 W
WAn abandoned mine is a mine or quarry which is no longer producing or operational, though definitions vary.
 W
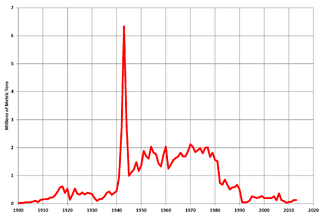
WBauxite mining in the United States produced an estimated 128,000 metric tonnes of bauxite in 2013. Although the United States was an important source of bauxite in the early 20th century, it now supplies less than one percent of world bauxite production.
 W
WThe General Mining Act of 1872 is a United States federal law that authorizes and governs prospecting and mining for economic minerals, such as gold, platinum, and silver, on federal public lands. This law, approved on May 10, 1872, codified the informal system of acquiring and protecting mining claims on public land, formed by prospectors in California and Nevada from the late 1840s through the 1860s, such as during the California Gold Rush. All citizens of the United States of America 18 years or older have the right under the 1872 mining law to locate a lode or placer (gravel) mining claim on federal lands open to mineral entry. These claims may be located once a discovery of a locatable mineral is made. Locatable minerals include but are not limited to platinum, gold, silver, copper, lead, zinc, uranium and tungsten.
 W
WHydraulic fracturing in the United States began in 1949. According to the Department of Energy (DOE), by 2013 at least two million oil and gas wells in the US had been hydraulically fractured, and that of new wells being drilled, up to 95% are hydraulically fractured. The output from these wells makes up 43% of the oil production and 67% of the natural gas production in the United States. Environmental safety and health concerns about hydraulic fracturing emerged in the 1980s, and are still being debated at the state and federal levels.
 W
WThe Molly Maguires were an Irish 19th-century secret society active in Ireland, Liverpool and parts of the Eastern United States, best known for their activism among Irish-American and Irish immigrant coal miners in Pennsylvania. After a series of often violent conflicts, twenty suspected members of the Molly Maguires were convicted of murder and other crimes and were executed by hanging in 1877 and 1878. This history remains part of local Pennsylvania lore.
 W
WMolybdenum mining in the United States produced 65,500 metric tons of molybdenum in 2014, worth US$1.8 billion. The US was the world's second-largest molybdenum producer, after China, and provided 25% of the world's supply of molybdenum.
 W
WThe National Mining Hall of Fame is a museum located in Leadville, Colorado, United States, dedicated to commemorating the work of miners and people who work with natural resources. The museum also participates in efforts to inform the public about the mining industry.
 W
WNew Jersey Amber, sometimes called Raritan amber, is amber found in the Raritan and Magothy Formations of the Central Atlantic (Eastern) coast of the United States. The amber is dated to be of Late Cretaceous, Turonian age, based on pollen analysis of the host formations. The amber has been known since the nineteenth century, with several of the old clay-pit sites now producing many amber specimens for study. A number of organism fossils have been described from inclusions in the amber, including fungi, plants, tardigrades, insects, and feathers. The first identified Cretaceous age ant was described from a fossil found in New Jersey in 1966.
 W
WThough different jurisdictions have varying criteria for what exactly qualifies as an abandoned oil well, generally speaking an oil well is considered abandoned when it has been permanently taken out of production. Similarly, orphaned wells may have different legal definitions across different jurisdictions, but can be thought of as wells whose legal owner it is not possible to determine. State legislatures in the United States have specific definitions based on local needs and priorities. For example, the section on abandoned wells in Texas' Natural Resource Code defines an "inactive well" as "an unplugged well that has had no reported production, disposal, injection, or other permitted activity for a period of greater than 12 months." Pennsylvania's definition of abandoned well includes not producing for 12 months, "considered dry and not equipped for production within 60 days after drilling, redrilling or deepening, and from which the equipment needed to extract resources or produce energy has been removed." Ohio legislation defines "idle and orphaned wells" based on whether or not a well bond has been forfeited or the money to plug it is unavailable. It defines a "temporary inactive well status" as not having produced for two or eight statutorily defined reporting periods or one that has produced "less than 100,000 cubic feet of natural gas or 15 barrels of crude oil."
 W
WThe Southeast Arizona Land Exchange and Conservation Act of 2013 is a bill that was introduced into the United States House of Representatives during the 113th United States Congress. H.R. 687 would authorize a land exchange in Arizona between the federal government and a mining company. Under H.R. 687, the United States Forest Service would convey about 2,400 acres of land in southeast Arizona to Resolution Copper Mining LLC in exchange for about 5,400 acres of company-owned land. Of the company land, about 1,200 acres would become part of the National Forest System, and about 4,200 acres would be administered as conservation areas by the Bureau of Land Management. If the property sought by Resolution Copper is appraised at more than the appraised value of the property that the company offers for exchange, the company could donate additional land or make a cash payment to the United States to make the final exchange of equal value. If the company’s property is appraised for more than the federal acreage, the difference in the value would be considered a donation to the federal government. According to the Committee Report on the bill, the "mine could provide up to one-quarter of the nation's estimated annual copper needs" and the mining company estimates that the "total economic impact of the mine will exceed $60 billion and support 3,700 jobs annually." Opponents of the bill argue that the swap has not been thoroughly studied, that the mining company has failed to indicate where it will get much needed water for the mine, and that Native American tribes have not been properly consulted.
 W
WThe United Mine Workers coal strike of 1919 saw coal miners strike for over a month, from November 1 to December 10 1919, for better wages.
 W
WThe Western Federation of Miners (WFM) was a labor union that gained a reputation for militancy in the mines of the western United States and British Columbia. Its efforts to organize both hard rock miners and smelter workers brought it into sharp conflicts – and often pitched battles – with both employers and governmental authorities. One of the most dramatic of these struggles occurred in the Cripple Creek district in 1903–04, and has been called the Colorado Labor Wars. The WFM also played a key role in the founding of the Industrial Workers of the World in 1905, but left that organization several years later.