 W
WAtopodentatus is an extinct genus of marine reptile, possibly basal sauropterygian, known from the early Middle Triassic of Luoping County, Yunnan Province, southwestern China. It contains a single species, Atopodentatus unicus. It is thought to have lived between 247 and 240 million years ago, during the Middle Triassic period, about six million years after the Permian extinction. Atopodentatus was an herbivorous marine reptile, although marine reptiles are usually omnivores or carnivores.
 W
WBienosaurus is a dubious genus of thyreophoran dinosaur from the Lower Jurassic Lower Lufeng Formation in Yunnan Province in China.
 W
WThe Chuanjie Formation, is a geological formation in Yunnan, China. It dates back to the Middle Jurassic. It was formerly referred to as being the lower member of the "Upper Lufeng" as opposed to the underlying "Lower Lufeng" now referred to as the Lufeng Formation. Tracks of theropods and sauropods, as well as thyreophorans are known from the formation.
 W
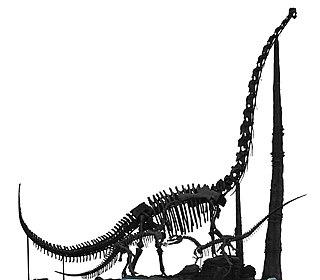
WChuanjiesaurus is a genus of sauropod dinosaurs from the middle Jurassic Period. They lived in what is now China. The type species, Chuanjiesaurus anaensis, was first described by Fang, Pang, Lü, Zhang, Pan, Wang, Li and Cheng in 2000. Fossils of the species were found in the village of Chuanjie, Lufeng County, Yunnan Province, and are named after the location where the fossils were discovered. Holtz gave a length of 25 meters.
 W
WEastmanosteus is a fossil genus of dunkleosteid placoderms. It was closely related to the giant Dunkleosteus, but differed from that genus in size, in possessing a distinctive tuberculated bone ornament, a differently shaped nuchal plate and a more zig-zagging course of the sutures of the skull roof.
 W
WThe Fengjiahe Formation is a geological formation in China. It dates back to the Early Jurassic. The formation is up to 1500 metres thick and consists of "purple-red mudstone and argillaceous siltstone interbedded with gray-green and yellow-green quartz sandstone and feldspathic quartz sandstone"
 W
WGyposaurus is a genus of basal sauropodomorph dinosaur from the early Jurassic of South Africa. It is usually considered to represent juveniles of other prosauropods, but "G." sinensis is regarded as a possibly valid species.
 W
WIrisosaurus, is an extinct genus of sauropodiform sauropodomorph dinosaur, from the Fengjiahe Formation of China. The type species, Irisosaurus yimenensis was formally described in 2020. It was the sister taxon to Mussaurus.
 W
WJingshanosaurus is a genus of sauropodomorph dinosaurs from the early Jurassic period.
 W
WJiuchengia longoccipita is a coccosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Emsian epoch of Wuding, Yunnan.
 W
WThe Lufeng Formation is a Lower Jurassic sedimentary rock formation found in Yunnan, China. It has two units: the lower Dull Purplish Beds/Shawan Member are of Hettangian age, and Dark Red Beds/Zhangjia'ao Member are of Sinemurian age. It is known for its fossils of early dinosaurs. The Dull Purplish Beds have yielded the possible therizinosaur Eshanosaurus, the possible theropod Lukousaurus, and the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus" sinensis, Lufengosaurus, Jingshanosaurus, and Yunnanosaurus. Dinosaurs discovered in the Dark Red Beds include the theropod Sinosaurus triassicus, the "prosauropods" "Gyposaurus", Lufengosaurus, and Yunnanosaurus, indeterminate remains of sauropods, and the early armored dinosaurs Bienosaurus and Tatisaurus.
 W
WLufengosaurus is a genus of massospondylid dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic period in what is now southwestern China. The dinosaur made international headlines in 2017 when Nature Communications reported scientists' discovery of 195-million-year-old collagen protein in the rib of a Lufengosarus fossil.
 W
WLyrarapax is a radiodont of the family Amplectobeluidae that lived in the early Cambrian period 520 million years ago. Its neural tissue indicates that the anomalocaridid frontal appendage is protocerebral, resolving parts of the arthropod head problem and showing that the frontal appendage is homologous to the antennae of Onychophorans and labrum of euarthropods. Its fossilized remains were found in Yunnan in southwestern China. A second species was described in 2016, differing principally in the morphology of its frontal appendages.
 W
WNebulasaurus is an extinct genus of basal eusauropod dinosaur known from the early Middle Jurassic Zhanghe Formation of Yunnan Province, China. It is known only from the holotype braincase LDRC-v.d.1. A phylogenetic analysis found Nebulasaurus to be a sister taxon to Spinophorosaurus from the Middle Jurassic of Africa. This discovery is significant paleontologically because it represents a clade of basal eusauropods previously unknown from Asia.
 W
WPsilophyton is a genus of extinct vascular plants. Described in 1859, it was one of the first fossil plants to be found which was of Devonian age. Specimens have been found in northern Maine, USA; Gaspé Bay, Quebec and New Brunswick, Canada; the Czech Republic; and Yunnan, China. Plants lacked leaves or true roots; spore-forming organs or sporangia were borne on the ends of branched clusters. It is significantly more complex than some other plants of comparable age and is thought to be part of the group from within which the modern ferns and seed plants evolved.
 W
WQilinyu rostrata is a "maxillate" placoderm from the late Ludlow epoch of Qujing, Yunnan, 419 million years ago.
 W
WSinosaurus was a tetanuran theropod dinosaur which lived during the Early Jurassic Period. It was a bipedal carnivore approximately 5.6 metres in length. Fossils of the animal were found at the Lufeng Formation, in the Yunnan Province of China.
 W
WTatisaurus is a genus of ornithischian dinosaur from the Early Jurassic from the Lower Lufeng Formation in Yunnan Province in China. Little is known as the remains are fragmentary. The type species is T. oehleri.
 W
WXiangshuiosteus wui is a brachythoracid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Emsian epoch of Wuding, Yunnan. It has recently been reassessed as a dunkleosteid.
 W
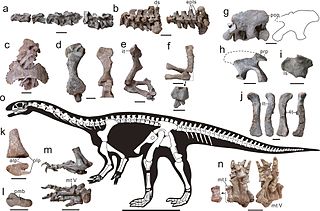
WXingxiulong is a genus of bipedal sauropodiform from the Early Jurassic of China. It contains a single species, X. chengi, described by Wang et al. in 2017 from three specimens, two adults and an immature individual, that collectively constitute a mostly complete skeleton. Adults of the genus measured 4–5 metres (13–16 ft) long and 1–1.5 metres tall. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that Xingxiulong is most closely related to its contemporary Jingshanosaurus, although an alternative position outside of both the Sauropodiformes and Massospondylidae is also plausible.
 W
WYizhousaurus is a genus of basal sauropodiform dinosaurs which existed in what is now Lufeng Formation, Yunnan Province of southern China during the lower Jurassic period. Identified from a nearly complete and exquisitely preserved skeleton, it is the most complete basal sauropod currently known with intact skull. Although its name was revealed in a 2010 Geological Society of America abstract by Sankar Chatterjee, T. Wang, S.G. Pan, Z. Dong, X.C. Wu, and Paul Upchurch, it wasn't validly named and described until 2018. The type species is Yizhousaurus sunae.
 W
WYunnanolepis is an extinct genus of primitive antiarch placoderm. The fossils of the various species are found in Early to Middle Devonian strata in Southern China.
 W
WYunnanosaurus is an extinct genus of sauropodomorph dinosaur that lived approximately 201 to 168 million years ago in what is now the Yunnan Province, in China, for which it was named. Yunnanosaurus was a large sized, moderately-built, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal herbivore, that could also walk bipedally, and ranged in size from 7 meters (23 feet) long and 2 m (6.5 ft) high to 4 m (13 ft) high in the largest species.