 W
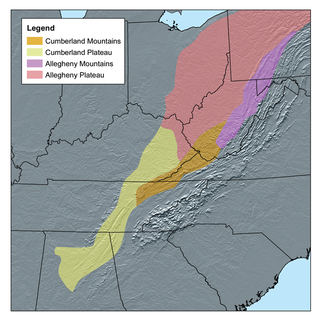
WThe Allegheny Plateau, in the United States, is a large dissected plateau area in western and central New York, northern and western Pennsylvania, northern and western West Virginia, and eastern Ohio. It is divided into the unglaciated Allegheny Plateau and the glaciated Allegheny Plateau.
 W
WThe Appalachian Plateau is a series of rugged dissected plateaus located on the western side of the Appalachian Mountains. The Appalachian Mountains are a mountain range that run down the East Coast of the United States. The Appalachian Plateau is the northwestern part of the Appalachian Mountains, stretching from New York to Alabama. The plateau is a second level United States physiographic region, covering parts of the states of New York, Pennsylvania, Ohio, Maryland, West Virginia, Virginia, Kentucky, Tennessee, Alabama, and Georgia.
 W
WThe Bee Cliff is a prominent northeast Tennessee geological limestone feature with high caves that overlooks the Watauga River and the Siam community of Carter County, Tennessee.
 W
WThe Chickasaw Bluff is the high ground rising about 50 to 200 feet (20–60 m) above the Mississippi River flood plain between Fulton in Lauderdale County, Tennessee and Memphis in Shelby County, Tennessee.
 W
WThe Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Allegheny Plateau" and the "Cumberland Plateau" both refer to the dissected plateau lands lying west of the main Appalachian Mountains. The terms stem from historical usage rather than geological difference, so there is no strict dividing line between the two. Two major rivers share the names of the plateaus, with the Allegheny River rising in the Allegheny Plateau and the Cumberland River rising in the Cumberland Plateau in Harlan County, Kentucky.
 W
WGrassy Cove is an enclosed valley in Cumberland County, Tennessee, United States. The valley is notable for its karst formations, which have been designated a National Natural Landmark. Grassy Cove is also home to a small unincorporated community.
 W
WThe Gulf Coastal Plain extends around the Gulf of Mexico in the Southern United States and eastern Mexico.
 W
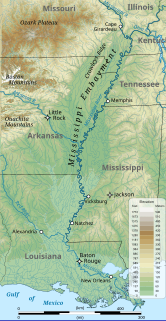
WThe Mississippi River Alluvial Plain is an alluvial plain created by the Mississippi River on which lie parts of seven U.S. states, from southern Louisiana to southern Illinois.
 W
WThe Mississippi Embayment is a physiographic feature in the south-central United States, part of the Mississippi Alluvial Plain. It is essentially a northward continuation of the fluvial sediments of the Mississippi River Delta to its confluence with the Ohio River at Cairo, Illinois. The current sedimentary area was formed in the Cretaceous and early Cenozoic by the filling with sediment of a pre-existing basin. An explanation for the embayment's formation was put forward by Van Arsdale and Cox in 2007: movement of the earth's crust brought this region over a volcanic "hotspot" in the Earth's mantle causing an upthrust of magma which formed the Appalachian-Ouachita range. Subsequent erosion caused a deep trough that was flooded by the Gulf of Mexico and eventually filled with sediment from the Mississippi River.
 W
WMud Island is a small peninsula, surrounded by the Mississippi River to the west and the Wolf River Harbor to the east. In 1960, the Wolf River was diverted so that it flows into the Mississippi River north of Mud Island. Mud Island River Park, located on the south end of the island, opened to the public in 1982. It is located within the Memphis city limits, 1.2 miles from the coast of downtown, and houses a museum, restaurants, and an amphitheater. It is accessible by the Memphis Suspension Railway, by foot, by ferry, or automobile.
 W
WPresident's Island is a peninsula on the Mississippi River in southwest Memphis, Tennessee. The city's major river port and an industrial park are located there.
 W
WThe Sycamore Shoals of the Watauga River, usually shortened to Sycamore Shoals, is a rocky stretch of river rapids along the Watauga River in Elizabethton, Tennessee. Archeological excavations have found Native Americans lived near the shoals since prehistoric times, and Cherokees gathered there. As Europeans began settling the Trans-Appalachian frontier, the shoals proved strategic militarily, as well as shaped the economies of Tennessee and Kentucky. Today, the shoals are protected as a National Historic Landmark and are maintained as part of Sycamore Shoals State Historic Park.
 W
WThe Tennessee River Gorge is a 26-mile (42 km) canyon formed by the Tennessee River known locally as Cash Canyon. It is the fourth largest river gorge in the Eastern United States. The gorge is cut into the Cumberland Plateau as the river winds its way into Alabama from Tennessee. The Tennessee River Gorge is home to endangered species like the mountain skullcap. Many archaeological sites have been discovered in the gorge that show that people have been dwelling in the canyon for at least 10,000 years.
 W
WWalden Ridge is a mountain ridge and escarpment located in Tennessee, in the United States. It marks the eastern edge of the Cumberland Plateau and is generally considered part of it. Walden Ridge is about 74 miles (119 km) long, running generally north-south. Its highest point is at Hinch Mountain, which reaches 3,048 feet (929 m) above sea level.
 W
WWells Creek is an impact crater located near Cumberland City, Tennessee. It is 7.5 miles (12 km) in diameter and the age is estimated to be 200±100 Ma, placing it in the Jurassic or a neighboring period. The crater is exposed to the surface. The center of the crater contains some of the finest shatter cones in the world. Many have been collected and are on display around the world.
 W
WWinstead Hill is a property in Franklin, Tennessee that has significance in 1864 for being in the Second Battle of Franklin battlefield. It is located within the Franklin Battlefield, a U.S. National Historic Landmark area.