 W
WColobomycter is an extinct genus of lanthanosuchoid parareptile known from the Early Permian of Oklahoma.
 W
WCretalamna is a genus of extinct otodontid shark that lived from the Late Cretaceous to Eocene epoch. It is considered by many to be the ancestor of the largest sharks to have ever lived, Carcharocles angustidens, and Carcharocles megalodon.
 W
WCretoxyrhina is an extinct genus of large mackerel shark that lived about 107 to 73 million years ago during the late Albian to late Campanian of the Late Cretaceous period. The type species, C. mantelli, is more commonly referred to as the Ginsu shark, first popularized in reference to the Ginsu knife, as its theoretical feeding mechanism is often compared with the "slicing and dicing" when one uses the knife. Cretoxyrhina is traditionally classified as the likely sole member of the family Cretoxyrhinidae but other taxonomic placements have been proposed, such as within the Alopiidae and Lamnidae.
 W
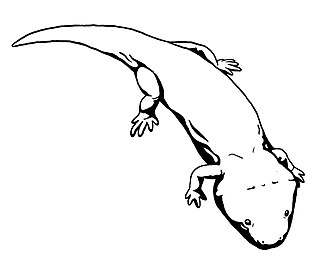
WEichstaettisaurus is a genus of lizards from the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of Germany, Spain, and Italy. With a flattened head, forward-oriented and partially symmetrical feet, and tall claws, Eichstaettisaurus bore many adaptations to a climbing lifestyle approaching those of geckoes. The type species, E. schroederi, is among the oldest and most complete members of the Squamata, being known by one specimen originating from the Tithonian-aged Solnhofen Limestone of Germany. A second species, E. gouldi, was described from another skeleton found in the Matese Mountains of Italy. Despite being very similar to E. schroederi, it lived much later, during the Albian stage. Fossils of both species show exceptional preservation due to deposition in low-oxygen marine environments.
 W
WIchthyolestes is an extinct genus of archaic cetacean that was endemic to Indo-Pakistan during the Lutetian stage. To date, this monotypic genus is only represented by Ichthyolestes pinfoldi.
 W
WIndobrachyops is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian from the Early Triassic of India. It is known from a nearly complete fossil skull that was first described by paleontologists Friedrich von Huene and M. R. Sahni in 1958 from the Panchet Formation in Raniganj Coalfield. Indobrachyops belongs to a group of mostly semi-aquatic temnospondyls called Stereospondyli, but its exact placement within the group has been uncertain since its first description.
 W
WKeichousaurus (key-cho-saurus) is a genus of marine reptile in the pachypleurosaur family which went extinct at the close of the Triassic in the Triassic-Jurassic extinction event. The name derives from Kweichow in China where the first fossil specimen was discovered in 1957. They are among the most common sauropterygian fossils recovered and are often found as nearly complete, articulated skeletons, making them popular among collectors. Keichousaurus, and the pachypleurosaur family broadly, are sometimes classified within Nothosauroidea, but are otherwise listed as a separate, more primitive lineage within Sauropterygia.
 W
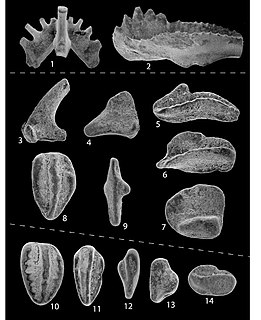
WKladognathus is an extinct genus of conodonts.
 W
WNyanzachoerus is an extinct genus of the pig family (Suidae) belonging to the subfamily Tetraconodontinae. The several species of Nyanzachoerus lived in Africa from the Miocene to Pliocene.
 W
WParacyclotosaurus is an extinct genus of temnospondyl amphibian, which would have appeared similar to today's salamander – but much larger, at up to 2.3 metres (7.5 ft) long. It lived in the Middle Triassic period, about 235 million years ago, and fossils have been found in Australia, India, and South Africa.
 W
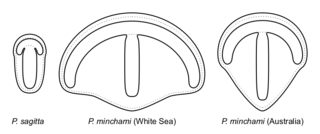
WParvancorina is a genus of shield-shaped bilaterally symmetrical fossil animal that lived in the late Ediacaran seafloor. It has some superficial similarities with the Cambrian trilobite-like arthropods.
 W
WTsintaosaurus is a genus of hadrosaurid dinosaur from China. It was about 8.3 metres (27 ft) long and weighed 2.5 tonnes. The type species is Tsintaosaurus spinorhinus, first described by Chinese paleontologist C. C. Young in 1958.