 W
WThe Central Pangean Mountains were an extensive northeast-southwest trending mountain range in the central portion of the supercontinent Pangaea during the Triassic period. They were formed as a result of collision between the minor supercontinents Laurussia and Gondwana during the formation of Pangaea. Remnants of this massive mountain range include the Appalachian Mountains of North America, the Little Atlas of Morocco, Africa and much of the Scottish Highlands including Ben Nevis.
 W
WThe Chugwater Formation is a mapped bedrock unit consisting primarily of red sandstone, in the states of Wyoming, Montana, and Colorado in the United States. It is recognized as a geologic formation in Colorado and Montana, but as a Group in Wyoming.
 W
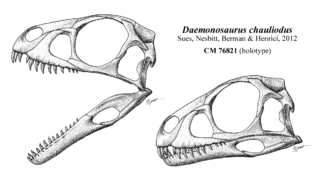
WDaemonosaurus is an extinct genus of possible theropod dinosaur from the Late Triassic of New Mexico. Fossils have been found from deposits in the Chinle Formation, which is latest Triassic in age. While theropods had diversified into several specialized groups by this time, Daemonosaurus is likely a very basal theropod, and lies outside the clade Neotheropoda. Daemonosaurus is unusual among putative early theropods in that it had a short skull with long protruding teeth.
 W
WHyperodapedon is a genus of rhynchosaurs from the Late Triassic period. Fossils of the genus have been found in Africa, Asia, Europe and North and South America. Its first discovery and naming was found by Thomas Henry Huxley in 1859. Hyperodapedon was a herbivore that used its beaked premaxilla and hindlimbs to dig for plants in dry land.
 W
WLagerpeton is a genus of basal dinosauromorph. First described by A. S. Romer in 1971, it includes only the species L. chanarensis. This species is incompletely known, with fossil specimens accounting for the pelvic girdle, hindlimbs and posterior presacral, sacral and anterior caudal vertebrae.
 W
WOmphalosaurus is an extinct genus of marine reptile from the Early Triassic to Middle Triassic, thought to be in the order of Ichthyosauria. Most of what is known about Omphalosaurus is based on multiple jaw fragments, ribs, and vertebrae. Specimens of Omphalosaurus have been described from the western United States, Germany, Austria and the island of Spitsbergen off the northern coast of Norway.
 W
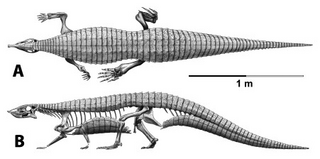
WSaurosuchus is a genus of large loricatan pseudosuchian archosaur that lived in South America during the Late Triassic period. It was a heavy, ground-dwelling, quadrupedal carnivore, being the major predator in the Ischigualasto Formation.
 W
WStagonolepis is an extinct genus of stagonolepidid aetosaur known from the Late Triassic Hassberge Formation of Germany, the Drawno Beds of Poland, the Lossiemouth Sandstone of Scotland, the Chinle Formation of Arizona and Utah and the Bluewater Creek Formation of New Mexico.
 W
WThalattoarchon is an extinct genus of ichthyosaur from the Middle Triassic of the western United States. The type species Thalattoarchon saurophagis was discovered in Nevada, USA, in 2010 and formally described in 2013. It is known from a single skeleton, holotype FMNH PR 3032, consisting of a partial skull, vertebral column, hip bones, and parts of the hind fins. The total length of Thalattoarchon is estimated to have been at least 8.6 metres (28 ft). Thalattoarchon is thought to have been one of the first marine macropredators capable of eating prey that was similar in size to itself, an ecological role that can be compared to that of modern orcas. Thalattoarchon lived four million years after the first appearance of ichthyosaurs in the Early Triassic and is therefore the oldest known marine reptile to have been an apex predator. It lived eight million years after the Permian-Triassic extinction event, indicating a fast recovery of marine ecosystems after the mass extinction.
 W
WTriodus is an extinct genus of xenacanthidan shark that lived from the Carboniferous to the Triassic. It was a freshwater shark, and fossils have been found in the Chinle Formation and Black Prince Limestone of Arizona, the Petrified Forest Member of New Mexico and the Tecovas Formation of Texas, United States. In 2017, a new species Triodus richterae was described from the Rio do Rasto Formation of Brazil.