 W
WThe Oceanian realm is one of the World Wildlife Fund (WWF) biogeographic realms, and is unique in not including any continental land mass. It is the smallest in land of an area of the WWF realms.
 W
WThe Carolines tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It includes the central and eastern Caroline Islands in the Federated States of Micronesia.
 W
WThe Central Polynesian tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Polynesia. It includes the northern Cook Islands, the Line Islands in Kiribati, and Johnston Atoll, Jarvis Island, Palmyra Atoll, and Kingman Reef which are possessions of the United States.
 W
WThe Cook Islands tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion that covers the Southern Cook Islands in the Cook Islands.
 W
WEaster Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. Easter Island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.
 W
WThe Eastern Micronesia tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It includes the Marshall Islands, the Gilbert Islands in Kiribati, Nauru, and Wake Island, a possession of the United States.
 W
WThe Fiji tropical dry forests are a tropical dry forest ecoregion in Fiji. The dry forests occupy the leeward northwestern portion of Fiji's two largest islands, Viti Levu and Vanua Levu.
 W
WThe Fiji tropical moist forests is a tropical moist forest ecoregion in Fiji and Wallis and Futuna. It covers the windward sides of Viti Levu and Vanua Levu, Fiji's largest islands, as well as the smaller Fijian islands and the three islands that make up Wallis and Futuna, an overseas territory of France.
 W
WThe Hawaiian tropical dry forests are a tropical dry broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands. They cover an area of 6,600 km2 (2,500 sq mi) on the leeward side of the main islands and the summits of Niʻihau and Kahoʻolawe. These forests are either seasonal or sclerophyllous. Annual rainfall is less than 127 cm (50 in) and may be as low as 25 cm (9.8 in); the rainy season lasts from November to March. Dominant tree species include koa, koaiʻa, ʻakoko, ʻōhiʻa lehua, lonomea, māmane, loulu, lama, olopua, wiliwili, and ʻiliahi. Endemic plant species in the dry forests include hau heleʻula, uhiuhi, and Gouania spp. The palila, a Hawaiian honeycreeper, is restricted to this type of habitat.
 W
WThe Hawaiian tropical high shrublands are a tropical savanna ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands.
 W
WThe Hawaiian tropical low shrublands are a tropical savanna ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands.
 W
WThe Hawaiian jungles are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Hawaiian Islands. They cover an area of 6,700 km2 (2,600 sq mi) in the windward lowlands and montane regions of the islands. Coastal mesic forests are found at elevations from sea level to 300 m (980 ft). Mixed mesic forests occur at elevations of 750 to 1,250 m, while wet forests are found from 1,250 to 1,700 m. Moist bogs and shrublands exist on montane plateaus and depressions. For the 28 million years of existence of the Hawaiian Islands, they have been isolated from the rest of the world by vast stretches of the Pacific Ocean, and this isolation has resulted in the evolution of an incredible diversity of endemic species, including fungi, mosses, snails, birds, and other wildlife. In the lush, moist forests high in the mountains, trees are draped with vines, orchids, ferns, and mosses. This ecoregion includes one of the world's wettest places, the slopes of Mount Waiʻaleʻale, which average 373 in (9,500 mm) of rainfall per year.
 W
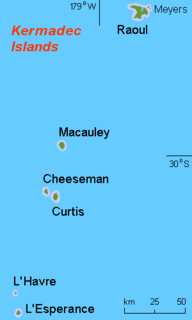
WThe Kermadec Islands are a subtropical island arc in the South Pacific Ocean 800–1,000 km (500–620 mi) northeast of New Zealand's North Island, and a similar distance southwest of Tonga. The islands are part of New Zealand, 33.6 km2 (13.0 sq mi) in total area and uninhabited, except for the permanently manned Raoul Island Station, the northernmost outpost of New Zealand.
 W
WThe Marianas tropical dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion on the Marianas Islands in the western Pacific Ocean.
 W
WThe Marquesas tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in the Marquesas Islands of French Polynesia.
 W
WThe Northwestern Hawaii scrub is a tropical and subtropical grasslands, savannas, and shrublands ecoregion on the Northwestern Hawaiian Islands in the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WThe Ogasawara subtropical moist forests is a terrestrial ecoregion which encompasses the Ogasawara Archipelago of Japan. The Ogasawara Archipelago lies in the Pacific Ocean south of Honshu, Japan's largest island, and north of the Marianas Islands. The ecoregion includes the Bonin Islands and Volcano Islands chains. The islands are volcanic in origin, and have never been linked to a continent. They are home to distinct plants and animals including many endemic species.
 W
WThe Palau tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It encompasses the nation of Palau.
 W
WEaster Island is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. Easter Island is most famous for its nearly 1,000 extant monumental statues, called moai, created by the early Rapa Nui people. In 1995, UNESCO named Easter Island a World Heritage Site, with much of the island protected within Rapa Nui National Park.
 W
WThe Samoan tropical moist forests are a tropical moist broadleaf forest ecoregion in the Samoan Islands of the Pacific Ocean.
 W
WThe Society Islands tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in the Society Islands of French Polynesia.
 W
WThe Tongan tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion that includes the Tonga archipelago and Niue.
 W
WThe Tuamotu tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in the Tuamotu Archipelago of French Polynesia and the Pitcairn Islands.
 W
WThe Tubuai tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in French Polynesia. It covers the Austral Islands.
 W
WThe Western Polynesian tropical moist forests is a tropical and subtropical moist broadleaf forests ecoregion in Polynesia. It includes Tuvalu, the Phoenix Islands in Kiribati, Tokelau, and Howland and Baker islands, which are possessions of the United States.
 W
WThe Yap tropical dry forests is a tropical and subtropical dry broadleaf forests ecoregion in Micronesia. It includes the Yap Islands and neighboring atolls in the Federated States of Micronesia.