 W
WCassinoceras is a genus of nautiloids belonging to the endocerid family Piloceratidae that comes from the late Early Ordovician of eastern North America and adjacent territories.
 W
WChiniquodon is an extinct genus of carnivorous cynodonts, which lived during the Late Triassic (Carnian) in South America and Africa. Chiniquodon is closely related to a contemporary genus, Probelesodon, and close to the ancestry of mammals.
 W
WClimacoceras is a genus of extinct artiodactyl ungulates that lived in Africa and Europe during the Miocene. The members of Climacoceras were related to giraffes, and the genus was formerly placed within the Giraffidae, but is now placed in the Climacoceratidae, a sister group within the superfamily Giraffoidea. Fossils of the two best known species of Climacoceras, C. africanus and C. gentryi, have both been found in Kenya. The animals measured about 1.5 m (4.9 ft) tall and had large ossicones resembling antlers. C. africanus had ossicones resembling tall, thorn-covered plant stems, while the ossicones of C. gentryi resembled thorny crescents.
 W
WCorosaurus is an extinct genus of pistosauroid known from Wyoming of the United States.
 W
WCtenospondylus is an extinct genus of sphenacodontid basal Eupelycosauria.
 W
WDinogorgon is a genus of gorgonopsid from the Late Permian of South Africa and Tanzania. The generic name Dinogorgon is derived from Greek, meaning "terrible gorgon", while its species name rubidgei is taken from the surname of renowned Karoo paleontologist, Professor Bruce Rubidge, who has contributed to much of the research conducted on therapsids of the Karoo Basin. The type species of the genus is D. rubidgei.
 W
WHarrington's mountain goat was a species of North American caprine that resided in the Southwest of the continent during the Pleistocene epoch. A relative of the modern mountain goat, which is the only existing species in the genus Oreamnos, O. harringtoni became extinct around 11,000 B.C.
 W
WHenodus is an extinct placodont of the Late Triassic period during the early Carnian age. Fossils of Henodus chelyops were found in Tübingen, Germany. It was around 1 metre (3.3 ft) in length. The single species within the genus is H. chelyops.
 W
WNanoparia is an extinct genus of pareiasaur that lived in the Permian.
 W
WNipponosaurus is a lambeosaurine hadrosaur from sediments of the Yezo Group, Sinegorsk, Sakhalin Island in Russia, part of Japan at the time of naming. The type and only species is N. sachalinensis, known only from a single juvenile specimen discovered in 1934 and named in 1936, by Takumi Nagao, with further material of the same individual found in 1937. Since then, the taxon has been largely ignored, and its validity has been doubted, with synonymy with other Asian hadrosaurs or status as a nomen dubium being suggested. Redescriptions from 2004 and 2017, however, have supported recognition as a distinct species. Dating the only specimen has been difficult, but based on associated mollusc taxa, the species likely lived sometime in the upper Santonian or lower Campanian, around 80 million years ago.
 W
WPediomeryx is an extinct genus of artiodactyl, of the family Palaeomerycidae, endemic to North America. It lived during the Late Miocene 10.3—4.9 Ma, existing for approximately 5 million years . Fossils have been recovered from the Midway Site in Florida, Saskatchewan, Boron, California, and several sites in Nebraska and Wyoming.
 W
WRana basaltica is an extinct species of frog from Middle Miocene of China. It is known from the Shanwang formation beds in the Shanwang National Geological Park, Shandong Province, China.
 W
WRhenopterus is an extinct prehistoric eurypterid. Fossils of Rhenopterus have been recovered from deposits of Lower Devonian age in Germany.
 W
WRoxochampsa is an extinct genus of crocodylomorph from the Late Cretaceous of Brazil belonging to the sebecosuchian clade Itasuchidae. The type species is R. paulistanus.
 W
WSecodontosaurus is an extinct genus of "pelycosaur" synapsids that lived from between about 285 to 272 million years ago during the Early Permian. Like the well known Dimetrodon, Secodontosaurus is a carnivorous member of the Eupelycosauria family Sphenacodontidae and has a similar tall dorsal sail. However, its skull is long, low, and narrow, with slender jaws that have teeth that are very similar in size and shape—unlike the shorter, deep skull of Dimetrodon, which has large, prominent canine-like teeth in front and smaller slicing teeth further back in its jaws. Its unusual long, narrow jaws suggest that Secodontosaurus may have been specialized for catching fish or for hunting prey that lived or hid in burrows or crevices. Although no complete skeletons are currently known, Secodontosaurus likely ranged from about 2 to 2.7 metres (7–9 ft) in length, weighing up to 110 kilograms (250 lb).
 W
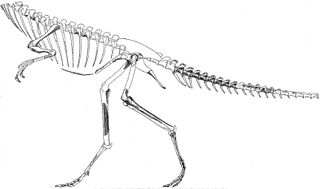
WSegisaurus is a genus of small coelophysoid theropod dinosaur, that measured approximately 1 metre in length. The only known specimen was discovered in early Jurassic strata in Tsegi Canyon, Arizona, for which it was named. Segisaurus is the only dinosaur to have ever been excavated from the area.
 W
WTraversodon is an extinct genus of cynodonts. It was a relative of the direct ancestor to modern mammals.
 W
WTriadobatrachus is an extinct genus of salientian frog-like amphibians, including only one known species, Triadobatrachus massinoti. It is the oldest member of the frog lineage known, and an excellent example of a transitional fossil. It lived during the Early Triassic about 250 million years ago, in what is now Madagascar.
 W
WYunnanocephalus is a genus of ptychopariid trilobite. It lived during the late Atdabanian and Botomian stages, in what are currently Antarctica, Australia and China. It was a "moderately common" member of the Chengjiang Fauna. Yunnanocephalus is the only genus currently assigned to the Yunnanocephalidae family.