 W
WThe Mesolithic is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymously, especially for outside northern Europe, and for the corresponding period in the Levant and Caucasus. The Mesolithic has different time spans in different parts of Eurasia. It refers to the final period of hunter-gatherer cultures in Europe and Western Asia, between the end of the Last Glacial Maximum and the Neolithic Revolution. In Europe it spans roughly 15,000 to 5,000 BP; in Southwest Asia roughly 20,000 to 8,000 BP. The term is less used of areas further east, and not at all beyond Eurasia and North Africa.
 W
WA Bann flake is a large, butt-trimmed, leaf-shaped lithic blade of flint or chert, dating from the Late Mesolithic period of prehistoric Ireland, from around 4500 BC onwards. They are named after the river Bann in Northern Ireland where large numbers have been found. The term is rather variably defined, and the uses of the flakes probably varied considerably, with many being all-purpose tools, and perhaps weapons. Some were probably used as spear heads attached to wooden shafts, despite many being rather heavy for this.
 W
WBouldnor Cliff is a submerged prehistoric settlement site in the Solent. The site dates from the Mesolithic era and is in approximately 11 metres (12 yd) of water just offshore of the village of Bouldnor on the Isle of Wight in the United Kingdom. The preservation of organic materials from this era that do not normally survive on dry land has made Bouldnor important to the understanding of Mesolithic Britain, and the BBC Radio 4's Making History programme described it "probably Europe's most important Mesolithic site" albeit concealed under water.
 W
WCaucasus hunter-gatherer (CHG), also called Satsurblia Cluster is an anatomically modern human genetic lineage, first identified in a 2015 study, based on the population genetics of several modern Western Eurasian populations. CHG ancestry was also found in an Upper Palaeolithic specimen from Satsurblia cave, and in a Mesolithic one from Kotias Klde cave, in western Georgia.
 W
WThe Cuevas de la Araña are a group of caves in the municipality of Bicorp in Valencia, eastern Spain. The caves are in the valley of the river Escalona and were used by prehistoric people who left rock art. They are known for painted images of a bow and arrow goat hunt and for a scene depicting a human figure.
 W
WThe Duvensee archaeological sites are a series of early Mesolithic archaeological sites that are located within the Duvensee bog near Duvensee in Schleswig Holstein, Germany. The bog is one of the oldest and well-researched archaeological settlement areas from the early Holocene in Central Europe. The archaeological sites are renowned for their well-preserved organic remains and are of great importance in understanding the subsistence and settlement strategies of post-glacial hunter-gatherer societies. Recent research has explored the Duvensee societies' diet and land use patterns in relation to the evolution of modern lifestyles and nutrition.
 W
WThe Duvensee paddles is the preserved part of a Mesolithic spade paddle, which was found during archaeological excavations of a Mesolithic dwelling area at Duvensee near Klinkrade Schleswig-Holstein, Germany in 1926. After a paddle from Star Carr in England, the Duvensee paddle is the second oldest known paddle and is considered among the earliest evidence for the use of water transport in the Mesolithic. The find is in the permanent exhibition of the Archaeological Museum Hamburg in Harburg, Hamburg.
 W
WDoggerland was an area of land, now submerged beneath the southern North Sea, that connected Great Britain to continental Europe. It was flooded by rising sea levels around 6500–6200 BC. Geological surveys have suggested that it stretched from where Great Britain's east coast now is to the present-day Netherlands, western coast of Germany, and peninsula of Jutland. It was probably a rich habitat with human habitation in the Mesolithic period, although rising sea levels gradually reduced it to low-lying islands before its final submergence, possibly following a tsunami caused by the Storegga Slide.
 W
WElk's Head of Huittinen is a Mesolithic moose head figurine of soapstone found in 1903 from Huittinen in the province of Satakunta, Finland. The sculpture is dated to between 8,000 and 9,000 years ago. It is placed in the permanent exhibition of National Museum of Finland in Helsinki. Replicas are displayed in the Museum of Huittinen and in the sculpture collection of University of Helsinki. Elk's Head is most likely the best-known archaeological artifact in Finland.
 W
WA Giant's Church is the name given to prehistoric stone enclosures found in the Ostrobothnia region of Finland. Dating from the sub-Neolithic period, they are thought to be a rare example of monumental architecture built by hunter-gatherers in northern Europe.
 W
WThe Howick house is a Mesolithic site located in Northumberland, England. It was found when an amateur archaeologist noticed flint tools eroding out of a sandy cliff face near the village of Howick. Investigations found a circle of substantial post holes with charcoal stains in their bases, a number of smaller stake holes, some angled in from outside a hollow, and inside the house a number of shallow hearths filled with charcoal, burnt nutshells and some fragments of bone. Radiocarbon dating of the charred hazelnut shells established that the building was constructed about 7600 BC and occupied for about 100 years, which led to the find being called "Britain's oldest house". This title was disputed in 2010 when the discovery of the even older 'house-structure' at Star Carr in North Yorkshire was announced.
 W
WEvidence of human activity during the Mesolithic period in Irish history has been found in excavations at the Mount Sandel Mesolithic site in the north of the island, cremations on the banks of the River Shannon in the west, campsites at Lough Boora in the midlands, and middens and other sites elsewhere in the country.
 W
WKamyana Mohyla is an archaeological site in the Molochna River valley, about a mile from the village of Terpinnya, Zaporizhzhia Oblast, Ukraine. Petroglyphs of Kamyana Mohyla are dated from Upper Paleolithic to Medieval, with Stone Age depictions subjected to most archaeological interest.
 W
WLepenski Vir, located in Serbia, is an important archaeological site of the Mesolithic Iron Gates culture of the Balkans. The latest radiocarbon and AMS data suggests that the chronology of Lepenski Vir is compressed between 9500/7200–6000 BC. There is some disagreement about the early start of the settlement and culture of Lepenski Vir, but the latest data suggest 9500–7200 to be the start. The late Lepenski Vir architectural development was the development of the trapezoidal buildings and monumental sculpture. The Lepenski Vir site consists of one large settlement with around ten satellite villages. Numerous piscine sculptures and peculiar architecture have been found at the site.
 W
WThe Loschbour man is a skeleton of Homo sapiens from the European Mesolithic discovered in 1935 in Mullerthal, in the commune of Waldbillig, Luxembourg.
 W
WThe Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is in Coleraine, County Londonderry, Northern Ireland, just to the east of the Iron Age Mount Sandel Fort. It is one of the oldest archaeological sites in Ireland with carbon dating indicating an age of 9,000 years old (7,000BC). Gwendoline Cave, County Clare is the only site in Ireland with evidence of human occupation which pre-dates this location. Mount Sandel Mesolithic site is a Scheduled Historic Monument in the townland of Mount Sandel, in Coleraine Borough Council area, at Grid Ref: C8533 3076. It was excavated by Peter Woodman in the 1970s.
 W
WThe group of over 700 sites of prehistoric Rock art of the Iberian Mediterranean Basin, also known as Levantine art, were collectively declared a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1998. The sites are in the eastern part of Spain and contain rock art dating to the Upper Paleolithic or Mesolithic periods of the Stone Age. The art consists of small painted figures of humans and animals, which are the most advanced and widespread surviving from this period, certainly in Europe, and arguably in the world, at least in the earlier works. It is notable for the number of places included, the largest concentration of such art in Europe. Its name refers to the Mediterranean Basin; however, while some sites are located near the sea, many of them are inland in Aragon and Castilla–La Mancha; it is also often referred to as Levantine Art.
 W
WStar Carr is a Mesolithic archaeological site in North Yorkshire, England. It is around five miles (8 km) south of Scarborough. It is generally regarded as the most important and informative Mesolithic site in Great Britain. It is as important to the Mesolithic period as Stonehenge is to the Neolithic period or Scandinavian York is to understanding Viking Age Britain.
 W
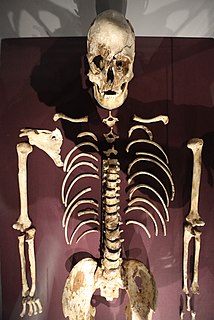
WTéviec or Théviec is an island situated to the west of the isthmus of the peninsula of Quiberon, near Saint-Pierre-Quiberon in Brittany, France. The island is an important archaeological site due to its occupation during the Mesolithic period. Many archaeological finds have been made dating back to over 6,700 years before the present day, including the remains of over 20 people. One of the most remarkable finds was that of the grave of two young women who had apparently died violently but had received an elaborate burial under a "roof" of antlers, their bodies decorated with jewellery made from shells.
 W
WIn archaeogenetics, the term Western Hunter-Gatherer, West European Hunter-Gatherer or Western European Hunter-Gatherer, is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent from Mesolithic hunter-gatherers of Western, Southern and Central Europe. The term is often abbreviated as WHG. During the Mesolithic, the WHGs inhabited an area stretching from the British Isles in the west to the Carpathians in the east.
 W
WIn many areas of Scandinavia, a wide variety of items were deposited in lakes and bogs from the Mesolithic period through to the Middle Ages. Such items include earthenware, decorative metalwork, weapons, and human corpses, known as bog bodies. As Kaul noted, "we cannot get away from the fact that the depositions in the bogs were connected with the ritual/religious sphere."