 W
WA vertical datum or height datum is a reference surface for vertical positions, such as the elevations of Earth features including terrain, bathymetry, water level, and man-made structures; in any particular case one must be assigned even if arbitrarily, and commonly adopted criteria for a vertical datum include the following approaches:Tidal, based on sea level when specific conditions occur, such as NOAA's National Geodetic Survey-produced Tidal Datums; Gravimetric, based on a geoid; or geodetic, based on the same ellipsoid models of the Earth that are used in computing a horizontal datum, such as NOAA's planned gravimetric and Global Navigation Satellite Systems (GNSS)-based Datum of 2022 set to be released that year by the National Geodetic Survey.
 W
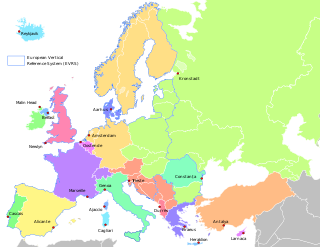
WAmsterdam Ordnance Datum or Normaal Amsterdams Peil (NAP) is a vertical datum in use in large parts of Western Europe. Originally created for use in the Netherlands, its height was used by Prussia in 1879 for defining Normalnull, and in 1955 by other European countries. In the 1990s, it was used as the reference level for the United European leveling Network (UELN) which in turn led to the European Vertical Reference System (EVRS).
 W
WThe Australian Height Datum was introduced in 1971 as the official vertical datum for Australia, and thereby serves as the benchmark for which all height measurements are referenced to. The Australian Height Datum is an amalgamation of decades of spirit levelling work conducted by numerous state and territory authorities across the country, and was corrected to align with the mean sea level observations of thirty tide gauges positioned around the entire coastline. While it still remains the published vertical datum for all surveying and engineering operations performed throughout Australia, newer technologies have uncovered numerous deficiencies, offsets and distortions within the Australian Height Datum, leading to discussions about defining a new Australian vertical datum.
 W
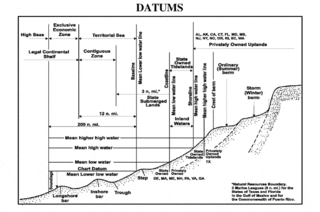
WA chart datum is the water level that depths displayed on a nautical chart are measured from. A chart datum is generally derived from some phase of the tide. Common chart datums are lowest astronomical tide and mean lower low water. In non-tidal areas, e.g. the Baltic Sea, mean sea level (MSL) is used.
 W
WThe Datum of 2022 is a placeholder name for a new vertical datum set to be produced by the U.S. National Geodetic Survey in 2022 to improve the National Spatial Reference System (NSRS) by replacing the North American Datum of 1983 and the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 with a new geometric reference frame and geopotential datum.
 W
WThe geoid is the shape that the ocean surface would take under the influence of the gravity and rotation of Earth alone, if other influences such as winds and tides were absent. This surface is extended through the continents. According to Gauss, who first described it, it is the "mathematical figure of the Earth", a smooth but irregular surface whose shape results from the uneven distribution of mass within and on the surface of Earth. It can be known only through extensive gravitational measurements and calculations. Despite being an important concept for almost 200 years in the history of geodesy and geophysics, it has been defined to high precision only since advances in satellite geodesy in the late 20th century.
 W
WMetres above the Adriatic is the vertical datum used in Austria, in the former Yugoslavian states of Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia-Hercegovina, Serbia, Montenegro, North Macedonia, as well as in Albania to measure elevation, referring to the average water level of the Adriatic Sea at the Sartorio mole in the Port of Trieste.
 W
WMetres above the Sea is the vertical datum used in Switzerland. Both the system and the term are also used in the Principality of Liechtenstein.
 W
WThe National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 is the official name since 1973 of the vertical datum established for vertical control surveying in the United States of America by the General Adjustment of 1929. Originally known as Sea Level Datum of 1929, NGVD 29 was determined and published by the National Geodetic Survey and used to measure the elevation of a point above and depression below mean sea level (MSL).
 W
WNormalhöhennull or NHN is a vertical datum used in Germany.
 W
WNormalnull or Normal-Null is an outdated official vertical datum used in Germany. Elevations using this reference system were to be marked "Meter über Normal-Null". Normalnull has been replaced by Normalhöhennull.
 W
WThe North American Vertical Datum of 1988 is the vertical datum for orthometric heights established for vertical control surveying in the United States of America based upon the General Adjustment of the North American Datum of 1988.
 W
WIn the British Isles, an ordnance datum or OD is a vertical datum used by an ordnance survey as the basis for deriving altitudes on maps. A spot height may be expressed as AOD for "above ordnance datum". Usually mean sea level (MSL) is used for the datum. In particular:In Great Britain, OD for the Ordnance Survey is ODN, defined as the MSL at Newlyn in Cornwall between 1915 and 1921. Prior to 1921, OD was taken from the level of the Victoria Dock, Liverpool (ODL). The difference between the different data varies across the country; full details are available from the Ordnance Survey website (below). In Northern Ireland, OD for the Ordnance Survey of Northern Ireland is Belfast Ordnance Datum, the MSL at Clarendon Dock, Belfast between 1951 and 1956. In the Republic of Ireland, OD for the Ordnance Survey of Ireland is Malin Ordnance Datum: the MSL at Portmoor Pier, Malin Head, County Donegal, between 1960 and 1969. Prior to 1970, Poolbeg Ordnance Datum was used: the low water of spring tide at Poolbeg Lighthouse, Dublin, on 8 April 1837. Poolbeg OD was about 2.7 metres lower than Malin OD.
 W
WMean sea level (MSL) is an average level of the surface of one or more of Earth's bodies of water from which heights such as elevation may be measured. The global MSL is a type of vertical datum – a standardised geodetic datum – that is used, for example, as a chart datum in cartography and marine navigation, or, in aviation, as the standard sea level at which atmospheric pressure is measured to calibrate altitude and, consequently, aircraft flight levels. A common and relatively straightforward mean sea-level standard is instead the midpoint between a mean low and mean high tide at a particular location.
 W
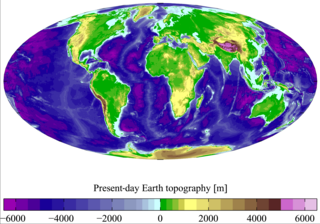
WTerrain or relief involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin word terra means "earth."
 W
WVERTCON is a computer program that computes the modeled difference in orthometric height between the North American Vertical Datum of 1988 and the National Geodetic Vertical Datum of 1929 for a location in the contiguous United States. The parameters required are the latitude and longitude of the location.
 W
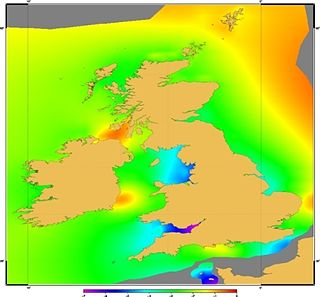
WVertical Offshore Reference Frames (VORF) is a set of high resolution surfaces which together define the vertical datum for hydrographic surveying and charting in the United Kingdom and Ireland. The following surfaces are included:Chart Datum (CD) Lowest Astronomical Tide (LAT) Mean Sea Level (MSL) Mean Low Water Springs (MLWS) Mean High Water Springs (MHWS) Highest Astronomical Tide (HAT) Land datums including Ordnance Datums Newlyn, Belfast and Poolbeg