 W
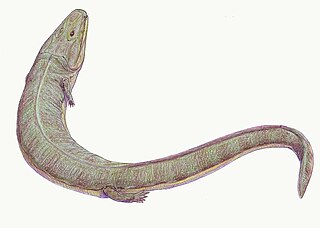
WAcherontiscus is an extinct genus of stegocephalians that lived in the Early Carboniferous of Scotland. The type and only species is Acherontiscus caledoniae, named by paleontologist Robert Carroll in 1969. Members of this genus have an unusual combination of features which makes their placement within amphibian-grade tetrapods uncertain. They possess multi-bone vertebrae similar to those of embolomeres, but also a skull similar to lepospondyls. The only known specimen of Acherontiscus possessed an elongated body similar to that of a snake or eel. No limbs were preserved, and evidence for their presence in close relatives of Acherontiscus is dubious at best. Phylogenetic analyses created by Marcello Ruta and other paleontologists in the 2000s indicate that Acherontiscus is part of Adelospondyli, closely related to other snake-like animals such as Adelogyrinus and Dolichopareias. Adelospondyls are traditionally placed within the group Lepospondyli due to their fused vertebrae. Some analyses published since 2007 have argued that adelospondyls such as Acherontiscus may not actually be lepospondyls, instead being close relatives or members of the family Colosteidae. This would indicate that they evolved prior to the split between the tetrapod lineage that leads to reptiles (Reptiliomorpha) and the one that leads to modern amphibians (Batrachomorpha). Members of this genus were probably aquatic animals that were able to swim using snake-like movements.
 W
WAndescynodon is a genus of traversodontid cynodonts from the Middle Triassic of Argentina. Fossils are known from the Cerro de las Cabras and Cacheutá Formations. Andescynodon is one of the most basal traversodontids. Another traversodontid called Rusconiodon has also been identified from the Cerro de las Cabras Formation but is now considered a junior synonym of Andescynodon.
 W
WBauruemys is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Podocnemididae.
 W
WBauruemys is an extinct genus of turtles in the family Podocnemididae.
 W
WCoelophysis rhodesiensis is an extinct species of coelophysid theropod dinosaur that lived approximately 188 million years ago during the early part of the Jurassic Period in what is now Africa. The species was a small to medium-sized, lightly built, ground-dwelling, bipedal carnivore, that could grow up to 3 m (9.8 ft) long. It was originally given the genus name Syntarsus, but that name was later determined to be preoccupied by a beetle. The species was subsequently given a new genus name, Megapnosaurus, by Ivie, Ślipiński & Węgrzynowicz in 2001. Many subsequent studies have classified it as a species within the genus Coelophysis.
 W
WColoraderpeton is an extinct genus of aïstopod lepospondyl within the family Oestocephalidae. Coloraderpeton is known from the Carboniferous Sangre de Cristo Formation of Colorado, and was initially known from vertebrae, ribs, and scales recovered from a UCLA field expedition in 1966. Peter Paul Vaughn described these remains in 1969. A skull was later reported in an unpublished 1983 thesis and formally described by Jason S. Anderson in 2003.
 W
WDeinonychus is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur with one described species, Deinonychus antirrhopus. This species, which could grow up to 3.4 meters (11 ft) long, lived during the early Cretaceous Period, about 115–108 million years ago. Fossils have been recovered from the U.S. states of Montana, Utah, Wyoming, and Oklahoma, in rocks of the Cloverly Formation, Cedar Mountain Formation and Antlers Formation, though teeth that may belong to Deinonychus have been found much farther east in Maryland.
 W
WDeinonychus is a genus of dromaeosaurid theropod dinosaur with one described species, Deinonychus antirrhopus. This species, which could grow up to 3.4 meters (11 ft) long, lived during the early Cretaceous Period, about 115–108 million years ago. Fossils have been recovered from the U.S. states of Montana, Utah, Wyoming, and Oklahoma, in rocks of the Cloverly Formation, Cedar Mountain Formation and Antlers Formation, though teeth that may belong to Deinonychus have been found much farther east in Maryland.
 W
WGreererpeton burkemorani is an extinct genus of colosteid stem-tetrapods from the Early Carboniferous period of North America. Greererpeton was first described by famed vertebrate paleontologist Alfred S. Romer in 1969. The skull was redescribed by Timothy R. Smithson in 1982, while postcranial remains were redescribed by Stephen J. Godfrey in 1989.
 W
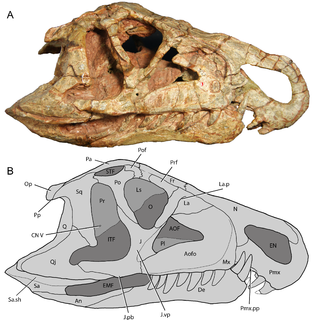
WHyperodapedontinae is a subfamily of rhynchosaurs within the family Hyperodapedontidae. Fossils have been found from Argentina, Brasil, Canada, India, Madagascar, Scotland, Tanzania, United States and Zimbabwe.
 W
WKallidecthes is an extinct genus of crustaceans.
 W
WMesaceratherium is an extinct genus of rhinoceros.
 W
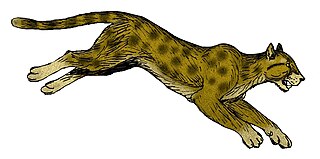
WThe American cheetah is either of two feline species of the extinct genus Miracinonyx, endemic to North America during the Pleistocene epoch and morphologically similar to the modern cheetah. These cats were originally known from fragments of skeletons, but nearly complete skeletons have been recovered from Natural Trap Cave in northern Wyoming.
 W
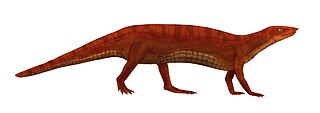
WNeoaetosauroides is an extinct genus of primitive aetosaur. Its type and only species is N. engaeus. Fossils have been found in Los Colorados Formation outcropping along the Sierra Morada River in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in La Rioja, Argentina, and date back to the Norian age of the Late Triassic. It was the first aetosaur known from the formation, with remains being discovered in the 1960s.
 W
WPaleothyris was a small, agile, anapsid romeriidan reptile which lived in the Middle Pennsylvanian epoch in Nova Scotia. Paleothyris had sharp teeth and large eyes, meaning that it was a nocturnal hunter. It was about a foot long. It probably fed on insects and other smaller animals found on the floor of its forest home. The reason that they were able to do this and hunt so well was not only due to the fact that they hunted in the dark, but because they had a long head structure which helped them catch small, quicker prey. Paleothyris was an early sauropsid, yet it still had some features that were more primitive, more labyrinthodont-like than reptile-like, especially its skull, which lacked fenestrae, holes found in the skulls of most modern reptiles and mammals.
 W
WParacolobus is an extinct genus of primate in the Colobini tribe, which also contains the living colobus monkeys. It lived in eastern Africa in the early to late Pliocene.
 W
WPseudhesperosuchus is a genus of sphenosuchian, a type of basal crocodylomorph, the clade that comprises the crocodilians and their closest kin. It is known from a partial skeleton and skull found in rocks of the Late Triassic (Norian-age) Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.
 W
WPterodaustro is a genus of ctenochasmatid pterodactyloid pterosaur from South America. Its fossil remains dated back to the Early Cretaceous period, about 105 million years ago. The most distinctive characteristic that separates Pterodaustro from other ctenochasmatids is its bristle-like teeth, a feature not seen in any other pterosaur.
 W
WRiojasaurus was a herbivorous sauropodomorph dinosaur named after La Rioja Province in Argentina where it was found in the Los Colorados Formation in the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin by José Bonaparte. It lived during the Late Triassic and grew to about 10 metres (33 ft) long. Riojasaurus is the only known riojasaurid to live in South America.
 W
WRiojasuchus is an extinct genus of Late Triassic (Norian) quadrupedal crurotarsan archosaur. Riojasuchus is a member of Ornithosuchidae, a family of facultatively bipedal carnivores that were geographically widespread during the Late Triassic. Two other genera, Ornithosuchus and Venaticosuchus, are currently known. The holotype specimen is PVL 3827. It was found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina.
 W
WVictoriapithecus macinnesi was a primate. It was described from a single fossil specimen, the oldest Old World monkey skull fossil. It was discovered near Lake Victoria in Kenya by Dr. Brenda Benefit. It dates from the middle Miocene and was closely related to the two or three extinct Prohylobates species.
 W
WWillwerathia is a genus of synziphosurine, a paraphyletic group of horseshoe crab-like fossil chelicerate arthropods. Willwerathia known only by one species, Willwerathia laticeps, discovered in deposits of the Devonian period from the Rhenish Slate Mountains of Germany.