regarded as a regional custom because of the strong support it has received in most Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) and European Union countries. It is a fundamental principle in US environmental law.
 W
WRegenerative design is a process-oriented whole systems approach to design. The term "regenerative" describes processes that restore, renew or revitalize their own sources of energy and materials. Regenerative design uses whole systems thinking to create resilient and equitable systems that integrate the needs of society with the integrity of nature.
 W
WThermoeconomics, also referred to as biophysical economics, is a school of heterodox economics that applies the laws of statistical mechanics to economic theory. Thermoeconomics can be thought of as the statistical physics of economic value and is a subfield of econophysics.
 W
WWaste hierarchy is a tool used in the evaluation of processes that protect the environment alongside resource and energy consumption from most favourable to least favourable actions. The hierarchy establishes preferred program priorities based on sustainability. To be sustainable, waste management cannot be solved only with technical end-of-pipe solutions and an integrated approach is necessary.
 W
WWaste minimisation is a set of processes and practices intended to reduce the amount of waste produced. By reducing or eliminating the generation of harmful and persistent wastes, waste minimisation supports efforts to promote a more sustainable society. Waste minimisation involves redesigning products and processes and/or changing societal patterns of consumption and production.
 W
WZero Waste is a set of principles focused on waste prevention that encourages the redesign of resource life cycles so that all products are reused. The goal is for no trash to be sent to landfills, incinerators or the ocean. Currently, only 9% of plastic is actually recycled. In a zero waste system, material will be reused until the optimum level of consumption. The definition adopted by the Zero Waste International Alliance (ZWIA) is:Zero Waste: The conservation of all resources by means of responsible production, consumption, reuse and recovery of all products, packaging, and materials, without burning them, and without discharges to land, water or air that threaten the environment or human health.