 W
WThe history of Sicily has been influenced by numerous ethnic groups. It has seen Sicily sometimes controlled by external powers – Phoenician and Carthaginian, Greek, Roman, Vandal and Ostrogoth, Byzantine Greek, Islamic, Norman, Aragonese and Spanish – but also experiencing important periods of independence, as under the indigenous Sicanians, Elymians and Sicels, and later as the County of Sicily and Kingdom of Sicily. The Kingdom was founded in 1130 by Roger II, belonging to the Siculo-Norman family of Hauteville. During this period, Sicily was prosperous and politically powerful, becoming one of the wealthiest states in all of Europe. As a result of the dynastic succession, then, the Kingdom passed into the hands of the Hohenstaufen. At the end of the 13th century, with the War of the Sicilian Vespers between the crowns of Anjou and Aragon, the island passed to the latter. In the following centuries the Kingdom entered into the personal union with the Spaniard and Bourbon crowns, preserving however its substantial independence until 1816. Although today an Autonomous Region of the Republic of Italy, it has its own distinct culture.
 W
WThe 1669 eruption of Mount Etna is the largest-recorded historical eruption of the volcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy. After several weeks of increasing seismic activity that damaged the town of Nicolosi and other settlements, an eruption fissure opened on the southeastern flank of Etna during the night of 10-11 March. Several more fissures became active during 11 March, erupting pyroclastics and tephra that fell over Sicily and accumulated to form the Monti Rossi scoria cone.
 W
WThe Dictatorship of Garibaldi was the provisional executive that Giuseppe Garibaldi appointed to govern the territory of Sicily during the Expedition of the Thousand in 1860. It governed in opposition to the Bourbons of Naples.
 W
WDwarf elephants are prehistoric members of the order Proboscidea which, through the process of allopatric speciation on islands, evolved much smaller body sizes in comparison with their immediate ancestors. Dwarf elephants are an example of insular dwarfism, the phenomenon whereby large terrestrial vertebrates that colonize islands evolve dwarf forms, a phenomenon attributed to adaptation to resource-poor environments and selection for early maturation and reproduction. Some modern populations of Asian elephants have also undergone size reduction on islands to a lesser degree, resulting in populations of pygmy elephants.
 W
WThe Fasci Siciliani [ˈfaʃʃi sitʃiˈljani], short for Fasci Siciliani dei Lavoratori, were a popular movement of democratic and socialist inspiration, which arose in Sicily in the years between 1889 and 1894. The Fasci gained the support of the poorest and most exploited classes of the island by channeling their frustration and discontent into a coherent programme based on the establishment of new rights. Consisting of a jumble of traditionalist sentiment, religiosity, and socialist consciousness, the movement reached its apex in the summer of 1893, when new conditions were presented to the landowners and mine owners of Sicily concerning the renewal of sharecropping and rental contracts.
 W
W«Panormus conca aurea suos devorat alienos nutrit» (Palermo the golden dell, devours hers and feeds the foreigners. Latin inscription on the edge of the basin of the Genius statue at City Hall of Palermo.)
 W
WThe history of Islam in Sicily and Southern Italy began with the first Arab settlement in Sicily, at Mazara, which was captured in 827. The subsequent rule of Sicily and Malta started in the 10th century. The Emirate of Sicily lasted from 831 until 1061, and controlled the whole island by 902. Though Sicily was the primary Muslim stronghold in Italy, some temporary footholds, the most substantial of which was the port city of Bari, were established on the mainland peninsula, especially in mainland Southern Italy, though Muslim raids, mainly those of Muhammad I ibn al-Aghlab, reached as far north as Naples, Rome and the northern region of Piedmont. The Muslim raids were part of a larger struggle for power in Italy and Europe, with Christian Byzantine, Frankish, Norman and local Italian forces also competing for control. Muslims were sometimes sought as allies by various Christian factions against other factions.
 W
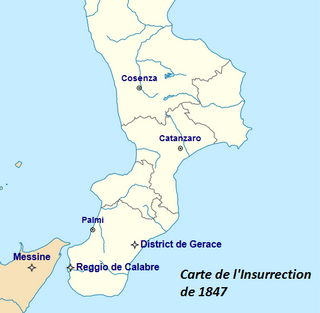
WThe Insurrection of 1847 in the Two Sicilies is a series of three revolts that happened in September 1847 in the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies. Its aim was the unification of Italy and the establishment of either a constitutional monarchy or a republic. The insurrection is often considered as a continuation of the Neapolitan revolution of 1820 and at the same time as a foretaste of the Sicilian revolution of 1848 and of the spring of nations.
 W
WThe Kingdom of Sicily was a state that existed in the south of the Italian peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 until 1816. It was a successor state of the County of Sicily, which had been founded in 1071 during the Norman conquest of the southern peninsula. The island was divided into three regions: Val di Mazara, Val Demone and Val di Noto; val being the apocopic form of the word vallo, derived from the Arabic word wilāya.
 W
WThe Kingdom of the Two Sicilies was a kingdom located in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy prior to Italian unification, comprising Sicily and all of the peninsula of Italy south of the Papal States, covering most of the area of today's Mezzogiorno.
 W
WVincenzo Mirabella Alagona was an Italian historian, archaeologist and architect, best known for his work Plans of Ancient Syracuse.
 W
WThe County of Modica was a feudal territory within the Kingdom of Sicily from 1296 to 1812. Its capital was Modica, on the southern tip of the island, although the cities of Ragusa and Scicli housed some government offices for a period. Today it perpetuates as a title only held by the head of the House of Alba, Carlos Fitz-James Stuart, 19th Duke of Alba.
 W
WThe Movement for the Independence of Sicily was a separatist Sicilian political party originally active in Sicily from 1943 to 1951. Its best electoral result was in 1947, when it won 8.8% of the votes in the Sicilian regional election and had nine regional deputies elected. The goal of the party was the annexation of Sicily to the United States.
 W
WThe Pizzolungo Bombing was a car-bomb attack on 2 April 1985 undertaken by the Sicilian Mafia in order to kill Carlo Palermo, a magistrate in Pizzolungo, Sicily. Palermo had been investigating an international drug and arms trafficking network in which Italian politicians may have been involved. Palermo was injured in the attack and three passersby were killed: Barbara Rizzo and her young twin sons, Salvatore and Giuseppe Asta.
 W
WPhilip of Naples and Sicily, "Duke of Calabria", Infante of Spain was the eldest son and heir-apparent of Charles III of Spain, but was excluded from the succession to the thrones of Spain and Naples due to his imbecility. His younger brothers, Charles IV of Spain and Ferdinand I of the Two Sicilies replaced him in the succession. When his father became King of Spain in 1759, Philip remained in Naples where he lived until his death from smallpox at the age of thirty.
 W
WSicilian Baroque is the distinctive form of Baroque architecture which evolved on the island of Sicily, off the southern coast of Italy, in the 17th and 18th centuries, when it was part of the Spanish Empire. The style is recognisable not only by its typical Baroque curves and flourishes, but also by its grinning masks and putti and a particular flamboyance that has given Sicily a unique architectural identity.
 W
WThe Sicilian revolution of independence of 1848 occurred in a year replete with revolutions and popular revolts. It commenced on 12 January 1848, and therefore was the first of the numerous revolutions to occur that year. Three revolutions against Bourbon rule had previously occurred on the island of Sicily starting from 1800: this final one resulted in an independent state surviving for 16 months. The constitution that survived the 16 months was quite advanced for its time in liberal democratic terms, as was the proposal of an Italian confederation of states. It was in effect a curtain raiser to the end of the Bourbon kingdom of the Two Sicilies which was started by Giuseppe Garibaldi's Expedition of the Thousand in 1860 and culminated with the Siege of Gaeta of 1860–1861.
 W
WIn Italy, there are some active movements and parties calling for autonomy or even independence for the areas comprised within the historical Kingdom of the two Sicilies: that is, Southern Italy and/or the region of Sicily. No political movement promoting these ideas has ever been successful in gaining traction among the population. The movement remains on the fringes with no representation in the Italian parliament.
 W
WThe Targa Florio was an open road endurance automobile race held in the mountains of Sicily near the island's capital of Palermo. Founded in 1906, it was the oldest sports car racing event, part of the World Sportscar Championship between 1955 and 1973. While the first races consisted of a whole tour of the island, the track length in the race's last decades was limited to the 72 kilometres (45 mi) of the Circuito Piccolo delle Madonie, which was lapped 11 times.
 W
WThe Tercio of Sicily is one of the tercios that were created by a 1534 decree of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor. Since the 18th century, the Spanish army has maintained the tradition of this tercio in its regiments.