 W
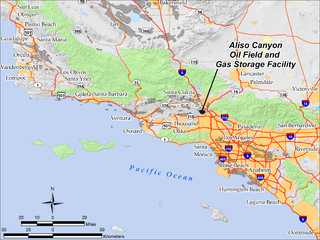
WThe Aliso Canyon Oil Field is an oil field and natural gas storage facility in the Santa Susana Mountains in Los Angeles County, California, north of the Porter Ranch neighborhood of the City of Los Angeles. Discovered in 1938 and quickly developed afterward, the field peaked as an oil producer in the 1950s, but has remained active since its discovery. One of its depleted oil and gas producing formations, the Sesnon-Frew zone, was converted into a gas storage reservoir in 1973 by the Southern California Gas Company, the gas utility servicing the southern half of California. This reservoir is the second-largest natural gas storage site in the western United States, with a capacity of over 86 billion cubic feet of natural gas. Currently it is one of four gas storage facilities owned by Southern California Gas, the others being the La Goleta Gas Field west of Santa Barbara, Honor Rancho near Newhall, and Playa del Rey.
 W
WThe Anadarko Basin is a geologic depositional and structural basin centered in the western part of the state of Oklahoma and the Texas Panhandle, and extending into southwestern Kansas and southeastern Colorado. The basin covers an area of 50,000 square miles (130,000 km2). By the end of the 20th Century, the Anadarko Basin was producing the largest amount of natural gas in the United States. Notable oil and gas fields within the basin include the Hugoton-Panhandle Gas Field, West Edmond Field, Union City Field and the Elk City Field. The basin is also the only commercial source of iodine in the United States and a major producer of helium.
 W
WThe Barnett Shale is a geological formation located in the Bend Arch-Fort Worth Basin. It consists of sedimentary rocks dating from the Mississippian period in Texas. The formation underlies the city of Fort Worth and underlies 5,000 mi² (13,000 km²) and at least 17 counties.
 W
WThe Buena Vista Oil Field, formerly the Naval Petroleum Reserve No. 2 (NPR-2) is a large oil field in Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States. Discovered in 1909, and having a cumulative production of approximately 667 million barrels (106,000,000 m3), it is the tenth-largest oil field in California. As of year end 2006 the field had a total reserve of only about one percent of its original oil, and having produced a mere 713,000 barrels (113,400 m3). Since, the field has gone through a revitalization. Crimson Resources initiated a waterflood in the Etchegoin formation, saw good response and sold the asset to Occidental Petroleum. CRC continued the development of the waterflood, but also tested the viability of the Monterey formation. The Monterey formation at Buena Vista has proven to be a viable target and is currently being developed.
 W
WOffshore oil and gas in California provides a significant portion of the state's petroleum production. Offshore oil and gas has been a contentious issue for decades, first over the question of state versus federal ownership, but since 1969 mostly over questions of resource development versus environmental protection.
 W
WThe Cymric Oil Field is a large oil field in Kern County, California in the United States. While only the 14th-largest oil field in California in total size, in terms of total remaining reserves it ranks fifth, with the equivalent of over 119 million barrels (18,900,000 m3) still in the ground. Production at Cymric has been increasing faster than at any other California oil field.
 W
WDevils Tower is a deep-water oil and gas production Spar oil platform located in the Gulf of Mexico and named after Devils Tower National Monument.
 W
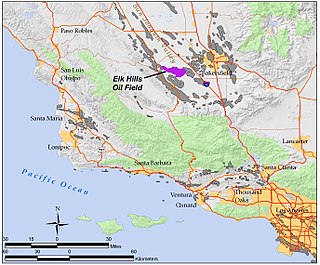
WThe Elk Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in western Kern County, in the Elk Hills of the San Joaquin Valley, California in the United States, about 20 miles (32 km) west of Bakersfield. Discovered in 1911, and having a cumulative production of close to 1.3 billion barrels (210,000 dam3) of oil at the end of 2006, it is the fifth-largest oil field in California, and the seventh-most productive field in the United States.
 W
WThe Fayetteville Shale is a geologic formation of Mississippian age composed of tight shale within the Arkoma Basin of Arkansas and Oklahoma. It is named for the city of Fayetteville, Arkansas, and requires hydraulic fracturing to release the natural gas contained within.
 W
WGreentown Oil and Gas Field is located in Grand County, approximately 26 miles (42 km) southwest of the city of Green River, Utah.
 W
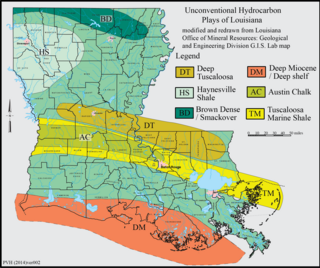
WThe Haynesville Shale is an informal, popular name for a Jurassic Period rock formation that underlies large parts of southwestern Arkansas, northwest Louisiana, and East Texas. It lies at depths of 10,500 to 13,000 feet below the land’s surface. It is part of a large rock formation which is known by geologists as the Haynesville Formation. The Haynesville Shale underlies an area of about 9,000 square miles and averages about 200 to 300 feet thick. The Haynesville Shale is overlain by sandstone of the Cotton Valley Group and underlain by limestone of the Smackover Formation.
 W
WThe Honor Rancho Oil Field is an approximately 600-acre oil field and natural gas storage facility in Los Angeles County, California, in the foothills north of Valencia, near the junction of Interstate 5 and westbound California State Route 126. Discovered in 1950 and quickly developed, the field's oil production peaked in the 1950s, but remains productive in 2016. In 1975 Southern California Gas Company (SoCalGas), the gas utility serving Southern California, began using one of its depleted oil producing zones, the Wayside 13 zone, as a gas storage reservoir, and it became the second-largest in their inventory after the Aliso Canyon gas storage facility. The field shares part of its extent with the Peter J. Pitchess Detention Center, which includes a maximum-security prison.
 W
WHugoton Gas Field is a large natural gas field in the U.S. states of Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas. Its name is derived from the town of Hugoton, Kansas, near which the Hugoton Field was first discovered.
 W
WThe Kettleman North Dome Oil Field is a large oil and gas field in Kings and Fresno counties, California. Discovered in 1928, it is the fifteenth largest field in the state by total ultimate oil recovery, and of the top twenty oil fields, it is the closest to exhaustion, with less than one-half of one percent of its original oil remaining in place.
 W
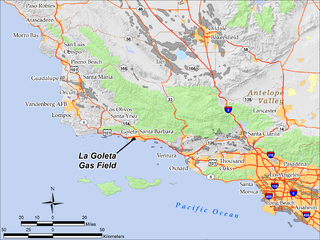
WThe La Goleta Gas Field is a natural gas field in unincorporated Santa Barbara County, California, adjacent to the city of Goleta. Discovered in 1929, and first put into production in 1932, it has been in continuous use ever since, producing approximately 12 billion cubic feet of gas. With production declining, the field was converted into a gas storage reservoir in 1941. As of 2016 it remains one of the four gas storage facilities maintained by Southern California Gas Company (SoCalGas), a division of Sempra Energy, with the others being Aliso Canyon, Honor Rancho and Playa del Rey. It is the oldest storage facility of the four and the third largest, with a maximum capacity of 21.5 billion cubic feet. The storage facilities are necessary to balance load for the over ten million customers of SoCalGas: during summer months, when gas usage is at a minimum, gas is pumped into the reservoirs; and in the winter when usage is high, gas is withdrawn. The La Goleta field serves the northern portion of SoCalGas's geographic range.
 W
WThe Lost Hills Oil Field is a large oil field in the Lost Hills Range, north of the town of Lost Hills in western Kern County, California, in the United States.
 W
WThe Marcellus natural gas trend is a large and prolific area of shale gas extraction from the Marcellus Shale or Marcellus Formation of Devonian age in the eastern United States. The shale play encompasses 104,000 square miles and stretches across Pennsylvania and West Virginia, and into eastern Ohio and western New York. In 2012, it was the largest source of natural gas in the United States, and production was still growing rapidly in 2013. The natural gas is trapped in low-permeability shale, and requires the well completion method of hydraulic fracturing to allow the gas to flow to the well bore. The surge in drilling activity in the Marcellus Shale since 2008 has generated both economic benefits and considerable controversy.
 W
WThe Marcellus Formation or the Marcellus Shale is a Middle Devonian age unit of sedimentary rock found in eastern North America. Named for a distinctive outcrop near the village of Marcellus, New York, in the United States, it extends throughout much of the Appalachian Basin.
 W
WThe North Belridge Oil Field is a large oil field along California State Route 33 in the northwestern portion of Kern County, California, about 45 miles west of Bakersfield. It is contiguous with the larger South Belridge Oil Field to the southeast, in a region of highly productive and mature fields. Discovered in 1912, it has had a cumulative production of 136,553,000 barrels (21,710,200 m3) of oil, and retains 27,443,000 barrels (4,363,100 m3) in reserve, as of the end of 2006, making it the 40th largest oil field in the state.
 W
WThe Rio Vista Gas Field is a large natural gas field in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta in northern California, adjacent to Rio Vista, California. Discovered in 1936, and in continuous operation since, it has produced over 3.6 trillion cubic feet (100 km3) of gas in its lifetime, and retains an estimated reserve of approximately 330 billion cubic feet (9.3×109 m3). In 2008 alone, the most recent year for which data was available, it produced 18 billion cubic feet (510,000,000 m3) of gas. Spanning portions of three counties and covering over 29,000 acres (120 km2), it is the largest natural gas field in California, and one of the fifteen largest in the United States.
 W
WThe South Belridge Oil Field is a large oil field in northwestern Kern County, San Joaquin Valley, California, about forty miles west of Bakersfield. Discovered in 1911, and having a cumulative production of over 1,500 million barrels (240,000,000 m3) of oil at the end of 2008, it is the fourth-largest oil field in California, after the Midway-Sunset Oil Field, Kern River Oil Field, and Wilmington Oil Field, and is the sixth-most productive field in the United States. Its estimated remaining reserves, as of the end of 2008, were around 494 million barrels (78,500,000 m3), the second-largest in the state, and it had 6,253 active wells. The principal operator on the field was Aera Energy LLC, a joint venture between Royal Dutch Shell and ExxonMobil. Additionally, the field included the only onshore wells in California owned and operated by ExxonMobil.
 W
WSquaw Canyon Oil Field is located in San Juan County, approximately 25 miles (40 km) southeast of Blanding, Utah. Production is from a northwest–southeast trending 20-foot-thick (6.1 m) carbonate buildup in the Pennsyslvanian Desert Creek. The field is part of the paradox basin that extends from the states of Colorado to Utah and New Mexico.
 W
WTin Cup Oil Field is located in San Juan County, approximately 21 miles (34 km) southeast of Blanding, Utah. Production is from a northwest–southeast trending 120-foot-thick (37 m) carbonate buildup in the Pennsylvanian Upper Ismay. The field is part of the Paradox Basin that extends from the states of Colorado to Utah and New Mexico.
 W
WThe Washington oil field is an oil field and in Washington County, Pennsylvania. It also produced natural gas.
 W
WThe Wattenberg Gas Field is a large producing area of natural gas and condensate in the Denver Basin of central Colorado, USA. Discovered in 1970, the field was one of the first places where massive hydraulic fracturing was performed routinely and successfully on thousands of wells. The field now covers more than 2,000 square miles between the cities of Denver and Greeley, and includes more than 23,000 wells producing from a number of Cretaceous formations. The bulk of the field is in Weld County, but it extends into Adams, Boulder, Broomfield, Denver, and Larimer Counties.